|
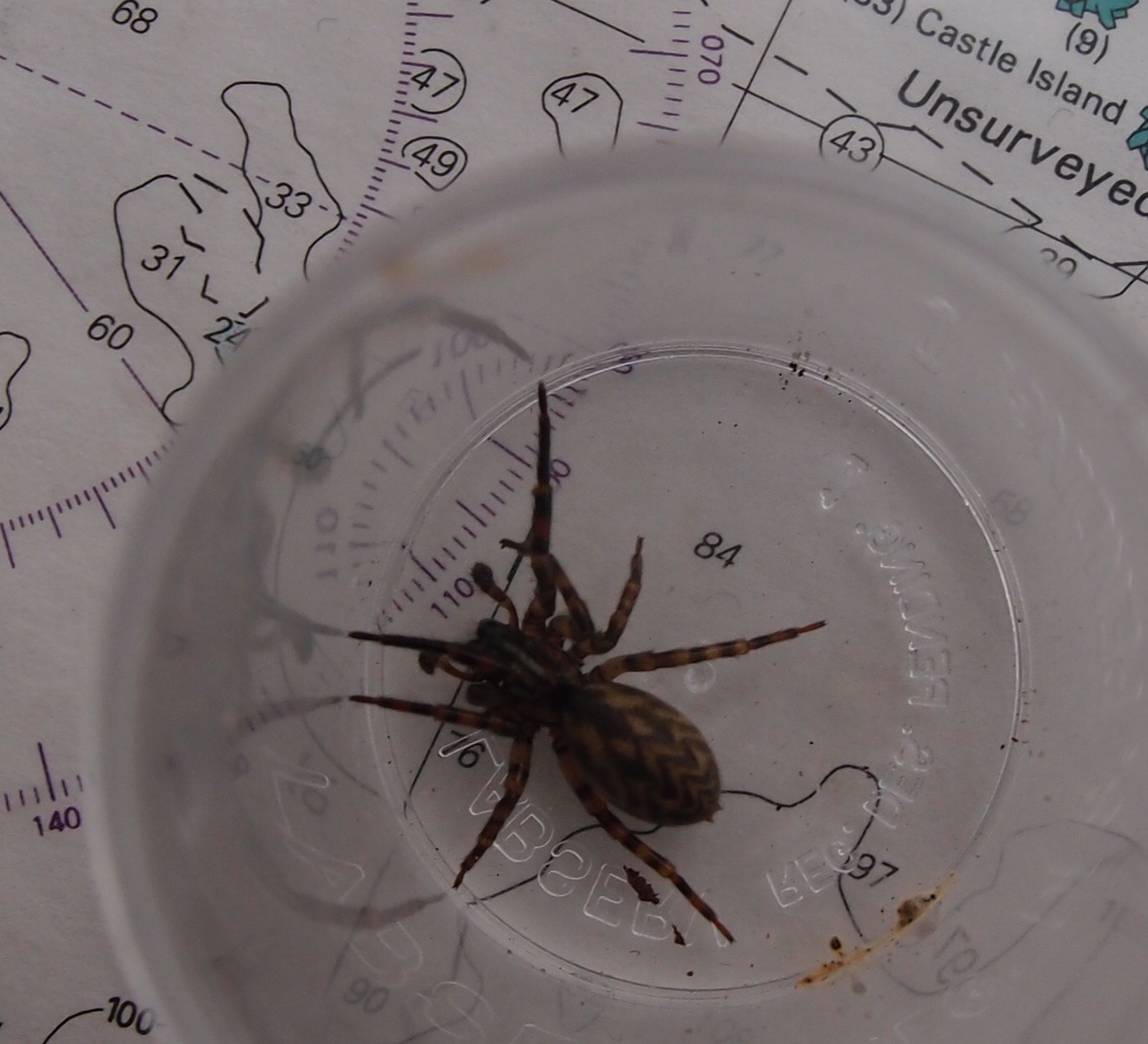
Eatoniella Rakiura
''Eatoniella rakiura'' is a species of marine gastropod mollusc in the family Eatoniellidae. First described by Winston Ponder in 1965, it is endemic to the waters of New Zealand. The first specimens of the species were exclusively found around Stewart Island. Description ''Eatoniella rakiura'' has a semi-transparent thin shell, with evenly convex and swollen whorls. The holotype measured 1.1mm by 0.65mm. It is similar in appearance to ''Eatoniella lampra'', but differs in its more swollen whorls. Distribution The species is endemic to New Zealand. The holotype was collected on 4 November, 1956 at a depth of 46 metres off the coast of Stewart Island, on the surface of bryozoan species. Originally described as occurring exclusively around Steward Island, the species has since been identified at Taieri Mouth in Otago and in the Bounty Islands The Bounty Islands ( mi, Moutere Hauriri; "Island of angry wind") are a small group of 13 uninhabited granite islets and numero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
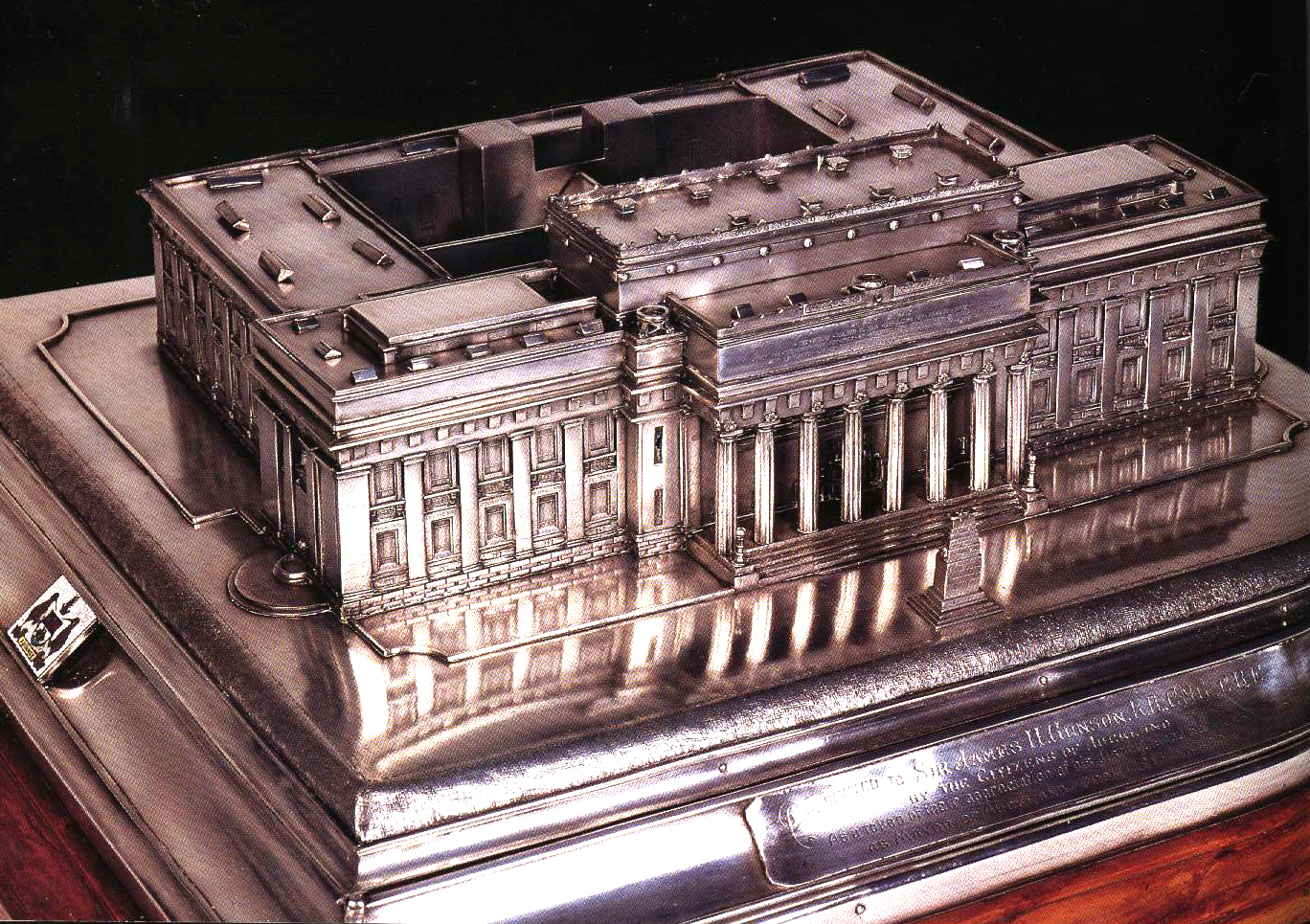
Auckland War Memorial Museum
The Auckland War Memorial Museum Tāmaki Paenga Hira (or simply the Auckland Museum) is one of New Zealand's most important museums and war memorials. Its collections concentrate on New Zealand history (and especially the history of the Auckland Region), natural history, and military history. The present museum building was constructed in the 1920s in the neo-classicist style, and sits on a grassed plinth (the remains of a dormant volcano) in the Auckland Domain, a large public park close to the Auckland CBD. Auckland Museum's collections and exhibits began in 1852. In 1867 Aucklanders formed a learned society – the Auckland Philosophical Society, later the Auckland Institute. Within a few years the society merged with the museum and '' Auckland Institute and Museum'' was the organisation's name until 1996. Auckland War Memorial Museum was the name of the new building opened in 1929, but since 1996 was more commonly used for the institution as well. From 1991 to 2003 the muse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Auckland Museum
The Auckland War Memorial Museum Tāmaki Paenga Hira (or simply the Auckland Museum) is one of New Zealand's most important museums and war memorials. Its collections concentrate on New Zealand history (and especially the history of the Auckland Region), natural history, and military history. The present museum building was constructed in the 1920s in the neo-classicist style, and sits on a grassed plinth (the remains of a dormant volcano) in the Auckland Domain, a large public park close to the Auckland CBD. Auckland Museum's collections and exhibits began in 1852. In 1867 Aucklanders formed a learned society – the Auckland Philosophical Society, later the Auckland Institute. Within a few years the society merged with the museum and '' Auckland Institute and Museum'' was the organisation's name until 1996. Auckland War Memorial Museum was the name of the new building opened in 1929, but since 1996 was more commonly used for the institution as well. From 1991 to 2003 the muse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Molluscs Of New Zealand
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Fauna Of New Zealand
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropods Of New Zealand
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, and reproduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropods Described In 1965
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, and reproduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Te Papa
The Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa is New Zealand's national museum and is located in Wellington. ''Te Papa Tongarewa'' translates literally to "container of treasures" or in full "container of treasured things and people that spring from mother Earth here in New Zealand". Usually known as Te Papa (Māori language, Māori for "Waka huia, the treasure box"), it opened in 1998 after the merging of the National Museum of New Zealand and the National Art Gallery. An average of more than 1.5 million people visit every year, making it the List of most-visited art museums, 17th-most-visited art gallery in the world. Te Papa's philosophy emphasises the living face behind its cultural treasures, many of which retain deep ancestral links to the indigenous Māori people. History Colonial Museum The first predecessor to Te Papa was the ''Colonial Museum'', founded in 1865, with James Hector, Sir James Hector as founding director. The Museum was built on Museum Street, roughly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bounty Islands
The Bounty Islands ( mi, Moutere Hauriri; "Island of angry wind") are a small group of 13 uninhabited granite islets and numerous rocks, with a combined area of , in the South Pacific Ocean. Territorially part of New Zealand, they lie about east-south-east of New Zealand's South Island, south-west of the Chatham Islands, and north of the Antipodes Islands. The group is a World Heritage Site. The islands are listed with the New Zealand Outlying Islands. The islands are an immediate part of New Zealand, but not part of any region or district. Rather, they are listed as an ''Area Outside Territorial Authority'', similar to all other outlying islands except for the Solander Islands / Hautere. History Captain William Bligh discovered the Bounty Islands en route from Spithead to Tahiti in 1788, and named them after his ship HMS ''Bounty'', just months before the famous mutiny. The location of the islands were only roughly marked on charts. In early 1866 Commander W. H. Norman o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otago
Otago (, ; mi, Ōtākou ) is a region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately , making it the country's second largest local government region. Its population was The name "Otago" is the local southern Māori dialect pronunciation of "Ōtākou", the name of the Māori village near the entrance to Otago Harbour. The exact meaning of the term is disputed, with common translations being "isolated village" and "place of red earth", the latter referring to the reddish-ochre clay which is common in the area around Dunedin. "Otago" is also the old name of the European settlement on the harbour, established by the Weller Brothers in 1831, which lies close to Otakou. The upper harbour later became the focus of the Otago Association, an offshoot of the Free Church of Scotland, notable for its adoption of the principle that ordinary people, not the landowner, should choose the ministe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taieri Mouth
Taieri Mouth is a small fishing village at the mouth of the Taieri River, New Zealand. Taieri Island (Moturata) lies in the ocean several hundred metres off the river's mouth. It has a white sand beach for swimming and several picnic areas. Moturata is a distinctive landmark which can be walked to at low-tide. Caution is advised as the tides can change quickly. Another feature is the millennium walking track that follows the Taieri River from the mouth through the lower gorge to Henley. The village is located 40 km southwest of central Dunedin on the Southern Scenic Route. It is located in the Clutha District on the boundary of Dunedin City and 10 km east of Lake Waihola. Immediately to its south is the smaller settlement of Taieri Beach, and the two are often considered parts of the same settlement. It gained a little notoriety or sadness in the 1990s as the place where the father of murder suspect David Bain worked. History There was a Māori occupation site at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steward Island
Steward Island ( da, Steward Ø; also ''Stewart Ø'' in some sources)''Prostar Sailing Directions 2005 Greenland and Iceland Enroute'', p. 111 is an uninhabited island in King Christian IX Land, at the eastern end of Greenland. Administratively it is part of the Sermersooq municipality. The island is mountainous and clearly visible from a distance. According to mariners' reports the island is a good landmark for vessels approaching Greenland from the east. Geography Steward is a coastal island of the Blosseville Coast located in a bay off the Savoia Peninsula. It lies 39 km to the SW of Cape Brewster and 7.5 km to the northeast of the small Manby Peninsula. To the west there is a wide glacier discharging in the bay and the island's western end is attached to the terminus of the glacier, so that it almost forms a peninsula with the mainland. The island is long with a maximum width of . The small Dunholm islets ''(Dunholm Øer)'' lie 4 km to the east and the high Pyramiden, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryozoa
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary colonies. Typically about long, they have a special feeding structure called a lophophore, a "crown" of tentacles used for filter feeding. Most marine bryozoans live in tropical waters, but a few are found in oceanic trenches and polar waters. The bryozoans are classified as the marine bryozoans (Stenolaemata), freshwater bryozoans (Phylactolaemata), and mostly-marine bryozoans (Gymnolaemata), a few members of which prefer brackish water. 5,869living species are known. At least two genera are solitary (''Aethozooides'' and ''Monobryozoon''); the rest are colonial. The terms Polyzoa and Bryozoa were introduced in 1830 and 1831, respectively. Soon after it was named, another group of animals was discovered whose filtering mechanism looked similar, so it was included in Bryozoa until 1869, when the two groups were no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.jpg)


