|
Dysplasia
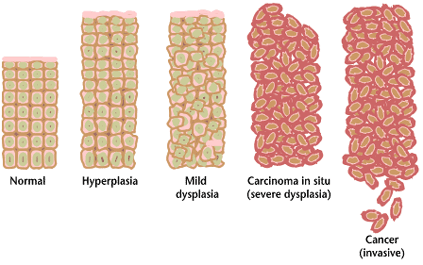
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic scale include epithelial dysplasia and fibrous dysplasia of bone. Dysplasias on a mainly macroscopic scale include hip dysplasia (human), hip dysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and multicystic dysplastic kidney. In one of the modern histopathology, histopathological senses of the term, dysplasia is sometimes differentiated from other categories of tissue change including hyperplasia, metaplasia, and neoplasia, and dysplasias are thus generally not cancerous. An exception is that the myelodysplasias include a range of benign tumor, benign, precancerous condition, precancerous, and cancerous forms. Various other dysplasias tend to be precancerous. The word's meanings thus cover a spectrum of histopathological variations. Microscopic sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hip Dysplasia (human)
Hip dysplasia is an abnormality of the hip joint where the socket portion does not fully cover the ball portion, resulting in an increased risk for joint dislocation. Hip dysplasia may occur at birth or develop in early life. Regardless, it does not typically produce symptoms in babies less than a year old. Occasionally one leg may be shorter than the other. The left hip is more often affected than the right. Complications without treatment can include arthritis, limping, and low back pain. Females are affected more often than males. Hip dysplasia was described at least as early as the 300s BC by Hippocrates. Risk factors for hip dysplasia include female sex, family history, certain swaddling practices, and breech presentation whether an infant is delivered vaginally or by cesarean section. If one identical twin is affected, there is a 40% risk the other will also be affected. Screening all babies for the condition by physical examination is recommended. Ultrasonography may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrous Dysplasia Of Bone
Fibrous dysplasia is a disorder where normal bone and marrow is replaced with fibrous tissue, resulting in formation of bone that is weak and prone to expansion. As a result, most complications result from fracture, deformity, functional impairment, and pain. Disease occurs along a broad clinical spectrum ranging from asymptomatic, incidental lesions, to severe disabling disease. Disease can affect one bone ( monostotic), multiple ( polyostotic), or all bones (panostotic) and may occur in isolation or in combination with café au lait skin macules and hyperfunctioning endocrinopathies, termed McCune–Albright syndrome. More rarely, fibrous dysplasia may be associated with intramuscular myxomas, termed Mazabraud's syndrome. Fibrous dysplasia is very rare, and there is no known cure. Fibrous dysplasia is not a form of cancer. Presentation Fibrous dysplasia is a mosaic disease that can involve any part or combination of the craniofacial, axillary, and/or appendicular skeleton. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
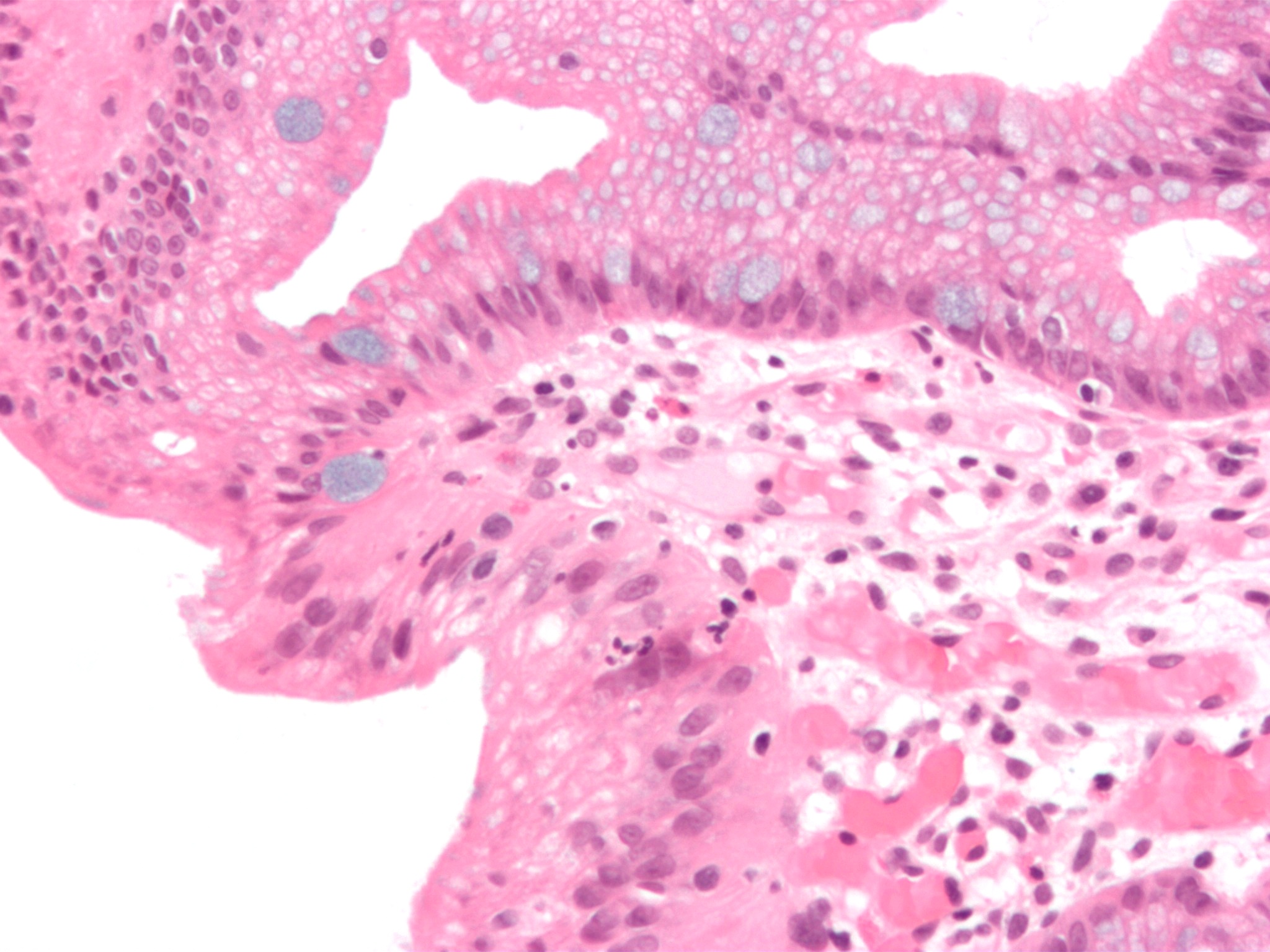
Epithelial Dysplasia
Epithelial dysplasia, a term becoming increasingly referred to as intraepithelial neoplasia, is the sum of various disturbances of epithelial proliferation and differentiation as seen microscopically. Individual cellular features of dysplasia are called epithelial atypia. Examples of epithelial dysplasia include cervical intraepithelial neoplasia – a disorder commonly detected by an abnormal pap smear) consisting of an increased population of immature (basal-like) cells which are restricted to the mucosal surface, and have not invaded through the basement membrane to the deeper soft tissues. Analogous conditions include vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia and vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. Metanephric dysplastic hematoma of the sacral region is a dysplastic overgrowth observed in infants. Screening Some tests which detect cancer could be called "screening for epithelial dysplasia". The principle behind these tests is that physicians expect dysplasia to occur at the same rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysplastic Cells
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic scale include epithelial dysplasia and fibrous dysplasia of bone. Dysplasias on a mainly macroscopic scale include hip dysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and multicystic dysplastic kidney. In one of the modern histopathological senses of the term, dysplasia is sometimes differentiated from other categories of tissue change including hyperplasia, metaplasia, and neoplasia, and dysplasias are thus generally not cancerous. An exception is that the myelodysplasias include a range of benign, precancerous, and cancerous forms. Various other dysplasias tend to be precancerous. The word's meanings thus cover a spectrum of histopathological variations. Microscopic scale Epithelial dysplasia Epithelial dysplasia consists of an expansion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelodysplastic Syndrome
A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, bleeding disorders, anemia, or frequent infections. Some types may develop into acute myeloid leukemia. Risk factors include previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, exposure to certain chemicals such as tobacco smoke, pesticides, and benzene, and exposure to heavy metals such as mercury or lead. Problems with blood cell formation result in some combination of low red blood cell, platelet, and white blood cell counts. Some types have an increase in immature blood cells, called blasts, in the bone marrow or blood. The types of MDS are based on specific changes in the blood cells and bone marrow. Treatments may include supportive care, drug therapy, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the outer layer of germ cells. The word ectoderm comes from the Greek ''ektos'' meaning "outside", and ''derma'' meaning "skin".Gilbert, Scott F. Developmental Biology. 9th ed. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates, 2010: 333-370. Print. Generally speaking, the ectoderm differentiates to form epithelial and neural tissues (spinal cord, peripheral nerves and brain). This includes the skin, linings of the mouth, anus, nostrils, sweat glands, hair and nails, and tooth enamel. Other types of epithelium are derived from the endoderm. In vertebrate embryos, the ectoderm can be divided into two parts: the dorsal surface ectoderm also known as the external ectoderm, and the neural plate, which invaginates to form the neural tube and neural crest. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precancerous Condition
A precancerous condition is a condition, tumor or lesion involving abnormal cells which are associated with an increased risk of developing into cancer. Clinically, precancerous conditions encompass a variety of abnormal tissues with an increased risk of developing into cancer. Some of the most common precancerous conditions include certain colon polyps, which can progress into colon cancer, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, which can progress into multiple myeloma or myelodysplastic syndrome. and cervical dysplasia, which can progress into cervical cancer. Bronchial premalignant lesions can progress to squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Pathologically, precancerous tissue can range from benign neoplasias, which are tumors which don't invade neighboring normal tissues or spread to distant organs, to dysplasia, a collection of highly abnormal cells which, in some cases, has an increased risk of progressing to anaplasia and invasive cancer which is life-threat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney
Multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK) is a condition that results from the malformation of the kidney during fetal development. The kidney consists of irregular cysts of varying sizes. Multicystic dysplastic kidney is a common type of renal cystic disease, and it is a cause of an abdominal mass in infants. Signs and symptoms When a diagnosis of multicystic kidney is made in utero by ultrasound, the disease is found to be bilateral in many cases. Those with bilateral disease often have other severe deformities or polysystemic malformation syndromes. In bilateral cases, the newborn has the classic characteristic of Potter's syndrome. The bilateral condition is incompatible with survival, as the contralateral system frequently is abnormal as well. Contralateral ureteropelvic junction obstruction is found in 3% to 12% of infants with multicystic kidney and contralateral vesicoureteral reflux is seen even more often, in 18% to 43% of infants. Because the high incidence of reflux, voi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hip Joint
In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or "coxa"Latin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest, and overlying the greater trochanter of the femur, or "thigh bone". In adults, three of the bones of the pelvis have fused into the hip bone or acetabulum which forms part of the hip region. The hip joint, scientifically referred to as the acetabulofemoral joint (''art. coxae''), is the joint between the head of the femur and acetabulum of the pelvis and its primary function is to support the weight of the body in both static (e.g., standing) and dynamic (e.g., walking or running) postures. The hip joints have very important roles in retaining balance, and for maintaining the pelvic inclination angle. Pain of the hip may be the result of numerous cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaplasia
Metaplasia ( gr, "change in form") is the transformation of one differentiated cell type to another differentiated cell type. The change from one type of cell to another may be part of a normal maturation process, or caused by some sort of abnormal stimulus. In simplistic terms, it is as if the original cells are not robust enough to withstand their environment, so they transform into another cell type better suited to their environment. If the stimulus causing metaplasia is removed or ceases, tissues return to their normal pattern of differentiation. Metaplasia is not synonymous with dysplasia, and is not considered to be an actual cancer. It is also contrasted with heteroplasia, which is the spontaneous abnormal growth of cytologic and histologic elements. Today, metaplastic changes are usually considered to be an early phase of carcinogenesis, specifically for those with a history of cancers or who are known to be susceptible to carcinogenic changes. Metaplastic change is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplasia
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |