|
Dyke Swarms Of Tandil And Azul
The dyke swarms of Tandil and Azul are groups of dykes of Proterozoic age located in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. The dyke swarms consists of two groups: 2000 million year old dykes of calc-alkaline type and 1600 million year old dykes of tholeiitic type. Description The tholeiitic dykes are made up of diabase and titanium-rich basalt, in contrast the calc-alkaline dykes are made up of andesite and rhyolite. The dyke swarms intrude the southern part of the Río de la Plata Craton, much the same way the Uruguayan dyke swarms intrude the northeastern part of the craton. The calc-alkaline dykes intruded in a period of transtensional tectonics during the Transamazonian orogeny The Transamazonian orogeny was a mountain building event in the Paleoproterozoic, affecting what is now the São Francisco Craton and Guyana Shield. During the orogeny from 2.14 to 1.94 billion years ago two small Archean proto-continents—includ ..., while the tholeiitic dykes intruded during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dike Swarm
A dike swarm (American spelling) or dyke swarm (British spelling) is a large geological structure consisting of a major group of parallel, linear, or radially oriented magmatic dikes intruded within continental crust or central volcanoes in rift zones. Examples exist in Iceland and near other large volcanoes, (stratovolcanoes, calderas, shield volcanoes and other fissure systems) around the world. They consist of several to hundreds of dikes emplaced more or less contemporaneously during a single intrusive event, are magmatic and stratigraphic, and may form a large igneous province. The occurrence of mafic dike swarms in Archean and Paleoproterozoic terrains is often cited as evidence for mantle plume activity associated with abnormally high mantle potential temperatures. Dike swarms may extend over in width and length. The largest dike swarm known on Earth is the Mackenzie dike swarm in the western half of the Canadian Shield in Canada, which is more than wide and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrusion (geology)
Intrusive rock is formed when magma penetrates existing rock, crystallizes, and solidifies underground to form '' intrusions'', such as batholiths, dikes, sills, laccoliths, and volcanic necks.Intrusive RocksIntrusive rocks accessdate: March 27, 2017.Igneous intrusive rocks, accessdate: March 27, 2017.Britannica.comintrusive rock , geology , Britannica.com accessdate: March 27, 2017. Intrusion is one of the two ways igneous rock can form. The other is extrusion, such as a volcanic eruption or similar event. An intrusion is any body of intrusive igneous rock, formed from magma that cools and solidifies within the crust of the planet. In contrast, an ''extrusion'' consists of extrusive rock, formed above the surface of the crust. Some geologists use the term plutonic rock synonymously with intrusive rock, but other geologists subdivide intrusive rock, by crystal size, into coarse-grained plutonic rock (typically formed deeper in the Earth's crust in batholiths or stocks) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoproterozoic Magmatism
The Paleoproterozoic Era (;, also spelled Palaeoproterozoic), spanning the time period from (2.5–1.6 Ga), is the first of the three sub-divisions (eras) of the Proterozoic Eon. The Paleoproterozoic is also the longest era of the Earth's geological history. It was during this era that the continents first stabilized. Paleontological evidence suggests that the Earth's rotational rate ~1.8 billion years ago equated to 20-hour days, implying a total of ~450 days per year. Atmosphere Before the enormous increase in atmospheric oxygen, almost all existing lifeforms were anaerobic organisms whose metabolism was based on a form of cellular respiration that did not require oxygen. Free oxygen in large amounts is toxic to most anaerobic organisms. Consequently, most died when the atmospheric free oxygen levels soared in an extinction event called the Great Oxidation Event, which brought atmospheric oxygen levels to up to 10% of their current level. The only creatures that survi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Buenos Aires Province
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dike Swarms
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to: General uses * Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian" * Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment * Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice * Dikes, diagonal pliers, also called side-cutting pliers, a hand tool used by electricians and others * Dyke (automobile company), established 1899 Structures * Dyke (embankment) or dike, a natural or artificial slope or wall to regulate water levels, often called a levee in American English * Ditch, a water-filled drainage trench * A regional term for a dry stone wall People * Dyke (surname) * Dyke baronets, a title in the Baronetage of England * Dykes (surname), a British surname found particularly in northern England Places Settlements * Dike, Iowa, United States * Dykes, Missouri, United States * Dyke, Moray, Scotland * Dike, Texas, United States * Dyke, Virginia, United States * Dyke, Lincolnshire, England * Little Dyke, Nova Scotia, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensional Tectonics
Extensional tectonics is concerned with the structures formed by, and the tectonic processes associated with, the stretching of a planetary body's crust or lithosphere. Deformation styles The types of structure and the geometries formed depend on the amount of stretching involved. Stretching is generally measured using the parameter ''β'', known as the ''beta factor'', where : \beta = \frac \,, ''t''0 is the initial crustal thickness and ''t''1 is the final crustal thickness. It is also the equivalent of the strain parameter ''stretch''. Low beta factor In areas of relatively low crustal stretching, the dominant structures are high to moderate angle normal faults, with associated half grabens and tilted fault blocks. High beta factor In areas of high crustal stretching, individual extensional faults may become rotated to too low a dip to remain active and a new set of faults may be generated. Large displacements may juxtapose syntectonic sediments against metamorphic roc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transamazonian Orogeny
The Transamazonian orogeny was a mountain building event in the Paleoproterozoic, affecting what is now the São Francisco Craton and Guyana Shield. During the orogeny from 2.14 to 1.94 billion years ago two small Archean proto-continents—including the greenstone belt-dominated Gavião Block and the calc-alkaline charnockite and enderbite-dominated Jequié Block—collided. The Contendas-Jacobina Lineament represents a suture zone where the collision occurred and the Gavião Block partially subducted under the Jequié Block. At the same time, another small continental fragment, the Serrinha Block, may have collided as well and was extensively reworked and metamorphosed, with orthogneiss and migmatite reaching amphibolite-grade on the sequence of metamorphic facies. The Serrinha Block is the basement rock of the Rio Itapicuru granite-greenstone belt. Several magmatic arcs formed between the colliding proto-continent blocks, including the Salvador-Curaçá Belt, Contendas-Mirante Bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transtensional Tectonics
Transtension is the state in which a rock mass or area of the Earth's crust experiences both ''extensive'' and ''transtensive'' shear. As such, transtensional regions are characterised by both extensional structures (normal faults, grabens) and wrench structures (strike-slip faults). In general, many tectonic regimes that were previously defined as simple strike-slip shear zones are actually transtensional. It is unlikely that a deforming body will experience 'pure' extension or 'pure' strike-slip. Transtensional shear zones are characterized by the co-existence of different structures, related to both strike-slip shear and extension. End member structures include pure strike-slip faults and purely extensional ("normal") dip-slip faults. Faults which have components of both (termed 'oblique' slip faults) are abundant. Releasing bend ''Releasing bends'' are transtensional structures that form where the orientation of a strike-slip fault becomes oblique to the regional slip vector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
