|
Eight-eight Fleet
The was a Japanese naval strategy formulated for the development of the Imperial Japanese Navy in the first quarter of the 20th century, which stipulated that the navy should include eight first-class battleships and eight armoured cruisers or battlecruisers. History and development The concept of the "Eight-Eight Fleet" originated in the aftermath of the Russo-Japanese War with the 1907 Imperial Defense Policy between the Japanese government and the competing services of the Army and Navy. The policy called for the construction of a battle fleet of eight modern battleships of 20,000 tons each and eight modern armored cruisers of 18,000 tons each. These were to be complemented by the construction of several lesser warship types, including cruisers and destroyers. The plan was inspired by the Mahanian doctrine of Satō Tetsutarō who advocated that Japanese security could only be guaranteed by a strong navy. Satō argued that to ensure security, Japan should be capable of defea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. It encompassed the Japanese archipelago and several colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories. Under the slogans of and following the Boshin War and restoration of power to the Emperor from the Shogun, Japan underwent a period of industrialization and militarization, the Meiji Restoration, which is often regarded as the fastest modernisation of any country to date. All of these aspects contributed to Japan's emergence as a great power and the establishment of a colonial empire following the First Sino-Japanese War, the Boxer Rebellion, the Russo-Japanese War, and World War I. Economic and political turmoil in the 1920s, including the Great Depression, led to the rise of militarism, nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamamoto Gonnohyoe
Yamamoto (written: lit. "base of the mountain") is the 9th most common Japanese surname. Notable people with the surname include: *, Japanese politician *, Japanese World War II flying ace *, Japanese judoka *, Japanese manga artist and character designer *, Japanese Paralympic athlete *, Japanese actress, voice actress and idol *, Japanese gravure idol, actress and television personality *, Japanese painter *Beatriz Yamamoto Cázarez (born 1950), Mexican politician *, Japanese actress *, birth name of Japanese yakuza boss Shimizu Jirocho *, Japanese footballer *Donald Yamamoto (born 1953), American diplomat *, Filipino-born Japanese basketball player *, Japanese film director and screenwriter *, Japanese women's footballer *Eric Yamamoto, American legal scholar *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese actress *, Japanese Zen Buddhist *, Japanese cyclist *, Japanese Nordic combined skier *, Imperial Japanese Navy admiral and Prime Minister of Japan *Guy Yamamoto (born 1961), American gol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Aircraft Carrier Akagi 1925
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies (Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amagi-class Battlecruiser
The was a series of four battlecruisers planned for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) as part of the Eight-eight fleet in the early 1920s. The ships were to be named ''Amagi'', , ''Atago'', and ''Takao''. The ''Amagi'' design was essentially a lengthened version of the battleship, but with a thinner armored belt and deck, a more powerful propulsion system, and a modified secondary armament arrangement. They were to have carried the same main battery of ten guns and been capable of a top speed of . Limitations imposed by the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty prevented the class from being completed as designed. However, the treaty had a limited allowance for hulls already under construction to be converted into aircraft carriers. ''Amagi'' and ''Akagi'' were both intended for conversion, but an earthquake damaged the hull of ''Amagi'' so extensively that the ship was scrapped. ''Akagi'' was reconstructed as an aircraft carrier and served with distinction as part of the ''Kido But ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosa-class Battleship
The The ships are sometimes referred to as the ''Kaga'' class, after the ship that was planned to have been completed first. were two dreadnoughts ordered as part of the " Eight-Eight" fleet for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during the early 1920s. The ships were larger versions of the preceding , and carried an additional twin-gun turret. The design for the class served as a basis for the s. Both ships were launched in late 1921, but the first ship, , was cancelled in accordance with the terms of the Washington Naval Treaty before it could be completed, and was used in experiments testing the effectiveness of its armor scheme before being scuttled in the Bungo Channel. The hull of the second ship, , was converted into an aircraft carrier of the same name. The carrier supported Japanese troops in China during the Second Sino-Japanese War of the late 1930s, and took part in the attack on Pearl Harbor on 7 December 1941 and the invasion of Rabaul in the Southwest Pacific in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagato-class Battleship
The were a pair of dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) towards the end of World War I, although they were not completed until after the war. The last of Japan's pre-Treaty capital ships, they were the first class to carry guns, the largest afloat and the first bigger than . , the lead ship of the class, frequently served as a flagship. Both ships carried supplies for the survivors of the Great Kantō earthquake in 1923. They were modernized in 1933–1936 with improvements to their armor and machinery and a rebuilt superstructure in the pagoda mast style. ''Nagato'' and her sister ship briefly participated in the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937 and ''Nagato'' was the flagship of Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto during the attack on Pearl Harbor on 7 December 1941 that began the Pacific War. The sisters participated in the Battle of Midway in June 1942, although they did not see any combat. ''Mutsu'' saw more active service than her sister because she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Ship
A sister ship is a ship of the same class or of virtually identical design to another ship. Such vessels share a nearly identical hull and superstructure layout, similar size, and roughly comparable features and equipment. They often share a common naming theme, either being named after the same type of thing or person (places, constellations, heads of state) or with some kind of alliteration. Typically the ship class is named for the first ship of that class. Often, sisters become more differentiated during their service as their equipment (in the case of naval vessels, their armament) are separately altered. For instance, the U.S. warships , , , and are all sister ships, each being an . Perhaps the most famous sister ships were the White Star Line's s, consisting of , and . As with some other liners, the sisters worked as running mates. Other sister ships include the Royal Caribbean International's and . ''Half-sister'' refers to a ship of the same class but with some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Battleship Hyūga
was the second and last built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during the 1910s. Although completed in 1918, she played no role in World War I. ''Hyūga'' supported Japanese forces in the early 1920s during the Siberian intervention in the Russian Civil War. In 1923, she assisted survivors of the Great Kantō earthquake. The ship was partially modernised in two stages in 1927–1928 and 1931–1932, during which her forward superstructure was rebuilt in the pagoda mast style. ''Hyūga'' was reconstructed in 1934–1936, improvements being made to her armour and propulsion machinery. Afterwards, she played a minor role in the Second Sino-Japanese War. Despite the expensive reconstruction, the ship was considered obsolete by the eve of the Pacific War, and did not see significant action in the early years of the war. After the loss of most of the IJN's large aircraft carriers during the Battle of Midway in mid-1942, she was rebuilt with a flight deck replacing the rear pair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Battleship Ise
was the lead ship of her class of two dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during the 1910s. Although completed in 1917, she played no role in World War I. ''Ise'' supported Japanese forces in the early 1920s during the Siberian Intervention in the Russian Civil War. In 1923, she assisted survivors of the Great Kantō earthquake. The ship was partially modernised in two stages in 1928–1929 and 1931–1932, during which her forward superstructure was rebuilt in the pagoda mast style. ''Ise'' was reconstructed in 1934–1937, with improvements to her armour and her propulsion machinery. Afterwards she played a minor role in the Second Sino-Japanese War. Despite the expensive reconstruction, the ship was considered obsolete by the eve of the Pacific War, and did not see significant action in the early years of the war. Following the loss of most of the IJN's large aircraft carriers during the Battle of Midway in mid-1942, she was rebuilt with a fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Battleship Yamashiro
was the second of two dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy. Launched in 1915 and commissioned in 1917, she initially patrolled off the coast of China, playing no part in World War I. In 1923, she assisted survivors of the Great Kantō earthquake. ''Yamashiro'' was modernized between 1930 and 1935, with improvements to her armor and machinery and a rebuilt superstructure in the pagoda mast style. Nevertheless, with only 14-inch guns, she was outclassed by other Japanese battleships at the beginning of World War II, and played auxiliary roles for most of the war. By 1944, though, she was forced into front-line duty, serving as the flagship of Vice-Admiral Shōji Nishimura's Southern Force at the Battle of Surigao Strait, the southernmost action of the Battle of Leyte Gulf. During fierce night fighting in the early hours of 25 October against a superior American and Australian force, ''Yamashiro'' was sunk by torpedoes and naval gunfire. Nishimura wen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Battleship Fusō
was the lead ship of the two dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy. Launched in 1914 and commissioned in 1915, she initially patrolled off the coast of China, playing no part in World War I. In 1923, she assisted survivors of the Great Kantō earthquake. ''Fusō'' was modernized in 1930–1935 and again in 1937–1941, with improvements to her armor and propulsion machinery and a rebuilt superstructure in the pagoda mast style. With only guns, she was outclassed by other Japanese battleships at the beginning of World War II, and played auxiliary roles for most of the war. ''Fusō'' was part of Vice-Admiral Shōji Nishimura's Southern Force at the Battle of Leyte Gulf. She was sunk in the early hours of 25 October 1944 by torpedoes and naval gunfire during the Battle of Surigao Strait. Some reports claimed ''Fusō'' broke in half, and that both halves remained afloat and burning for an hour; according to survivors' accounts, however, the ship sank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
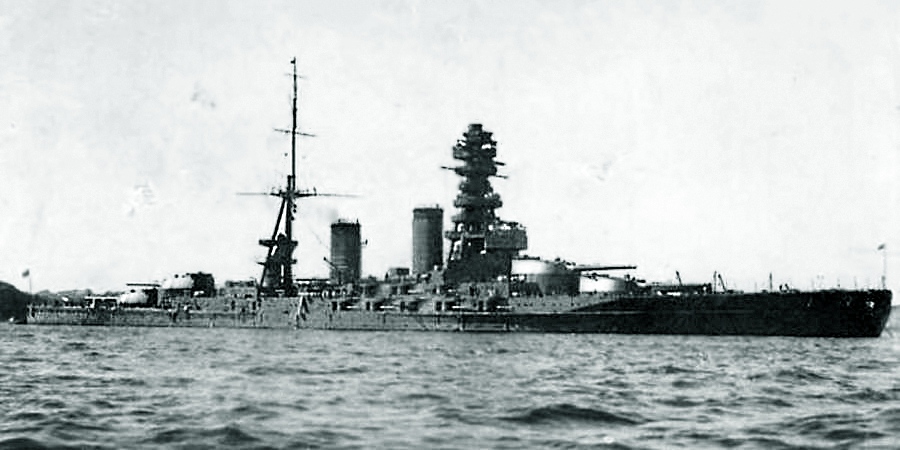
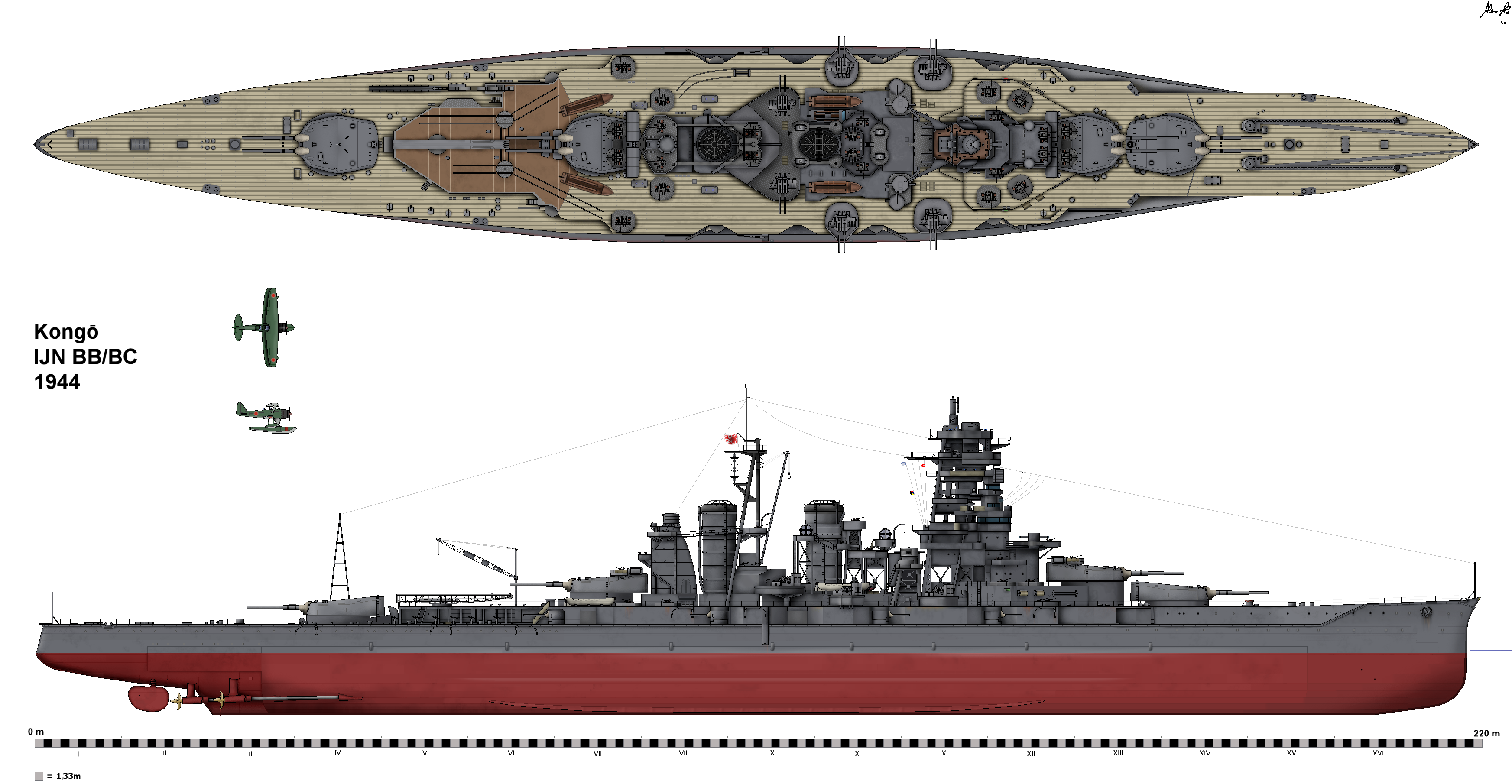
Kongō-class Battlecruiser
The was a class of four battlecruisers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) immediately before World War I. Designed by British naval architect George Thurston, the lead ship of the class, , was the last Japanese capital ship constructed outside Japan, by Vickers at Barrow-in-Furness. Her sister ships, , and , were all completed in Japan. During the late 1920s, all but ''Hiei'' were reconstructed and reclassified as battleships. After the signing of the London Naval Treaty in 1930, ''Hiei'' was reconfigured as a training ship to avoid being scrapped. Following Japan's withdrawal from the treaty, all four underwent a massive second reconstruction in the late 1930s. Following the completion of these modifications, which increased top speeds to over , all four were reclassified as fast battleships. The ''Kongō''-class battleships were the most active capital ships of the Japanese Navy during World War II, participating in most major engagements of the war. ''Hiei'' and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |