|
Edward Elwall
Edward Elwall, born 9 November 1676, died 29 November 1744, was a mercer and grocer, born at Sedgley near Wolverhampton. He was a Unitarian and a Sabbatarian Baptist; that is, his day of rest and worship was the seventh day, the biblical Sabbath, rather than the first day of the week, the “papal pagan Sunday,” as he called it, which is kept by orthodox Christians. The people of Wolverhampton referred to him as ‘Jew Elwall,’ because of his Sabbath-keeping. He is said to have occasionally attended the Mill Yard Seventh Day Baptist Church in London. In 1727 Elwall published his Unitarian beliefs in ''A true testimony for God and his sacred Law; being a plain, honest defence of the First Commandment of God, against all the Trinitarians under Heaven: ‘Thou shalt have no other gods but me.’'' Trial The Anglican clergy charged him with blasphemy and heresy, for which he was brought to trial at the Stafford Summer Assizes 1726. The judge appears to have sought a mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercery
Mercery (from French , meaning "habderdashery" (goods) or "haberdashery" (a shop trading in textiles and notions) initially referred to silk, linen and fustian textiles among various other piece goods imported to England in the 12th century. Eventually, the term evolved to refer to a merchant or trader of textile goods, especially imported textile goods, particularly in England. A merchant would be known as a ''mercer'', and the profession as ''mercery''. The occupation of mercery has a rich and complex history dating back over 1,000 years in what is now the United Kingdom. London was the major trade centre in England for silk during the Middle Ages, and the trade enjoyed a special position in the economy amongst the wealthy. A typical mercery business was family-run, consisting of a mercer, wife, their family, servants, and apprentices. The husband would be tasked with the marketing and sale of the business' wares to the public in places such as a small storefront, at market ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity
The Christian doctrine of the Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the central dogma concerning the nature of God in most Christian churches, which defines one God existing in three coequal, coeternal, consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son (Jesus Christ) and God the Holy Spirit, three distinct persons sharing one ''homoousion'' (essence) "each is God, complete and whole." As the Fourth Lateran Council declared, it is the Father who begets, the Son who is begotten, and the Holy Spirit who proceeds. In this context, the three persons define God is, while the one essence defines God is. This expresses at once their distinction and their indissoluble unity. Thus, the entire process of creation and grace is viewed as a single shared action of the three divine persons, in which each person manifests the attributes unique to them in the Trinity, thereby proving that everything comes "from the Father," "through the Son," and "in the Holy Spirit." This doctrine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
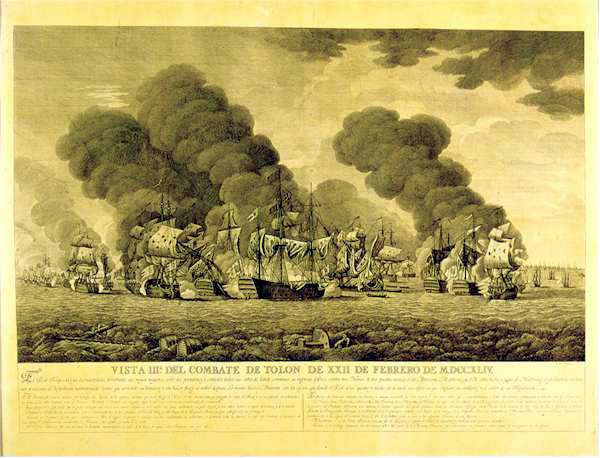
1744 Deaths
Events January–March * January 6 – The Royal Navy ship ''Bacchus'' engages the Spanish Navy privateer ''Begona'', and sinks it; 90 of the 120 Spanish sailors die, but 30 of the crew are rescued. * January 24 – The Dagohoy rebellion in the Philippines begins, with the killing of Father Giuseppe Lamberti. * February – Violent storms frustrate a planned French invasion of Britain. * February 22– 23 – Battle of Toulon: The British fleet is defeated by a joint Franco-Spanish fleet. * March 1 (approximately) – The Great Comet of 1744, one of the brightest ever seen, reaches perihelion. * March 13 – The British ship ''Betty'' capsizes and sinks off of the Gold Coast (modern-day Ghana) near Anomabu. More than 200 people on board die, although there are a few survivors. * March 15 – France declares war on Great Britain. April–June * April – ''The Female Spectator'' (a monthly) is founded by Eliza Haywood in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1676 Births
Events January–March * January 29 – Feodor III becomes Tsar of Russia. * January 31 – Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala, the oldest institution of higher education in Central America, is founded. * January – Six months into King Philip's War, Metacomet (King Philip), leader of the Algonquian tribe known as the Wampanoag, travels westward to the Mohawk nation, seeking an alliance with the Mohawks against the English colonists of New England; his efforts in creating such an alliance are a failure. * February 10 – After the Nipmuc tribe attacks Lancaster, Massachusetts, colonist Mary Rowlandson is taken captive, and lives with the Indians until May. * February 14 – Metacomet and his Wampanoags attack Northampton, Massachusetts; meanwhile, the Massachusetts Council debates whether a wall should be erected around Boston. * February 23 – While the Massachusetts Council debates how to handle the Christian Indians they had exile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disestablishment
The separation of church and state is a philosophical and jurisprudential concept for defining political distance in the relationship between religious organizations and the state. Conceptually, the term refers to the creation of a secular state (with or without legally explicit church-state separation) and to disestablishment, the changing of an existing, formal relationship between the church and the state. Although the concept is older, the exact phrase "separation of church and state" is derived from "wall of separation between church and state", a term coined by Thomas Jefferson. The concept was promoted by Enlightenment philosophers such as John Locke. In a society, the degree of political separation between the church and the civil state is determined by the legal structures and prevalent legal views that define the proper relationship between organized religion and the state. The arm's length principle proposes a relationship wherein the two political entities interact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tithe