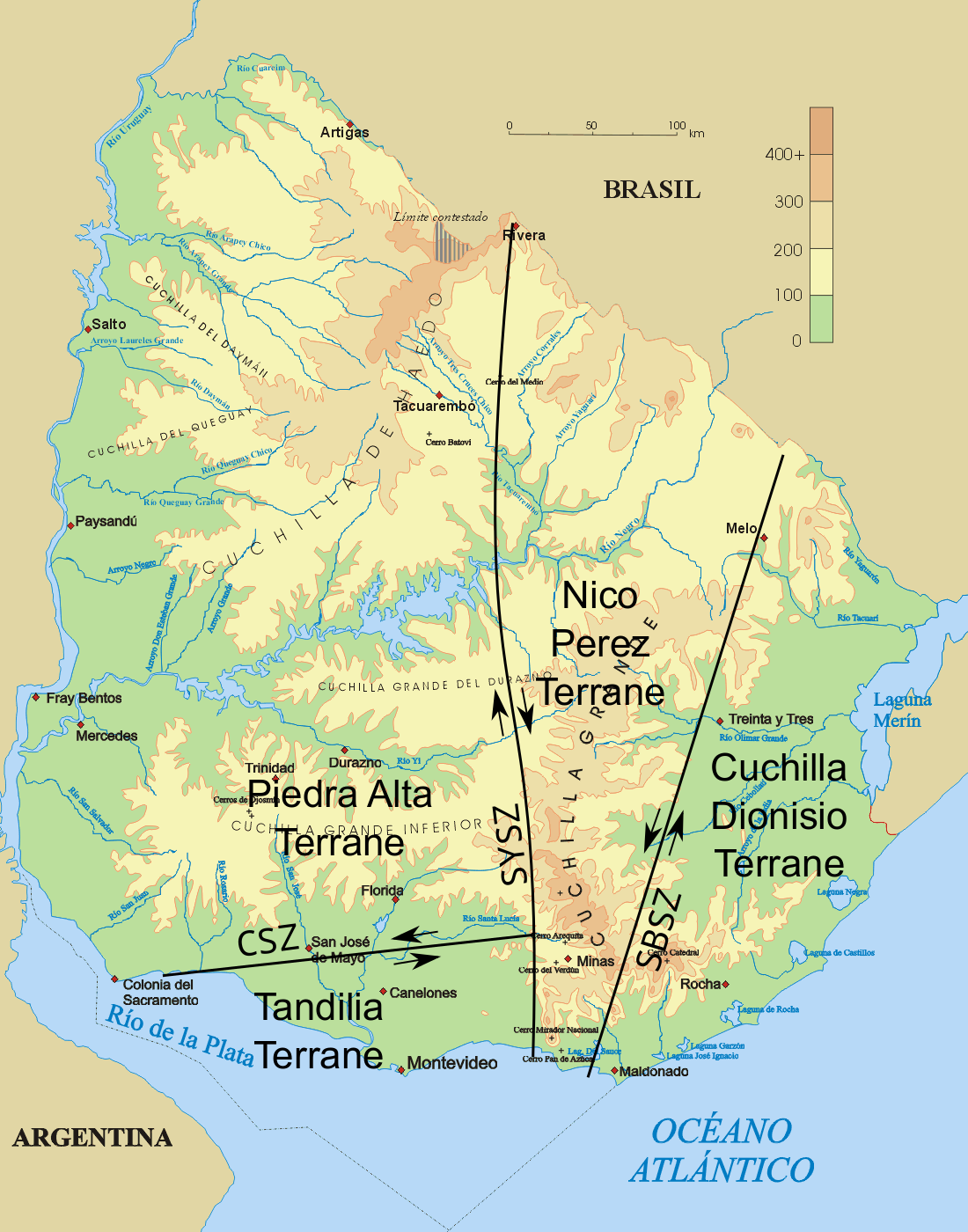
Uruguayan Dyke Swarms
The Uruguayan dyke swarms consist of three groups of Dike (geology), dykes of Precambrian age that intrude Río de la Plata Craton and Brasiliano orogeny, Brasiliano Cycle continental crust in Uruguay. The dykes – including the Florida dyke swarm, the Nico Perez dyke swarm, and the Treinta y Tres dyke swarm – are of mafic to intermediate composition and each group lies in a separate terrane, tectono-stratigraphic terrane. The rocks of the Florida dyke swarm have been quarried since the 1960s and are used in the construction industry as black dimension stone of very high quality, being marketed as "black granite". Florida dyke swarm The Florida dyke swarm (also known as Piedra Alta dyke swarm and Uruguayan dyke swarm) crops out in the Piedra Alta Terrane of Río de la Plata Craton west of Sarandí del Yí Shear Zone. The strike of the dykes has an arcuate pattern: it changes from west to east from NE-SW to E-W and then near the shear zone to NW-SE. The Florida dykes ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Río De La Plata Craton
The Rio de la Plata Craton (RPC) is a medium-sized continental block found in Uruguay, eastern Argentina and southern Brazil. During its complex and protracted history it interacted with a series other blocks and is therefore considered important for the understanding of the amalgamation of West Gondwana. Two orogenic cycles have been identified in the RPC: a 2000 Ma-old western domain representing the old craton and a 700–500 Ma-old eastern domain assigned to the Brasiliano Cycle. It is one of the five cratons (ancient nuclei) of the South American continent. The other four cratons are: Amazonia, São Francisco, Río Apa and Arequipa–Antofalla. Geology Three shear zones divides the Precambrian basement of Uruguay and southern Brazil into four terranes. Along the Uruguayan east coast (reaching into Brazil) is the Cuchilla Dionisio Terrane, an allochthonous African block juxtaposed to the RPC along the Sierra Ballena Shear Zone (SBSZ). West of Cuchilla Dio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revista De La Asociación Geológica Argentina
The ''Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina'' is an open access peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Asociación Geológica Argentina. The journal is released under a CC-BY-NC 2.5 license. - official website See also * ''Andean Geology
''Andean Geology'' (formerly ''Revista Geológica de Chile'') is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published three times per year by the National Geology and Mining Service, Chile's geology and mining agency. The journal covers the field of geol ... ''
* '' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided into three geologic eras (from oldest to youngest): the Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic, and Neoproterozoic. The Proterozoic covers the time from the appearance of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere to just before the proliferation of complex life (such as trilobites or corals) on the Earth. The name ''Proterozoic'' combines two forms of ultimately Greek origin: meaning 'former, earlier', and , 'of life'. The well-identified events of this eon were the transition to an oxygenated atmosphere during the Paleoproterozoic; the evolution of eukaryotes; several glaciations, which produced the hypothesized Snowball Earth during the Cryogenian Period in the late Neoproterozoic Era; and the Ediacaran Period (635 to 538.8 Ma) which is characterize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |