|
Education In Latin America
Despite significant progress, education remains a challenge in Latin America. The region has made great progress in educational coverage; almost all children attend primary school and access to secondary education has increased considerably. Children complete on average two more years of schooling than their parents' generation. Most educational systems in the region have implemented various types of administrative and institutional reforms that have enabled reach for places and communities that had no access to education services in the early 90s. However, there are still 23 million children in the region between the ages of 4 and 17 outside of the formal education system. Estimates indicate that 30% of preschool age children (ages 4 –5) do not attend school, and for the most vulnerable populations – poor, rural, indigenous and afro-descendants – this calculation exceeds 40 percent. Among primary school age children (ages 6 to 12), coverage is almost universal; however there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figure 4 Distribution Of Youth Aged 18 To 24 Years, By Schooling Condition And By Educational Attainment In Each Country Youth And Changing Realities
Figure may refer to: General *A shape, drawing, depiction, or geometric configuration * Figure (wood), wood appearance * Figure (music), distinguished from musical motif * Noise figure, in telecommunication * Dance figure, an elementary dance pattern *A person's figure, human physical appearance Arts * Figurine, a miniature statuette representation of a creature * Action figure, a posable jointed solid plastic character figurine * Figure painting, realistic representation, especially of the human form * Figure drawing * Model figure, a scale model of a creature Writing *figure, in writing, a type of floating block (text, table, or graphic separate from the main text) *Figure of speech, also called a rhetorical figure * Christ figure, a type of character * in typesetting, text figures and lining figures Accounting *Figure, a synonym for number * Significant figures in a decimal number Science *Figure of the Earth, the size and shape of the Earth in geodesy Sports * Fig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, and Maritime boundary, maritime border with Ecuador to the south of Cocos Island. It has a population of around five million in a land area of . An estimated 333,980 people live in the capital and largest city, San José, Costa Rica, San José, with around two million people in the surrounding metropolitan area. The sovereign state is a Unitary state, unitary Presidential system, presidential Constitution of Costa Rica, constitutional republic. It has a long-standing and stable democracy and a highly educated workforce. The country spends roughly 6.9% of its budget (2016) on education, compared to a global average of 4.4%. Its economy, once heavily dependent on agricultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Standard Classification Of Education
The International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED) is a statistical framework for organizing information on education maintained by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). It is a member of the international family of economic and social classifications of the United Nations. History The ISCED was designed in the early 1970s to serve as an instrument suitable for assembling, compiling and presenting statistics of education both within individual countries and internationally. The first version, known as ISCED 1976, was approved by the International Conference on Education (Geneva, 1975), and was subsequently endorsed by UNESCO’s 19th General Conference in 1976. The second version, known as ISCED 1997, was approved by the UNESCO General Conference at its 29th session in November 1997 as part of efforts to increase the international comparability of education statistics. It covered primarily two cross-classification variables: ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIT Press
The MIT Press is a university press affiliated with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts (United States). It was established in 1962. History The MIT Press traces its origins back to 1926 when MIT published under its own name a lecture series entitled ''Problems of Atomic Dynamics'' given by the visiting German physicist and later Nobel Prize winner, Max Born. Six years later, MIT's publishing operations were first formally instituted by the creation of an imprint called Technology Press in 1932. This imprint was founded by James R. Killian, Jr., at the time editor of MIT's alumni magazine and later to become MIT president. Technology Press published eight titles independently, then in 1937 entered into an arrangement with John Wiley & Sons in which Wiley took over marketing and editorial responsibilities. In 1962 the association with Wiley came to an end after a further 125 titles had been published. The press acquired its modern name af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric A
The given name Eric, Erich, Erikk, Erik, Erick, or Eirik is derived from the Old Norse name ''Eiríkr'' (or ''Eríkr'' in Old East Norse due to monophthongization). The first element, ''ei-'' may be derived from the older Proto-Norse ''* aina(z)'', meaning "one, alone, unique", ''as in the form'' ''Æ∆inrikr'' explicitly, but it could also be from ''* aiwa(z)'' "everlasting, eternity", as in the Gothic form ''Euric''. The second element ''- ríkr'' stems either from Proto-Germanic ''* ríks'' "king, ruler" (cf. Gothic ''reiks'') or the therefrom derived ''* ríkijaz'' "kingly, powerful, rich, prince"; from the common Proto-Indo-European root * h₃rḗǵs. The name is thus usually taken to mean "sole ruler, autocrat" or "eternal ruler, ever powerful". ''Eric'' used in the sense of a proper noun meaning "one ruler" may be the origin of ''Eriksgata'', and if so it would have meant "one ruler's journey". The tour was the medieval Swedish king's journey, when newly elected, to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludger Woessmann
Ludger ( la, Ludgerus; also Lüdiger or Liudger) (born at Zuilen near Utrecht 742; died 26 March 809 at Billerbeck) was a missionary among the Frisians and Saxons, founder of Werden Abbey and the first Bishop of Münster in Westphalia. He has been called the "Apostle of Saxony". Early life to ordination Ludger's parents, Thiadgrim and Liafburg, were wealthy Christian Frisians of noble descent. In 753 Ludger saw the great Apostle of Germany, Boniface, which, together with the subsequent martyrdom of the saint, made a deep impression on him. At his own request he was sent to the Utrecht Cathedral School (''Martinsstift''), founded by Gregory of Utrecht in 756 or 757, and made good progress. In 767 Gregory, who did not wish to receive episcopal consecration himself, sent Alubert, who had come from England to assist him in his missionary work, to York to be consecrated bishop. Ludger accompanied him to be ordained into the diaconate (as he duly was, by Ethelbert of York) and to stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Hanushek
Eric Alan Hanushek (; born May 22, 1943) is an economist who has written prolifically on public policy with a special emphasis on the economics of education. Since 2000, he has been a Paul and Jean Hanna Senior Fellow at the Hoover Institution, an American public policy think tank located at Stanford University in California. He was awarded the Yidan Prize for Education Research in 2021. Hanushek advocates using economic analysis to improve student performance. He has authored numerous, highly cited articles on the effects of class size reduction, high-stakes accountability, teacher effectiveness, and other education related topics. In a 1971 paper he introduced the concept of evaluating teacher effectiveness on the basis of student learning gains. This idea is the basis of value-added assessments of teacher quality. In his most recent book, ''The Knowledge Capital of Nations'', Hanushek concludes that the quality of education is causally related to economic growth. Hanushek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
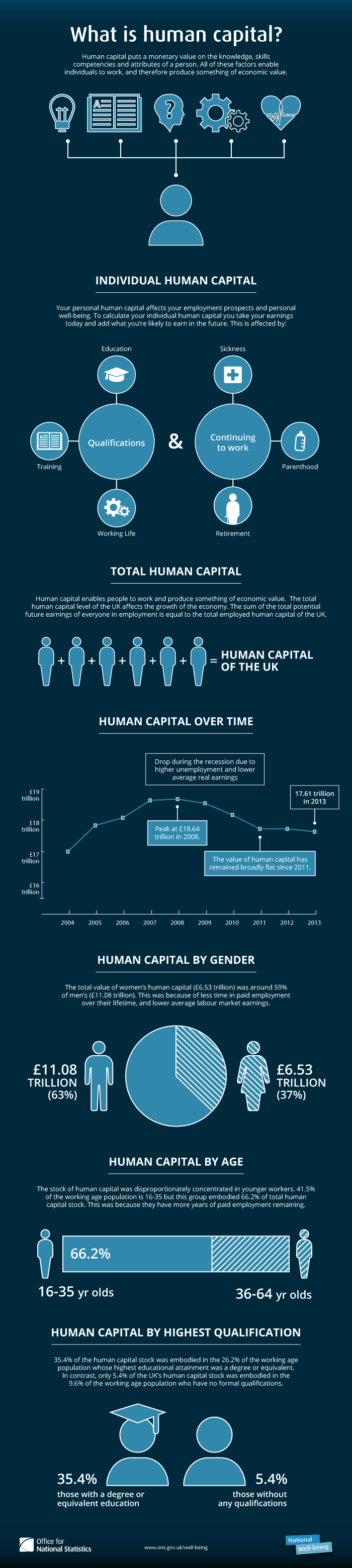
Human Capital
Human capital is a concept used by social scientists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial impact on individual earnings. Research indicates that human capital investments have high economic returns throughout childhood and young adulthood. Companies can invest in human capital, for example, through education and training, enabling improved levels of quality and production. As a result of his conceptualization and modeling work using Human Capital as a key factor, the 2018 Nobel Prize for Economics was jointly awarded to Paul Romer, who founded the modern innovation-driven approach to understanding economic growth. In the recent literature, the new concept of task-specific human capital was coined in 2004 by Robert Gibbons, an economist at MIT, and Michael Waldman, an economist at Cornell University. The concept emphasizes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Physical Appearance
Human physical appearance is the outward phenotype or look of human beings. There are infinite variations in human phenotypes, though society reduces the variability to distinct categories. The physical appearance of humans, in particular those attributes which regarded as important for physical attractiveness, are believed by anthropologists to affect the development of personality significantly and social relations. Humans are acutely sensitive to their physical appearance. Some differences in human appearance are genetic, others are the result of age, lifestyle or disease, and many are the result of personal adornment. Some people have linked some differences with ethnicity, such as skeletal shape, prognathism or elongated stride. Different cultures place different degrees of emphasis on physical appearance and its importance to social status and other phenomena. Aspects Various aspects are considered relevant to the physical appearance of humans. Physiological differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast. It is part of the Southern Cone region of South America. Uruguay covers an area of approximately and has a population of an estimated 3.4 million, of whom around 2 million live in the metropolitan area of its capital and largest city, Montevideo. The area that became Uruguay was first inhabited by groups of hunter–gatherers 13,000 years ago. The predominant tribe at the moment of the arrival of Europeans was the Charrúa people, when the Portuguese first established Colónia do Sacramento in 1680; Uruguay was colonized by Europeans late relative to neighboring countries. The Spanish founded Montevideo as a military stronghold in the early 18th century bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat
Combat ( French for ''fight'') is a purposeful violent conflict meant to physically harm or kill the opposition. Combat may be armed (using weapons) or unarmed ( not using weapons). Combat is sometimes resorted to as a method of self-defense, or can be used as a tool to impose one's will on others. An instance of combat can be a stand-alone confrontation or a small part of a much larger violent conflict. Instances of combat may also be benign and recreational, as in the cases of combat sports and mock combat. Combat may comply with, or be in violation of local or international laws regarding conflict. Examples of rules include the Geneva Conventions (covering the treatment of people in war), medieval chivalry, the Marquess of Queensberry rules (covering boxing) and several forms of combat sports. Hand-to-hand combat Hand-to-hand combat (melee) is combat at very close range, attacking the opponent with the body ( striking, kicking, strangling, etc.) and/or with a melee we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Race (human Categorization)
A race is a categorization of humans based on shared physical or social qualities into groups generally viewed as distinct within a given society. The term came into common usage during the 1500s, when it was used to refer to groups of various kinds, including those characterized by close kinship relations. By the 17th century, the term began to refer to physical (phenotypical) traits, and then later to national affiliations. Modern science regards race as a social construct, an identity which is assigned based on rules made by society. While partly based on physical similarities within groups, race does not have an inherent physical or biological meaning. The concept of race is foundational to racism, the belief that humans can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. Social conceptions and groupings of races have varied over time, often involving folk taxonomies that define essential types of individuals based on perceived traits. Today, scientists con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |