|
Early Middle Ages In Azerbaijan
In the history of Azerbaijan, the Early Middle Ages lasted from the 3rd to the 11th century. This period in the territories of today's Azerbaijan Republic began with the incorporation of these territories into the Sasanian Persian Empire in the 3rd century AD. Feudalism took shape in Azerbaijan in the Early Middle Ages. The territories of Caucasian Albania became an arena of wars between the Byzantine Empire and the Sassanid Empire. After the Sassanid Empire was felled by the Arab Caliphate, Albania also weakened and was overthrown in 705 AD by the Abbasid Caliphate under the name of Arran. As the control of the Arab Caliphate over the Caucasus region weakened, independent states began to emerge in the territory of Azerbaijan. Sassanid conquest History In 252-253 AD, Caucasian Albania was conquered and annexed by the Sassanid Empire. It became a vassal state, but retained its monarchy; however the Albanian king had no real power and most civil, religious, and milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia (Republic of Dagestan) to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia and Turkey to the west, and Iran to the south. Baku is the capital and largest city. The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic proclaimed its independence from the Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic in 1918 and became the first secular democratic Muslim-majority state. In 1920, the country was incorporated into the Soviet Union as the Azerbaijan SSR. The modern Republic of Azerbaijan proclaimed its independence on 30 August 1991, shortly before the dissolution of the Soviet Union in the same year. In September 1991, the ethnic Armenian majority of the Nagorno-Karabakh region formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urnayr
Urnayr (attested only as Old Armenian Ուռնայր ''Uṙnayr'') was the third Arsacid king of Caucasian Albania from approximately 350 to 375. He was the successor of Vache I (). Biography The Treaty of Nisibis in 299 between the Sasanian King of Kings (''shahanshah'') Narseh () and the Roman emperor Diocletian had ended disastrously for the Sasanians, who ceded them huge chunks of their territory, including the Caucasian kingdoms of Armenia and Iberia. The Sasanians would not take part in the political affairs of the Caucasus for almost 40 years. The modern historian Murtazali Gadjiev argues that it was during this period the Arsacids gained the kingship of Albania, by being appointed as proxies by the Romans in order to gain complete control over the Caucasus. In the 330s, a reinvigorated Iran re-entered the Caucasian political scene, forcing the Arsacid Albanian king Vachagan I (or Vache I) to acknowledge Sasanian suzerainty. Urnayr, whose mother was a Sasanian princess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yazdegerd II
Yazdegerd II (also spelled Yazdgerd and Yazdgird; pal, 𐭩𐭦𐭣𐭪𐭥𐭲𐭩), was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 438 to 457. He was the successor and son of Bahram V (). His reign was marked by wars against the Eastern Roman Empire in the west and the Kidarites in the east, as well as by his efforts and attempts to strengthen royal centralisation in the bureaucracy by imposing Zoroastrianism on the non-Zoroastrians within the country, namely the Christians. This backfired in Armenia, culminating in a large-scale rebellion led by the military leader Vardan Mamikonian, who was ultimately defeated and killed at the Battle of Avarayr in 451. Nevertheless, religious freedom was subsequently allowed in the country. Yazdegerd II was the first Sasanian ruler to assume the title of '' kay'' ("king"), which evidently associates him and the dynasty to the mythical Kayanian dynasty commemorated in the Avesta. His death led to a dynastic struggle between his two sons Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion and one of the world's History of religion, oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian peoples, Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a Dualism in cosmology, dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a Monotheism, monotheistic ontology and an eschatology which predicts the ultimate conquest of evil by good. Zoroastrianism exalts an uncreated and benevolent deity of wisdom known as ''Ahura Mazda'' () as its supreme being. Historically, the unique features of Zoroastrianism, such as its monotheism, messianism, belief in Free will in theology, free will and Judgement (afterlife), judgement after death, conception of heaven, hell, Angel, angels, and Demon, demons, among other concepts, may have influenced other religious and philosophical systems, including the Abrahamic religions and Gnosticism, Southern, Eastern and Northern Buddhism, Northern Buddhism, and Ancient Greek philosoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakasene
Sakasena{{clarify, date=October 2020 ( Armenian: Շակաշեն - ''Shakashen'', Greek: Σακασηνήν - ''Sakasena''; from Persian ''Saka-anaayana'' - "inhabited territory of the Saks") is a historical region on the territory of modern Azerbaijan. The former core of the 7th - 6th century BCE of the Scythian kingdom of Ishkuz. It got its name from the tribes of the Scythians (Saks in the Eastern tradition), who later entered the tribal union of the Caucasian Albanians. At the end of the 6th - beginning of the 5th century BCE it was part of the satrapy Media under the Achaemenid Empire. At the beginning of the 2nd century BCE it was annexed to Greater Armenia, becoming the Gavar (district) of the Nahanga (province) of Utic. In the division of Great Armenia in 387, it went to the Caucasian Albania, which was, under the treaty, subordinate to the Sassanids. It was located South of the middle course of the Kura, in the area of modern Ganja. Description It is assumed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utik
Utik ( hy, Ուտիք, also known as Uti, Utiq, or Outi) was a historic province of the Kingdom of Armenia. It was ceded to Caucasian Albania following the partition of Armenia between Sassanid Persia and the Eastern Roman Empire in 387 AD. Most of the region is located within present-day Azerbaijan immediately west of the Kura River, while a part of it lies within the Tavush province of present-day northeastern Armenia. History According to Strabo, in the 2nd century BC, Armenians conquered from the Medes the lands of Syunik and Caspiane, and the lands that lay between them, including Utik,Robert H. Hewsen. "Ethno-History and the Armenian Influence upon the Caucasian Albanians," in: Samuelian, Thomas J. (Hg.), Classical Armenian Culture. Influences and Creativity, Chicago: 1982, 27-40. that was populated by the people called Utis, after whom it received its name. Modern historians agree that "Utis" were a people of non-Armenian origin, and the modern ethnic group of Udi is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bagavan
The Battle of Bagavan (also spelled Bagawan) or the Battle of Vagabanta was fought in 371 near the settlement of Bagavan, in the district of Bagrevand in Greater Armenia, between a joint Roman-Armenian force and a Sassanid army, with the Romans and Armenians emerging victorious. It is recorded by the Roman historian Ammianus Marcellinus, as well as the Armenian historian Faustus of Byzantium. The Armenian historian Movses Khorenatsi and several later Armenian historians following him place the battle in a field called Dzirav, and so the battle is called the Battle of Dzirav in some Armenian sources. In the view of historians Hakob Manandian and Nina Garsoïan, this is an error by Khorenatsi or a conflation of the Battle of Bagavan with the battle at Gandzak described in the next chapter of Faustus's history. Background In the aftermath of the Perso-Roman peace treaty of 363, whereby Rome had pledged not to intervene in Armenian affairs, Armenia was left at the mercy of the Sassa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grumbates
Grumbates or Krumbates was a king of the Chionitae, probably of the Kidarites tribe, an ancient nomadic tribe of Transoxiana. Etymology The exact origin of his name is not fully known. Hyun Jin Kim etymologized his name as ''*Qurum-pat'', "ruling prince"; containing Iranian element ''pat'' "chieftain, ruler" and Turkic ''qurum'' "rule, leadership, administration" which is attested in the name of Bulgarian khan Krum. Attacks on the Sasanian Empire The Kidarite king Grumbates mentioned by Ammianus Marcellinus was a cause of much concern to the Persians. Between 353 AD and 358 CE, the Xionites under Grumbates attacked in the eastern frontiers of Shapur II's empire along with other nomad tribes. After a prolonged struggle they were forced to conclude a peace, and their king Grumbates accompanied Shapur II in the war against the Romans. Alliance with Shapur II against the Romans Grumbates thus participated in the Siege of Amida in 359 CE as an ally of Shapur II. His participati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xionites
Xionites, Chionites, or Chionitae (Middle Persian: ''Xiyōn'' or ''Hiyōn''; Avestan: ''Xiiaona''; Sogdian ''xwn''; Pahlavi ''Xyon'') were a nomadic people in the Central Asian regions of Transoxiana and Bactria. The Xionites appear to be synonymous with the Huna peoples of the South Asian regions of classical/medieval India, and possibly also the Huns of European late antiquity, who were in turn connected onomastically to the Xiongnu in Chinese history. They were first described by the Roman historian, Ammianus Marcellinus, who was in Bactria during 356–357 CE; he described the ''Chionitæ'' as living with the Kushans. Ammianus indicates that the Xionites had previously lived in Transoxiana and, after entering Bactria, became vassals of the Kushans, were influenced culturally by them and had adopted the Bactrian language. They had attacked the Sassanid Empire, but later (led by a chief named Grumbates), served as mercenaries in the Persian Sassanian army. Within the Xi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
The Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic ( az, Naxçıvan Muxtar Respublikası, ), is a landlocked exclave of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The region covers Official portal of Nakhchivan Autonomous RepublicNakhchivan Autonomous Republic with a population of 459,600 bordered by Armenia to the east and north, Iran to the southwest, and Turkey to the west. The republic, especially the capital city of Nakhchivan, has a long history dating back to about 1500 BCE. ''Nakhijevan'' was one the cantons of the historical Armenian province of Vaspurakan in the Kingdom of Armenia. Historically though, the Persians, Armenians, Mongols, and Turks all competed for the region. The area that is now Nakhchivan became part of Safavid Iran in the 16th century. In 1828, after the last Russo-Persian War and the Treaty of Turkmenchay, the Nakhchivan Khanate passed from Iranian into Imperial Russian possession. After the 1917 February Revolution, Nakhchivan and its surrounding region were under the autho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Artsakh
The Kingdom of Artsakh ( hy, Արցախի թագավորություն) was a medieval dependent Armenian kingdom on the territory of Syunik and Artsakh provinces, Gardman canton of Utik province, Mazaz and Varazhnunik canton of Ayrarat province. Contemporary sources referred to it as the Khachen. However, because the domain of Khachen during the reign of Prince Hasan Jalal included the entire territory of the modern Nagorno Karabakh Republic plus many contiguous lands to its west, south and north, his principality was often called the Kingdom of Artsakh. The royal house of Khachen was a cadet branch of the ancient Syunid dynasty and was named Khachen, after its main stronghold. Hasan-Jalal traced his descent to the Armenian Aranshahik dynasty, a family that predated the establishment of the Parthian Arsacids in the region. Artsakh maintained its sovereign rulers, though in the early 13th century they accepted Georgian, then Mongol suzerainty.Hewsen, Robert H. "The Mel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
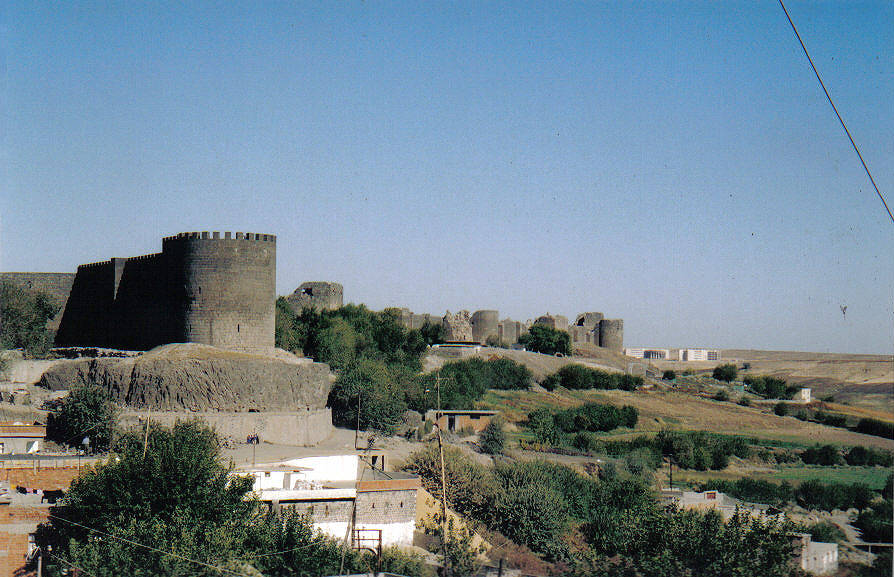
Siege Of Amida (359)
The siege of Amida was a military investment of the Roman fortified frontier city of Amida (modern Diyarbakır, Turkey) by the Sasanian Empire. It took place in AD 359 when the Sasanian army under king Shapur II invaded the eastern provinces of the Roman Empire. Shapur wanted to exploit the absence of the Roman Emperor Constantius II who was overseeing affairs in the western part of the Empire. The city fell, but the strategic gain was little. Ammianus Marcellinus, a Roman army officer, provided a vivid description of the siege in his work (''Res Gestae''). Ammianus served on the staff of Ursicinus, the Magister Equitum (master of horse) of the East, during the events of the siege. Background Persian When Shapur II took control of the Sasanian Empire, he sought to regain old territories previously lost to the Roman Empire. After crushing the Arabs in the south, he moved east to deal with nomadic forces, the most prominent being the Xionites. Following a prolonged struggle f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_p012_BAKU%2C_FIRE_TEMPLE_(cropped).jpg)