A tithe (; from Old English: ''teogoþa'' "tenth") is a one-tenth part of something, paid as a contribution to a religious organization or compulsory tax to government. Today, tithes are normally voluntary and paid in cash or cheques or more recently via online giving, whereas historically tithes were required and paid in kind, such as agricultural produce. After the separation of church and state, church tax linked to the tax system are instead used in many countries to support their national church. Donations to the church beyond what is owed in the tithe, or by those attending a congregation who are not members or adherents, are known as offerings, and often are designated for specific purposes such as a building program, debt retirement, or mission work. Many Christian denominations hold Jesus taught that tithing must be done in conjunction with a deep concern for "justice, mercy and faithfulness" (cf. Matthew 23:23). Tithing was taught at early Christian church councils, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Society Of Friends
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's ability to experience the light within or see "that of God in every one". Some profess a priesthood of all believers inspired by the First Epistle of Peter. They include those with evangelical, holiness, liberal, and traditional Quaker understandings of Christianity. There are also Nontheist Quakers, whose spiritual practice does not rely on the existence of God. To differing extents, the Friends avoid creeds and hierarchical structures. In 2017, there were an estimated 377,557 adult Quakers, 49% of them in Africa. Some 89% of Quakers worldwide belong to ''evangelical'' and ''programmed'' branches that hold services with singing and a prepared Bible message coordinated by a pastor. Some 11% practice ''waiting worship'' or ''unprogrammed wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain by the 3rd century and to the 6th-century Gregorian mission to Kent led by Augustine of Canterbury. The English church renounced papal authority in 1534 when Henry VIII failed to secure a papal annulment of his marriage to Catherine of Aragon. The English Reformation accelerated under Edward VI's regents, before a brief restoration of papal authority under Queen Mary I and King Philip. The Act of Supremacy 1558 renewed the breach, and the Elizabethan Settlement charted a course enabling the English church to describe itself as both Reformed and Catholic. In the earlier phase of the English Reformation there were both Roman Catholic martyrs and radical Protestant martyrs. The later phases saw the Penal Laws punish Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tithe
A tithe (; from Old English: ''teogoþa'' "tenth") is a one-tenth part of something, paid as a contribution to a religious organization or compulsory tax to government. Today, tithes are normally voluntary and paid in cash or cheques or more recently via online giving, whereas historically tithes were required and paid in kind, such as agricultural produce. After the separation of church and state, church tax linked to the tax system are instead used in many countries to support their national church. Donations to the church beyond what is owed in the tithe, or by those attending a congregation who are not members or adherents, are known as offerings, and often are designated for specific purposes such as a building program, debt retirement, or mission work. Many Christian denominations hold Jesus taught that tithing must be done in conjunction with a deep concern for "justice, mercy and faithfulness" (cf. Matthew 23:23). Tithing was taught at early Christian church councils, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissenter
A dissenter (from the Latin ''dissentire'', "to disagree") is one who dissents (disagrees) in matters of opinion, belief, etc. Usage in Christianity Dissent from the Anglican church In the social and religious history of England and Wales, and, by extension, Ireland, however, it refers particularly to a member of a religious body who has, for one reason or another, separated from the established church or any other kind of Protestant who refuses to recognise the supremacy of the established church in areas where the established church is or was Anglican.. Originally, the term included English and Welsh Roman Catholics whom the original draft of the Nonconformist Relief Act 1779 styled " Protesting Catholic Dissenters". In practice, however, it designates Protestant Dissenters referred to in sec. ii. of the Act of Toleration of 1689 (see English Dissenters). The term recusant, in contrast, came to refer to Roman Catholics rather than Protestant dissenters. Dissent from the Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctrine Of The Trinity Act 1813
The Act 53 Geo 3 c 160, sometimes called the Doctrine of the Trinity Act 1813, the Trinitarian Act 1812, the Unitarian Relief Act, the Trinity Act, the Unitarian Toleration Bill, or Mr William Smith's Bill (after Whig politician William Smith), was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which amended its blasphemy laws and granted toleration for Unitarian worship. * Section 1 amended the Toleration Act 1689 (passed by the Parliament of England) to include non-Trinitarians among the Protestant dissenters whose practices would be tolerated. * Section 2 repealed the provision of the Blasphemy Act 1697 (also English) which imposed civil penalties on anyone professed or educated as a Christian who denied the Trinity. * Section 3 repealed two Acts of the Scottish Parliament which made blasphemy punishable by death: the Act against Blasphemy 1661 and Act against Blasphemy 1695. The Dissenters (Ireland) Act 1817 (57 Geo 3 c 70) extended the Doctrine of the Trinity Act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Toleration 1689
The Toleration Act 1688 (1 Will & Mary c 18), also referred to as the Act of Toleration, was an Act of the Parliament of England. Passed in the aftermath of the Glorious Revolution, it received royal assent on 24 May 1689. The Act allowed for freedom of worship to nonconformists who had pledged to the oaths of Allegiance and Supremacy and rejected transubstantiation, i.e., to Protestants who dissented from the Church of England such as Baptists, Congregationalists or English Presbyterians, but not to Roman Catholics. Nonconformists were allowed their own places of worship and their own schoolteachers, so long as they accepted certain oaths of allegiance. The Act intentionally did not apply to Roman Catholics, Jews, nontrinitarians, and atheists. It continued the existing social and political disabilities for dissenters, including their exclusion from holding political offices and also from the universities. Dissenters were required to register their meeting houses and were fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |