|
Edwards And Chapman Building
The Edwards and Chapman Building is a heritage-listed retail warehouse at 120 Queen Street, Brisbane City, City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by Francis Drummond Greville Stanley and built from 1881 to 1882 by Henry Holmes. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 October 1992. History This building was erected as a retail warehouse during 1881–1882 and occupied by Edwards and Chapman in December 1882. Welsh businessman Richard Edwards joined Scotsman James Chapman in the establishment of a drapery store in Brisbane in 1877. Successful in their venture, the two required larger premises and in September 1881 acquired deeds of grant to Allotments 13, 13A and 14 of Section 12. The convict barracks, later first parliamentary buildings and supreme court had stood on this site from 1827 until its demolition in early 1881. A government decision to dispose of this Crown land prompted the redevelopment of the northern side of Queen street boun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
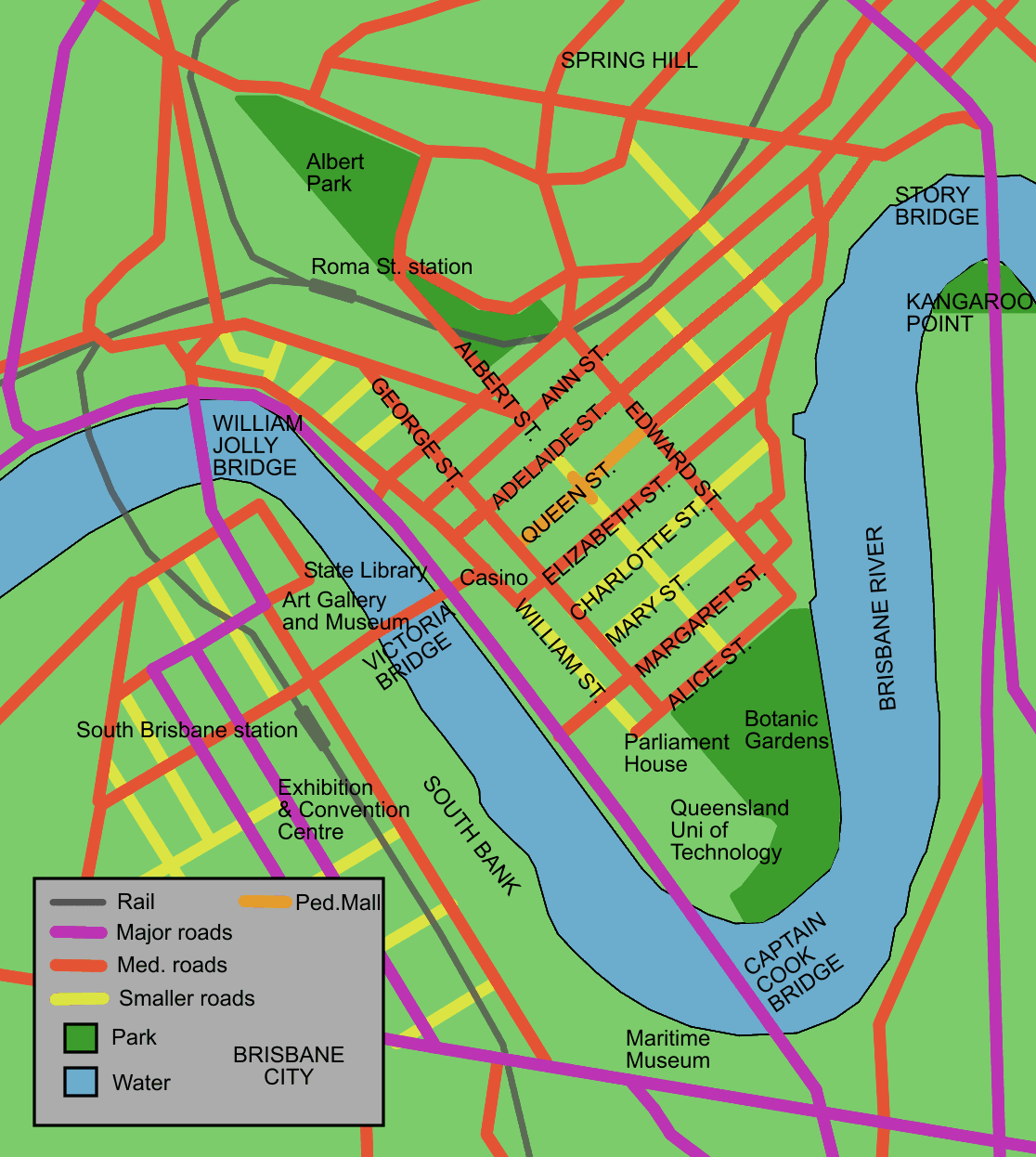
Brisbane City, Queensland
Brisbane City is the central suburb and central business district of Brisbane, the state capital of Queensland, Australia. It is colloquially referred to as the "Brisbane CBD" or "the city". It is located on a point on the northern bank of the Brisbane River, historically known as ''Meanjin'', ''Mianjin'' or ''Meeanjin'' in the local Aboriginal Australian dialect. The triangular shaped area is bounded by the median of the Brisbane River to the east, south and west. The point, known at its tip as Gardens Point, slopes upward to the north-west where the city is bounded by parkland and the inner city suburb of Spring Hill to the north. The CBD is bounded to the north-east by the suburb of Fortitude Valley. To the west the CBD is bounded by Petrie Terrace, which in 2010 was reinstated as a suburb (after being made a locality of Brisbane City in the 1970s). In the the suburb of Brisbane City had a population of 9,460 people. Geography The Brisbane central business district is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall And Prentice
Hall and Prentice was an architectural firm established in 1919 in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, through the partnership of Thomas Ramsay Hall (T. R. Hall) and George Gray Prentice (G. G. Prentice). The firm designed many prestigious buildings in the Brisbane area, including Musket Villa, Brisbane City Hall, Sandgate Town Hall and the Tattersalls Club Tattersalls Club is a heritage-listed club house at 206 Edward Street (with a second frontage on Queen Street), Brisbane City, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by Hall and Prentice and built from 1925 to 1949. It was added to the Qu .... In 1930 Hall left the firm to partner with Lionel Blythewood Phillips. In 1931 Prentice entered into a partnership with William 'Bill' Atkinson to form Atkinson Prentice. References Attribution {{Authority control Architects from Brisbane Australian companies established in 1919 Design companies established in 1919 Companies based in Brisbane Articles incorporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthus Leaves
The acanthus ( grc, ἄκανθος) is one of the most common plant forms to make foliage ornament and decoration, and even as the leaf distinguishing the heraldic coronet of a manorial lord from other coronets of royalty or nobility, which use strawberry leaves. Architecture In architecture, an ornament may be carved into stone or wood to resemble leaves from the Mediterranean species of the '' Acanthus'' genus of plants, which have deeply cut leaves with some similarity to those of the thistle and poppy. Both ''Acanthus mollis'' and the still more deeply cut ''Acanthus spinosus'' have been claimed as the main model, and particular examples of the motif may be closer in form to one or the other species; the leaves of both are, in any case, rather variable in form. The motif is found in decoration in nearly every medium. The relationship between acanthus ornament and the acanthus plant has been the subject of a long-standing controversy. Alois Riegl argued in his ''Stilfragen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keystone (architecture)
A keystone (or capstone) is the wedge-shaped stone at the apex of a masonry arch or typically round-shaped one at the apex of a vault. In both cases it is the final piece placed during construction and locks all the stones into position, allowing the arch or vault to bear weight. In arches and vaults (such as quasi-domes) keystones are often enlarged beyond the structural requirements and decorated. A variant in domes and crowning vaults is a lantern. Keystones, as a hallmark of strength or good architecture, or their suggested form are sometimes placed in the centre of the flat top of doors, recesses and windows for decorative effect, so as to form an upward projection of a lintel. Although a masonry arch or vault cannot be self-supporting until the keystone is placed, the keystone experiences the least stress of any of the voussoirs, due to its position at the apex. Old keystones can decay due to vibration, a condition known as bald arch. Architecture In a rib-vaulted c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital (architecture)
In architecture the capital (from the Latin ''caput'', or "head") or chapiter forms the topmost member of a column (or a pilaster). It mediates between the column and the load thrusting down upon it, broadening the area of the column's supporting surface. The capital, projecting on each side as it rises to support the abacus, joins the usually square abacus and the usually circular shaft of the column. The capital may be convex, as in the Doric order; concave, as in the inverted bell of the Corinthian order; or scrolling out, as in the Ionic order. These form the three principal types on which all capitals in the classical tradition are based. The Composite order established in the 16th century on a hint from the Arch of Titus, adds Ionic volutes to Corinthian acanthus leaves. From the highly visible position it occupies in all colonnaded monumental buildings, the capital is often selected for ornamentation; and is often the clearest indicator of the architectural orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Order
The Corinthian order (Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects other than the capitals of the columns. When classical architecture was revived during the Renaissance, two more orders were added to the canon: the Tuscan order and the Composite order. The Corinthian, with its offshoot the Composite, is the most ornate of the orders. This architectural style is characterized by slender fluted columns and elaborate capitals decorated with acanthus leaves and scrolls. There are many variations. The name ''Corinthian'' is derived from the ancient Greek city of Corinth, although the style had its own model in Roman practice, following precedents set by the Tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilasters
In classical architecture, a pilaster is an architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wall surface, usually treated as though it were a column, with a capital at the top, plinth (base) at the bottom, and the various other column elements. In contrast to a pilaster, an engaged column or buttress can support the structure of a wall and roof above. In human anatomy, a pilaster is a ridge that extends vertically across the femur, which is unique to modern humans. Its structural function is unclear. Definition In discussing Leon Battista Alberti's use of pilasters, which Alberti reintroduced into wall-architecture, Rudolf Wittkower wrote: "The pilaster is the logical transformation of the column for the decoration of a wall. It may be defined as a flattened column which has lost its three-dimensional and tactile value." A pil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcade (architecture)
An arcade is a succession of contiguous arches, with each arch supported by a colonnade of columns or piers. Exterior arcades are designed to provide a sheltered walkway for pedestrians. The walkway may be lined with retail stores. An arcade may feature arches on both sides of the walkway. Alternatively, a blind arcade superimposes arcading against a solid wall. Blind arcades are a feature of Romanesque architecture that influenced Gothic architecture. In the Gothic architectural tradition, the arcade can be located in the interior, in the lowest part of the wall of the nave, supporting the triforium and the clerestory in a cathedral, or on the exterior, in which they are usually part of the walkways that surround the courtyard and cloisters. Many medieval arcades housed shops or stalls, either in the arcaded space itself, or set into the main wall behind. From this, "arcade" has become a general word for a group of shops in a single building, regardless of the architectural f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriel Window
An oriel window is a form of bay window which protrudes from the main wall of a building but does not reach to the ground. Supported by corbels, bracket (architecture), brackets, or similar cantilevers, an oriel window is most commonly found projecting from an upper floor but is also sometimes used on the ground floor. Oriel windows are seen in Arab architecture in the form of mashrabiya and in Turkish are known as ''şahnişin'' or ''cumba''. In Islamic culture, these windows and balconies project from the street-front of a house, providing an area in which women could peer out and see the activities below while remaining invisible. Origins According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the term ''oriel'' is derived from Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman ' and Late Latin ', both meaning "gallery" or "porch", perhaps from Classical Latin ' ("curtain"). * Oriel College, Oxford, took its name from a balcony or oriel window forming a feature of a building which occupied the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Window
A bay window is a window space projecting outward from the main walls of a building and forming a bay in a room. Types Bay window is a generic term for all protruding window constructions, regardless of whether they are curved or angular, or run over one or multiple storey A storey (British English) or story (American English) is any level part of a building with a floor that could be used by people (for living, work, storage, recreation, etc.). Plurals for the word are ''storeys'' (UK) and ''stories'' (US). T ...s. In plan, the most frequently used shapes are isosceles trapezoid (which may be referred to as a ''canted (architecture), canted bay window'') and rectangle. But other polygonal shapes with more than two corners are also common as are curved shapes. If a bay window is curved it may alternatively be called ''bow window.'' Bay windows in a triangular shape with just one corner exist but are relatively rare. A bay window supported by a corbel, Bracket (archite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awning
An awning or overhang is a secondary covering attached to the exterior wall of a building. It is typically composed of canvas woven of acrylic, cotton or polyester yarn, or vinyl laminated to polyester fabric that is stretched tightly over a light structure of aluminium, iron or steel, possibly wood or transparent material (used to cover solar thermal panels in the summer, but that must allow as much light as possible in the winter). The configuration of this structure is something of a truss, space frame or planar frame. Awnings are also often constructed of aluminium understructure with aluminium sheeting. These aluminium awnings are often used when a fabric awning is not a practical application where snow load as well as wind loads may be a factor. The location of an awning on a building may be above a window, a door, or above the area along a sidewalk. With the addition of columns an awning becomes a canopy, which is able to extend further from a building, as in the case of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oamaru Limestone
Oamaru stone, sometimes called whitestone, is a hard, compact limestone, quarried at Weston, near Oamaru in Otago, New Zealand. Oamaru stone was used on many of the grand public buildings in the towns and cities of the southern South Island, especially after the financial boom caused by the Central Otago goldrush of the 1860s. Initially used primarily in Oamaru itself, it became popular in Dunedin in around 1866, with the University of Otago's Registry Building being the first major structure in the city to make use of it.Limestones , ''Transactions and Proceedings of the Royal Society of New Zealand'', vol 8 (1875), pp. 138–148. The city of and town of Oamaru both have many fine examples of Oamaru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)

.jpg)




