|
EHD Protein Family
The EHD protein family is a relatively small group of proteins which have been shown to play a role in several physiological functions, the most notable being the regulation of endocytotic vesicles. This family is recognized by its highly conserved EH (Eps15 homology) domain, a structural motif that has been shown to facilitate specificity and interaction between protein and ligand. The four mammalian EHD proteins that have been classified are: EHD1, EHD2, EHD3, and EHD4. History During the late 20th century, several advances were made regarding the identification of proteins involved in endocytotic recycling and other mechanisms of intracellular trafficking. This period of research led to the discovery of over 60 proteins which collectively make up the Rab family. Rab proteins have been found to play a major role in endocytotic recycling via SNARE-based vesicle fusion and transport. When bound to GTP, Rab proteins have a large affinity for their respective effectors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamin
Dynamin is a GTPase responsible for endocytosis in the eukaryotic cell. Dynamin is part of the "dynamin superfamily", which includes classical dynamins, dynamin-like proteins, Mx proteins, OPA1, mitofusins, and GBPs. Members of the dynamin family are principally involved in the scission of newly formed vesicles from the membrane of one cellular compartment and their targeting to, and fusion with, another compartment, both at the cell surface (particularly caveolae internalization) as well as at the Golgi apparatus.Hinshaw, J"Research statement, Jenny E. Hinshaw, Ph.D."National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases, Laboratory of Cell Biochemistry and Biology. Accessed 19 March 2013. Dynamin family members also play a role in many processes including division of organelles, cytokinesis and microbial pathogen resistance. Structure Dynamin itself is a 96 kDa enzyme, and was first isolated when researchers were attempting to isolate new microtubule-based motors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-affinity Nerve Growth Factor Receptor
The p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) was first identified in 1973 as the low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor (LNGFR) before discovery that p75NTR bound other neurotrophins equally well as nerve growth factor. p75NTR is a neurotrophic factor receptor. Neurotrophic factor receptors bind Neurotrophins including Nerve growth factor, Neurotrophin-3, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and Neurotrophin-4. All neurotrophins bind to p75NTR. This also includes the immature pro-neurotrophin forms. Neurotrophic factor receptors, including p75NTR, are responsible for ensuring a proper density to target ratio of developing neurons, refining broader maps in development into precise connections. p75NTR is involved in pathways that promote neuronal survival and neuronal death. Receptor family p75NTR is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. p75NTR/LNGFR was the first member of this large family of receptors to be characterized, that now contains about 25 receptors, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamate Receptor
Glutamate receptors are synaptic and non synaptic receptors located primarily on the membranes of neuronal and glial cells. Glutamate (the conjugate base of glutamic acid) is abundant in the human body, but particularly in the nervous system and especially prominent in the human brain where it is the body's most prominent neurotransmitter, the brain's main excitatory neurotransmitter, and also the precursor for GABA, the brain's main inhibitory neurotransmitter. Glutamate receptors are responsible for the glutamate-mediated postsynaptic excitation of neural cells, and are important for neural communication, memory formation, learning, and regulation. Glutamate receptors are implicated in a number of neurological conditions. Their central role in excitotoxicity and prevalence in the central nervous system has been linked or speculated to be linked to many neurodegenerative diseases, and several other conditions have been further linked to glutamate receptor gene mutations o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GLUT4
Glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4), also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 4, is a protein encoded, in humans, by the ''SLC2A4'' gene. GLUT4 is the insulin-regulated glucose transporter found primarily in adipose tissues and striated muscle (skeletal and cardiac). The first evidence for this distinct glucose transport protein was provided by David James in 1988. The gene that encodes GLUT4 was cloned and mapped in 1989. At the cell surface, GLUT4 permits the facilitated diffusion of circulating glucose down its concentration gradient into muscle and fat cells. Once within cells, glucose is rapidly phosphorylated by glucokinase in the liver and hexokinase in other tissues to form glucose-6-phosphate, which then enters glycolysis or is polymerized into glycogen. Glucose-6-phosphate cannot diffuse back out of cells, which also serves to maintain the concentration gradient for glucose to passively enter cells. Structure Like all proteins, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
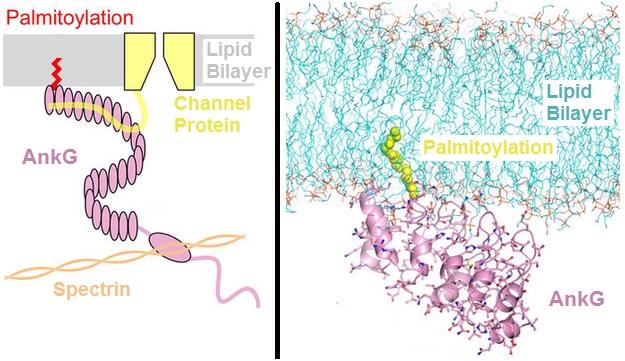
Ankyrin
Ankyrins are a family of proteins that mediate the attachment of integral membrane proteins to the spectrin-actin based membrane cytoskeleton. Ankyrins have binding sites for the beta subunit of spectrin and at least 12 families of integral membrane proteins. This linkage is required to maintain the integrity of the plasma membranes and to anchor specific ion channels, ion exchangers and ion transporters in the plasma membrane. The name is derived from the Greek word ἄγκυρα (''ankyra'') for "anchor". Structure Ankyrins contain four functional domains: an N-terminal domain that contains 24 tandem ankyrin repeats, a central domain that binds to spectrin, a death domain that binds to proteins involved in apoptosis, and a C-terminal regulatory domain that is highly variable between different ankyrin proteins. Membrane protein recognition The 24 tandem ankyrin repeats are responsible for the recognition of a wide range of membrane proteins. These 24 repeats contain 3 struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase B
Tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB), also known as tyrosine receptor kinase B, or BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor or neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NTRK2'' gene. TrkB is a receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Standard pronunciation is "track bee". Function Tropomyosin receptor kinase B is the high affinity catalytic receptor for several " neurotrophins", which are small protein growth factors that induce the survival and differentiation of distinct cell populations. The neurotrophins that activate TrkB are: BDNF (Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor), neurotrophin-4 (NT-4), and neurotrophin-3 (NT-3).> As such, TrkB mediates the multiple effects of these neurotrophic factors, which includes neuronal differentiation and survival. Research has shown that activation of the TrkB receptor can lead to down regulation of the KCC2 chloride transporter in cells of the CNS. Except for the role of the pathw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase A
Tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA), also known as high affinity nerve growth factor receptor, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 1, or TRK1-transforming tyrosine kinase protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NTRK1'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor (NTKR) family. This kinase is a membrane-bound receptor that, upon neurotrophin binding, phosphorylates itself (autophosphorylation) and members of the MAPK pathway. The presence of this kinase leads to cell differentiation and may play a role in specifying sensory neuron subtypes. Mutations in this gene have been associated with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis, self-mutilating behaviors, intellectual disability and/or cognitive impairment and certain cancers. Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene have been found, but only three have been characterized to date. Function and Interaction with NGF TrkA is the high affinity cataly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine Receptor
Dopamine receptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are prominent in the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). Dopamine receptors activate different effectors through not only G-protein coupling, but also signaling through different protein (dopamine receptor-interacting proteins) interactions. The neurotransmitter dopamine is the primary endogenous ligand for dopamine receptors. Dopamine receptors are implicated in many neurological processes, including motivational and incentive salience, cognition, memory, learning, and fine motor control, as well as modulation of neuroendocrine signaling. Abnormal dopamine receptor signaling and dopaminergic nerve function is implicated in several neuropsychiatric disorders. Thus, dopamine receptors are common neurologic drug targets; antipsychotics are often dopamine receptor antagonists while psychostimulants are typically indirect agonists of dopamine receptors. Subtypes The existence of multiple types of receptors for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LDL Receptor
The low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) is a mosaic protein of 839 amino acids (after removal of 21-amino acid signal peptide) that mediates the endocytosis of cholesterol-rich low-density lipoprotein (LDL). It is a cell-surface receptor that recognizes apolipoprotein B100 (ApoB100), which is embedded in the outer phospholipid layer of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), their remnants—i.e. intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), and LDL particles. The receptor also recognizes apolipoprotein E (ApoE) which is found in chylomicron remnants and IDL. In humans, the LDL receptor protein is encoded by the gene on chromosome 19. It belongs to the low density lipoprotein receptor gene family. It is most significantly expressed in bronchial epithelial cells and adrenal gland and cortex tissue. Michael S. Brown and Joseph L. Goldstein were awarded the 1985 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their identification of LDL-R and its relation to cholesterol metabolism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transferrin Receptor
Transferrin receptor (TfR) is a carrier protein for transferrin. It is needed for the import of iron into the cell and is regulated in response to intracellular iron concentration. It imports iron by internalizing the transferrin-iron complex through receptor-mediated endocytosis.Figure 3: The cycle of transferrin and transferrin receptor 1-mediated cellular iron uptake./ref> The existence of a receptor for transferrin iron uptake had been recognized over half a century back. Earlier two transferrin receptors in humans, transferrin receptor 1 and transferrin receptor 2 had been characterized and until recently cellular iron uptake was believed to occur chiefly via these two well documented transferrin receptors. Both these receptors are transmembrane glycoproteins. TfR1 is a high affinity ubiquitously expressed receptor while expression of TfR2 is restricted to certain cell types and is unaffected by intracellular iron concentrations. TfR2 binds to transferrin with a 25-30 fold low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
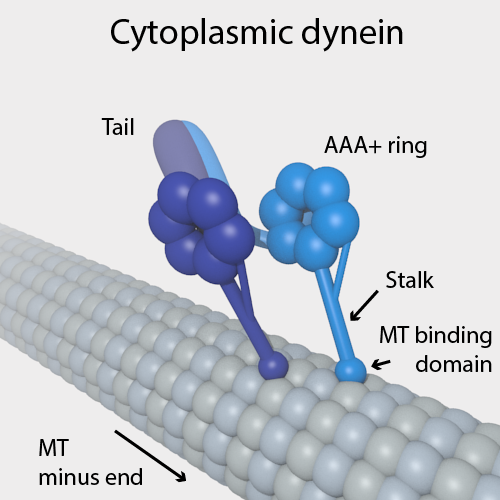
Dynein
Dyneins are a family of cytoskeletal motor proteins that move along microtubules in cells. They convert the chemical energy stored in ATP to mechanical work. Dynein transports various cellular cargos, provides forces and displacements important in mitosis, and drives the beat of eukaryotic cilia and flagella. All of these functions rely on dynein's ability to move towards the minus-end of the microtubules, known as retrograde transport; thus, they are called "minus-end directed motors". In contrast, most kinesin motor proteins move toward the microtubules' plus-end, in what is called anterograde transport. Classification Dyneins can be divided into two groups: cytoplasmic dyneins and axonemal dyneins, which are also called ciliary or flagellar dyneins. * cytoplasmic ** heavy chain: DYNC1H1, DYNC2H1 ** intermediate chain: DYNC1I1, DYNC1I2 ** light intermediate chain: DYNC1LI1, DYNC1LI2, DYNC2LI1 ** light chain: DYNLL1, DYNLL2, DYNLRB1, DYNLRB2, DYNLT1, DYNLT3 * axo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |