|
Economic History Of The United States
The economic history of the United States is about characteristics of and important developments in the U.S. economy from colonial times to the present. The emphasis is on productivity and economic performance and how the economy was affected by new technologies, the change of size in economic sectors and the effects of legislation and government policy. Specialized business history is covered in American business history. Colonial economy The colonial economy was characterized by an abundance of land and natural resources and a severe scarcity of labor. This was the opposite of Europe and attracted immigrants despite the high death rate caused by New World diseases. From 1700 to 1774 the output of the thirteen colonies increased 12-fold, giving the colonies an economy about 30% the size of Britain's at the time of independence. Population growth was responsible for over three-quarters of the economic growth of the British American colonies. The free white population had th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Business History
American business history is a history of business, entrepreneurship, and corporations, together with responses by consumers, critics, and government, in the United States from colonial times to the present. In broader context, it is a major part of the Economic history of the United States, but focuses on specific business enterprises. New England The New England region's economy grew steadily over the entire colonial era, despite the lack of a staple crop that could be exported. All the provinces and many towns as well, tried to foster economic growth by subsidizing projects that improved the infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, inns and ferries. They gave bounties and subsidies or monopolies to sawmills, grist mills, iron mills, pulling mills (which treated cloth), salt works and glassworks. Most important, colonial legislatures set up a legal system that was conducive to business enterprise by resolving disputes, enforcing contracts, and protecting property rights. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
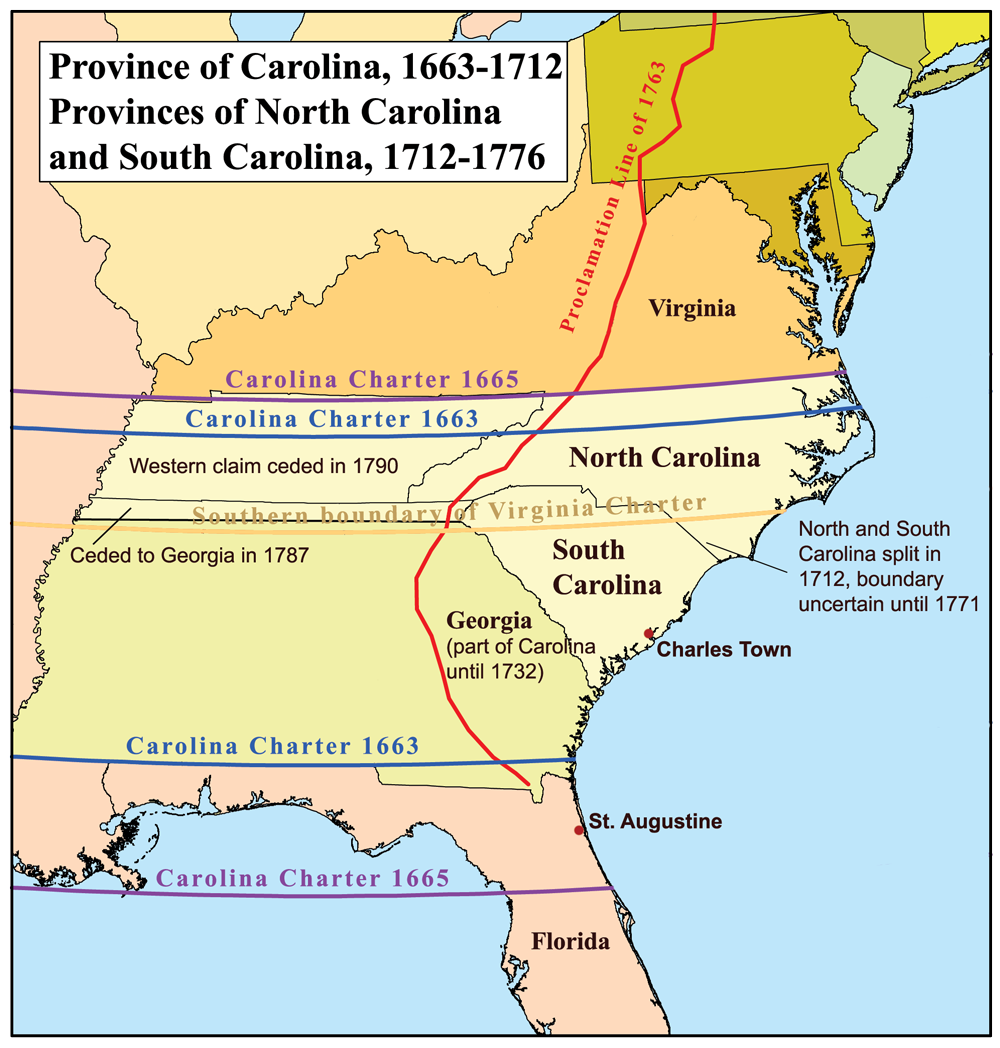
Province Of North Carolina
Province of North Carolina was a province of Great Britain that existed in North America from 1712(p. 80) to 1776. It was one of the five Southern colonies and one of the thirteen American colonies. The monarch of Great Britain was represented by the Governor of North Carolina, until the colonies declared independence on July 4, 1776. Etymology "Carolina" is taken from the Latin word for "Charles" ( Carolus), honoring King Charles II, and was first named in the 1663 Royal Charter granting to Edward, Earl of Clarendon; George, Duke of Albemarle; William, Lord Craven; John, Lord Berkeley; Anthony, Lord Ashley; Sir George Carteret, Sir William Berkeley, and Sir John Colleton the right to settle lands in the present-day U.S. states of North Carolina, Tennessee, South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and Florida. History King Charles II granted the Charter of Carolina in 1663 for land south of the British Colony of Virginia and north of Spanish Fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pig Iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate product of the iron industry in the production of steel which is obtained by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with silica and other constituents of dross, which makes it brittle and not useful directly as a material except for limited applications. The traditional shape of the molds used for pig iron ingots is a branching structure formed in sand, with many individual ingots at right angles to a central channel or "runner", resembling a litter of piglets being nursed by a sow. When the metal had cooled and hardened, the smaller ingots (the "pigs") were simply broken from the runner (the "sow"), hence the name "pig iron". As pig iron is intended for remelting, the uneven size of the ingots and the inclusion of small amounts of sand cause only insignificant problems considering the ease of casting and handling them. History Smelting and producing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coke (fuel)
Coke is a grey, hard, and porous coal-based fuel with a high carbon content and few impurities, made by heating coal or oil in the absence of air—a destructive distillation process. It is an important industrial product, used mainly in iron ore smelting, but also as a fuel in stoves and forges when air pollution is a concern. The unqualified term "coke" usually refers to the product derived from low-ash and low-sulphur bituminous coal by a process called coking. A similar product called petroleum coke, or pet coke, is obtained from crude oil in oil refineries. Coke may also be formed naturally by geologic processes.B. Kwiecińska and H. I. Petersen (2004): "Graphite, semi-graphite, natural coke, and natural char classification — ICCP system". ''International Journal of Coal Geology'', volume 57, issue 2, pages 99-116. History China Historical sources dating to the 4th century describe the production of coke in ancient China. The Chinese first used coke for hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, called charcoal burning, often by forming a charcoal kiln, the heat is supplied by burning part of the starting material itself, with a limited supply of oxygen. The material can also be heated in a closed retort. Modern "charcoal" briquettes used for outdoor cooking may contain many other additives, e.g. coal. This process happens naturally when combustion is incomplete, and is sometimes used in radiocarbon dating. It also happens inadvertently while burning wood, as in a fireplace or wood stove. The visible flame in these is due to combustion of the volatile gases exuded as the wood turns into charcoal. The soot and smoke commonly given off by wood fires result from incomplete combustion of those volatiles. Charcoal burns at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forests Of The United States
It has been estimated that before European settlement, forests in the United States mainland, covered nearly . Since the mid-1600s, about of forest have been cleared, primarily for agriculture during the 19th century." As of 2016, roughly 36.21% (about one-third of the U.S.) is forested.https://www.fs.fed.us/sites/default/files/fs_media/fs_document/publication-15817-usda-forest-service-fia-annual-report-508.pdf USDA - Forest Inventory And Analysis Fiscal Year 2016 Business Report. Page 71-72 (Page 79-80 of PDF). ''Table B-11. Land and forest area and FIA annualized implementation status by State and region, FY 2016.'' Data for territories: ''Table B-10. Status of FIA special project areas excluded from annualized inventory.'' Retrieved January 8, 2019. Excluding the U.S. territories, forested land in the U.S. covers roughly 818,814,000 acres (3,313,622 square kilometers). As of 2005, the United States ranked seventh in the rate of loss of its old growth forests. Current covera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Ore In The United States
Iron mining in the United States produced 48 million metric tons of iron ore in 2019. Iron ore was the third-highest-value metal mined in the United States, after gold and copper. Iron ore was mined from nine active mines and three reclamation operations in Michigan, Minnesota, and Utah. Most of the iron ore was mined in northern Minnesota's Mesabi Range. Net exports (exports minus imports) were 3.9 million tons. US iron ore made up 2.5 percent of the total mined worldwide in 2015. Employment as of 2014 was 5,750 in iron mines and iron ore treatment plants. US iron ore mining is dominated by the Precambrian banded iron formation deposits around Lake Superior, in Minnesota and Michigan; such deposits were also formerly mined in Wisconsin. For the past 50 years, more than 90 percent of US iron ore production has been mined from the Lake Superior deposits. None of the iron ore now mined in the US is “direct shipping” ore ready to be fed into the iron- and steel-making process. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobacco In The United States
Tobacco has a long history in the United States. Tobacco distribution is measured in the United States using the term, "tobacco outlet density." An estimated 34.3 million people, or 14% of all adults (aged 18 years or older), in the United States smoked cigarettes in 2015. By state, in 2015, smoking prevalence ranged from between 9.1% and 12.8% in Utah to between 23.7% and 27.4% in West Virginia. By region, in 2015, smoking prevalence was highest in the Midwest (18.7%) and South (15.3%) and lowest in the West (12.4%). Men tend to smoke more than women. In 2015, 16.7% of men smoked compared to 13.6% of women. In 2018, 13.7% of U.S. adults were smokers. Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of preventable death in the United States, accounting for approximately 443,000 deaths, or 1 of every 5 deaths, in the United States each year. Cigarette smoking alone has cost the United States $96 billion in direct medical expenses and $97 billion in lost productivity per year or an average ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navigation Acts
The Navigation Acts, or more broadly the Acts of Trade and Navigation, were a long series of English laws that developed, promoted, and regulated English ships, shipping, trade, and commerce between other countries and with its own colonies. The laws also regulated England's fisheries and restricted foreigners' participation in its colonial trade. While based on earlier precedents, they were first enacted in 1651 under the Commonwealth. The system was reenacted and broadened with the Restoration by the Act of 1660, and further developed and tightened by the Navigation Acts of 1663, 1673, and 1696. Upon this basis during the 18th century, the Acts were modified by subsequent amendments, changes, and the addition of enforcement mechanisms and staff. Additionally, a major change in the very purpose of the Acts in the 1760s – that of generating a colonial revenue, rather than only regulating the Empire's trade – would help lead to major rebellions, and significant changes in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finished Goods
Finished goods are goods that have completed the manufacturing process but have not yet been sold or distributed to the end user. Manufacturing Manufacturing has three classes of inventory: # Raw material # Work in process # Finished goods A good purchased as a "raw material" goes into the manufacture of a product. A good only partially completed during the manufacturing process is called "work in process". When the good is completed as to manufacturing but not yet sold or distributed to the end-user, it is called a "finished good". This is the last stage for the processing of goods. The goods are ready to be consumed or distributed. There is no processing required in term of the goods after this stage by the seller. Though there maybe instance that seller finished goods become buyer’s raw materials Finished goods is a relative term. In a Supply chain management flow, the finished goods of a supplier can constitute the raw material of a buyer Procurement is the metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
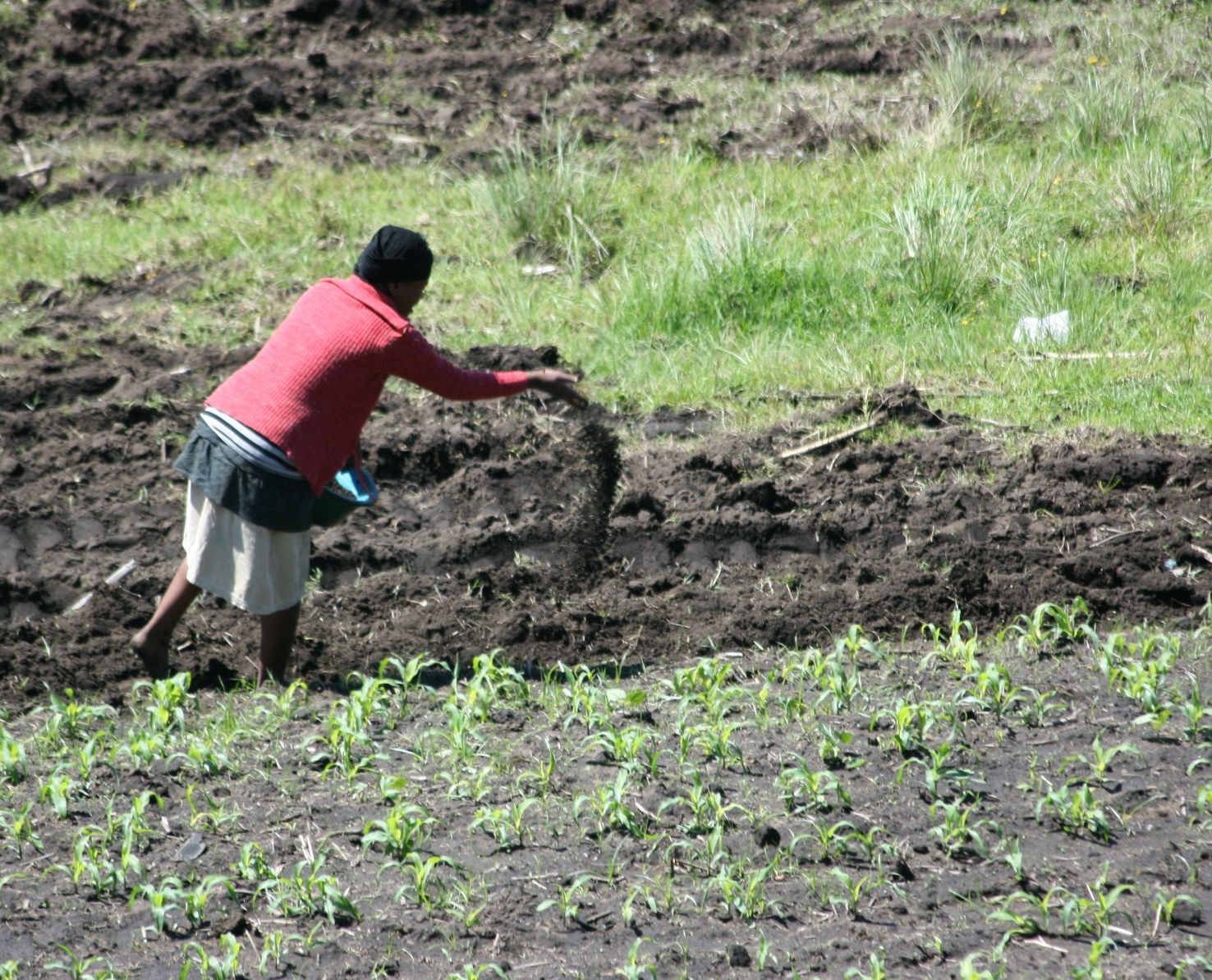
Fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) with occasional addition of supplements like rock flour for micronutrients. Farmers apply these fertilizers in a variety of ways: through dry or pelletized or liquid application processes, using large agricultural equipment or hand-tool methods. Historically fertilization came from natural or organic sources: compost, animal manure, human manure, harvested minerals, crop rotations and byproducts of human-nature industries (i.e. fish processing waste, or bloodmeal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water- soluble form.Potash USGS 2008 Minerals Yearbook The name derives from ''pot ash'', plant ashes or wood ash soaked in water in a pot, the primary means of manufacturing potash before the Industrial Era. The word '''' is derived from ''potash''. Potash is produced worldwide in amounts exceeding 90 million s (40 mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)