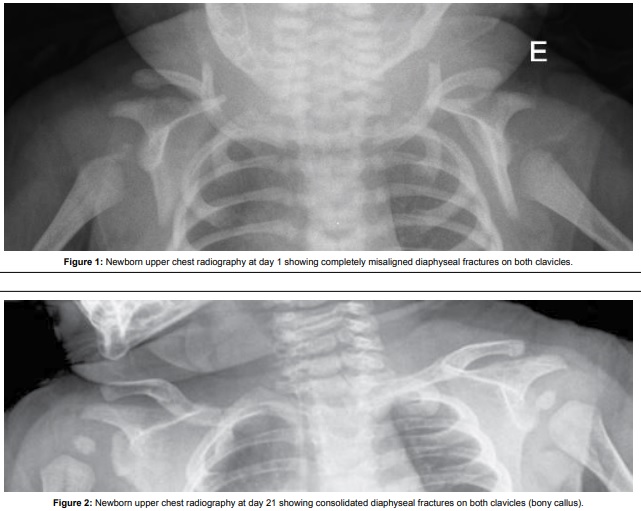
|
Dystocia
Obstructed labour, also known as labour dystocia, is the baby not exiting the pelvis because it is physically block during childbirth although the uterus contracts normally. Complications for the baby include not getting enough oxygen which may result in death. It increases the risk of the mother getting an infection, having uterine rupture, or having post-partum bleeding. Long-term complications for the mother include obstetrical fistula. Obstructed labour is said to result in prolonged labour, when the active phase of labour is longer than 12 hours. The main causes of obstructed labour include a large or abnormally positioned baby, a small pelvis, and problems with the birth canal. Abnormal positioning includes shoulder dystocia where the anterior shoulder does not pass easily below the pubic bone. Risk factors for a small pelvis include malnutrition and a lack of exposure to sunlight causing vitamin D deficiency. It is also more common in adolescence as the pelvis may not ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoulder Dystocia
Shoulder dystocia is when, after vaginal delivery of the head, the baby's anterior shoulder gets caught above the mother's pubic bone. Signs include retraction of the baby's head back into the vagina, known as "turtle sign". Complications for the baby may include brachial plexus injury, or clavicle fracture. Complications for the mother may include vaginal or perineal tears, postpartum bleeding, or uterine rupture. Risk factors include gestational diabetes, previous history of the condition, operative vaginal delivery, obesity in the mother, an overly large baby, and epidural anesthesia. It is diagnosed when the body fails to deliver within one minute of delivery of the baby's head. It is a type of obstructed labour. Shoulder dystocia is an obstetric emergency. Initial efforts to release a shoulder typically include: with a woman on her back pushing the legs outward and upward, pushing on the abdomen above the pubic bone, and making a cut in the vagina. If these are not effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoulder Dystocia
Shoulder dystocia is when, after vaginal delivery of the head, the baby's anterior shoulder gets caught above the mother's pubic bone. Signs include retraction of the baby's head back into the vagina, known as "turtle sign". Complications for the baby may include brachial plexus injury, or clavicle fracture. Complications for the mother may include vaginal or perineal tears, postpartum bleeding, or uterine rupture. Risk factors include gestational diabetes, previous history of the condition, operative vaginal delivery, obesity in the mother, an overly large baby, and epidural anesthesia. It is diagnosed when the body fails to deliver within one minute of delivery of the baby's head. It is a type of obstructed labour. Shoulder dystocia is an obstetric emergency. Initial efforts to release a shoulder typically include: with a woman on her back pushing the legs outward and upward, pushing on the abdomen above the pubic bone, and making a cut in the vagina. If these are not effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetrics
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field. Main areas Prenatal care Prenatal care is important in screening for various complications of pregnancy. This includes routine office visits with physical exams and routine lab tests along with telehealth care for women with low-risk pregnancies: Image:Ultrasound_image_of_a_fetus.jpg, 3D ultrasound of fetus (about 14 weeks gestational age) Image:Sucking his thumb and waving.jpg, Fetus at 17 weeks Image:3dultrasound 20 weeks.jpg, Fetus at 20 weeks First trimester Routine tests in the first trimester of pregnancy generally include: * Complete blood count * Blood type ** Rh-negative antenatal patients should receive RhoGAM at 28 weeks to prevent Rh disease. * Indirect Coombs test (AGT) to assess risk of hemolytic dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births globally. In the developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing countries most are home births. The most common childbirth method worldwide is vaginal delivery. It involves four stages of labour: the shortening and opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the placenta during the third, and the recovery of the mother and infant during the fourth stage, which is referred to as the postpartum. The first stage is characterized by abdominal cramping or back pain that typically lasts half a minute and occurs every 10 to 30 minutes. Contractions gradually becomes stronger and closer together. Since the pain of childbirth correlates with contractions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Phase Of Labour
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births globally. In the developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing countries most are home births. The most common childbirth method worldwide is vaginal delivery. It involves four stages of labour: the shortening and opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the placenta during the third, and the recovery of the mother and infant during the fourth stage, which is referred to as the postpartum. The first stage is characterized by abdominal cramping or back pain that typically lasts half a minute and occurs every 10 to 30 minutes. Contractions gradually becomes stronger and closer together. Since the pain of childbirth correlates with contractions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolonged Labour
Prolonged labor is the inability of a woman to proceed with childbirth upon going into labor. Prolonged labor typically lasts over 20 hours for first time mothers, and over 14 hours for women that have already had children. Failure to progress can take place during two different phases; the latent phase and active phase of labor. The latent phase of labor can be emotionally tiring and cause fatigue, but it typically does not result in further problems. The active phase of labor, on the other hand, if prolonged, can result in long term complications. It is important that the vital signs of the woman and fetus are being monitored so preventive measures can be taken if prolonged labor begins. Women experiencing prolonged labor should be under supervision of a surgically equipped doctor. Prolonged labor is determined based on the information that is being collected regarding the strength and time between contractions. Medical teams track this data using intrauterine pressure catheter pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniotic Membrane
The amnion is a membrane that closely covers the human and various other embryos when first formed. It fills with amniotic fluid, which causes the amnion to expand and become the amniotic sac that provides a protective environment for the developing embryo. The amnion, along with the chorion, the yolk sac and the allantois protect the embryo. In birds, reptiles and monotremes, the protective sac is enclosed in a shell. In marsupials and placental mammals, it is enclosed in a uterus. The term is from Ancient Greek ἀμνίον 'little lamb', diminutive of ἀμνός 'lamb'. it is cognate with the English verb 'yean', bring forth young (usually lambs). The amnion is a feature of the vertebrate clade ''Amniota'', which includes reptiles, birds, and mammals. Amphibians and fish are not amniotes and thus lack the amnion. The amnion stems from the extra-embryonic somatic mesoderm on the outer side and the extra-embryonic ectoderm or trophoblast on the inner side. In humans In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maternal Deaths
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pregnancy, underlying conditions worsened by the pregnancy or management of these conditions. This can occur either while they are pregnant or within six weeks of resolution of the pregnancy. The CDC definition of pregnancy-related deaths extends the period of consideration to include one year from the resolution of the pregnancy. Pregnancy associated death, as defined by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), are all deaths occurring within one year of a pregnancy resolution. Identification of pregnancy associated deaths is important for deciding whether or not the pregnancy was a direct or indirect contributing cause of the death. There are two main measures used when talking about the rates of maternal mortality in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antiseptics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cesarean Section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or mother at risk. Reasons for the operation include obstructed labor, twin pregnancy, high blood pressure in the mother, breech birth, and problems with the placenta or umbilical cord. A caesarean delivery may be performed based upon the shape of the mother's pelvis or history of a previous C-section. A trial of vaginal birth after C-section may be possible. The World Health Organization recommends that caesarean section be performed only when medically necessary. Most C-sections are performed without a medical reason, upon request by someone, usually the mother. A C-section typically takes 45 minutes to an hour. It may be done with a spinal block, where the woman is awake, or under general anesthesia. A urinary catheter is used to drain t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stillbirth
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, where the baby dies a short time after being born alive. Often the cause is unknown. Causes may include pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia and birth complications, problems with the placenta or umbilical cord, birth defects, infections such as malaria and syphilis, and poor health in the mother. Risk factors include a mother's age over 35, smoking, drug use, use of assisted reproductive technology, and first pregnancy. Stillbirth may be suspected when no fetal movement is felt. Confirmation is by ultrasound. Worldwide prevention of most stillbirths is possible with improved health systems. Around half of stillbirths occur durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partograph
A partogram or partograph is a composite graphical record of key data (maternal and fetal) during labour entered against time on a single sheet of paper. Relevant measurements might include statistics such as cervical dilation, fetal heart rate, duration of labour and vital signs. It is intended to provide an accurate record of the progress in labour, so that any delay or deviation from normal may be detected quickly and treated accordingly. However, a Cochrane review came to the conclusion that there is insufficient evidence to recommend partographs in standard labour management and care. Components * Patient identification * Time: It is recorded at an interval of one hour. Zero time for spontaneous labour is time of admission in the labour ward and for induced labour is time of induction. * Fetal heart rate: It is recorded at an interval of thirty minutes. * State of membranes and colour of liquor: "I" designates intact membranes, "C" designates clear and "M" designates meconium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |