|
Duplitized Film
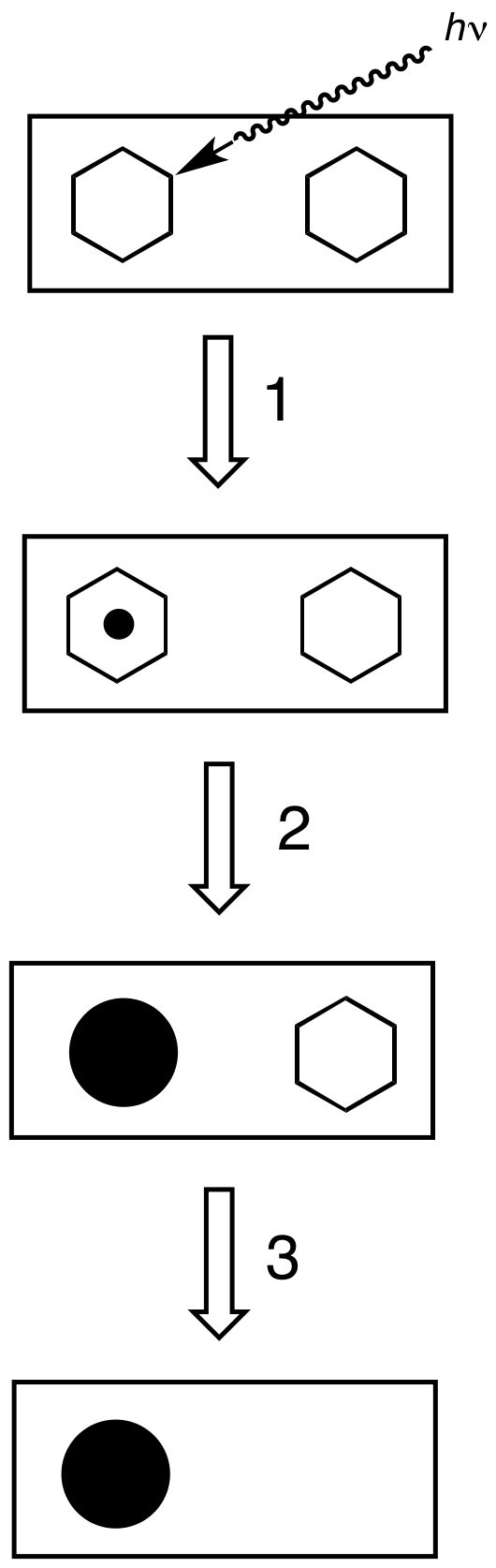
Duplitized film was a type of motion picture print film stock used for some two-color natural color processes. It was introduced by Eastman Kodak around 1913. The stock was of standard gauge and thickness, but it had a photographic emulsion coated on both sides of the film base instead of on one surface only. In color film processes such as Cinecolor and Prizma, two black-and-white negatives photographed through red and blue-green filters, or by an equivalent bipack method, were photographically printed onto opposite sides of the duplitized film. Because its emulsion was sensitive only to blue light, a temporary yellow dye incorporated into the film prevented each printing light from also exposing the emulsion on the other side. The exposed film was developed like ordinary black-and-white film, producing a series of black-and-white silver images on each side. These were then chemically converted into single-color images of a color roughly complementary to that being used for the im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Color
Natural color was a term used in the beginning of film and later on in the 1920s, and early 1930s as a color film process that actually filmed color images, rather than a color tinted or colorized movie. The first natural color processes were in the 1900s and 1910s and were two color additive color processes or red and green missing primary color blue, one additive process of time was Kinemacolor. By the 1920s, subtractive color was mostly in use with such processes as Technicolor, Prizma and Multicolor, but Multicolor was mostly never in use in the late 1920s, Technicolor was mostly in use. The only one who cared to mess with Multicolor was William Fox, probably because Multicolor was more cheaper of a process and at the time in 1929 William Fox was in debt. The difference between additive color and subtractive color were that an additive color film required a special projector that could project two components of film at the same time, a green record and a red record. But addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastman Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company (referred to simply as Kodak ) is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in analogue photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorporated in New Jersey. Kodak provides packaging, functional printing, graphic communications, and professional services for businesses around the world. Its main business segments are Print Systems, Enterprise Inkjet Systems, Micro 3D Printing and Packaging, Software and Solutions, and Consumer and Film. It is best known for photographic film products. Kodak was founded by George Eastman and Henry A. Strong on May 23, 1892. During most of the 20th century, Kodak held a dominant position in photographic film. The company's ubiquity was such that its " Kodak moment" tagline entered the common lexicon to describe a personal event that deserved to be recorded for posterity. Kodak began to struggle financially in the late 1990s, as a result of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Emulsion
Photographic emulsion is a light-sensitive colloid used in film-based photography. Most commonly, in silver-gelatin photography, it consists of silver halide crystals dispersed in gelatin. The emulsion is usually coated onto a substrate of glass, films (of cellulose nitrate, cellulose acetate or polyester), paper, or fabric. Photographic emulsion is not a true emulsion, but a suspension of solid particles (silver halide) in a fluid (gelatin in solution). However, the word ''emulsion'' is customarily used in a photographic context. Gelatin or gum arabic layers sensitized with dichromate used in the dichromated colloid processes carbon and gum bichromate are sometimes called ''emulsions''. Some processes do not have emulsions, such as platinum, cyanotype, salted paper, or kallitype. Components Photographic emulsion is a fine suspension of insoluble light-sensitive crystals in a colloid sol, usually consisting of gelatin. The light-sensitive component is one or a mixture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Base
A film base is a transparent substrate which acts as a support medium for the photosensitive emulsion that lies atop it. Despite the numerous layers and coatings associated with the emulsion layer, the base generally accounts for the vast majority of the thickness of any given film stock. Since the late 19th century, there have been three major types of film base in use: nitrate (until about 1951), acetate, and polyester. Nitrate In the literature of photography "nitrate" is used as a synonym for the chemical nitrocellulose. It is also referred to as "cellulose nitrate". Nitrocellulose is guncotton, the first replacement propellant for gun powder in firearms. Film stock with a nitrate base was the first transparent flexible plasticized base commercially available, thanks to celluloid developments by John Carbutt, Hannibal Goodwin, and Eastman Kodak in the 1880s. Eastman was the first to manufacture the film stock for public sale, in 1889. Unfortunately, nitrate also had the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinecolor
Cinecolor was an early subtractive color-model two-color motion picture process that was based upon the Prizma system of the 1910s and 1920s and the Multicolor system of the late 1920s and the 1930s. It was developed by William T. Crispinel and Alan M. Gundelfinger, and its various formats were in use from 1932 to 1955. Method As a bipack color process, the photographer loaded a standard camera with two film stocks: an orthochromatic strip dyed red and a panchromatic strip behind it. The ortho film stock recorded only blue and green, and its red filtration passed red light to the panchromatic film stock. In the laboratory, the negatives were processed on duplitized film, and each emulsion was toned red or cyan. Cinecolor could produce vibrant reds, oranges, blues, browns and flesh tones, but its renderings of other colors such as bright greens (rendered dark green) and purples (rendered a sort of dark magenta) were muted. History The Cinecolor process was invented in 1932 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prizma
The Prizma Color system was a color motion picture process, invented in 1913 by William Van Doren Kelley and Charles Raleigh. Initially, it was a two-color additive color system, similar to its predecessor, Kinemacolor. However, Kelley eventually transformed Prizma into a bi-pack color system that itself became the predecessor for future color processes such as Multicolor and Cinecolor. Experimental Prizma gave a demonstration of color motion pictures in 1917 that used an additive four-color process, using a disk of four filters acting on a single strip of panchromatic film in the camera. The colors were red, yellow, green, and blue, with overlapping wavelengths to prevent pulsating effects on the screen with vivid colors. The film was photographed at 26 to 32 frames per second, and projected at 32 frame/s. The disk used in projection consisted mainly of two colors, red-orange and blue-green, adapted to the four-color process by the superimposition of two small magenta filters o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-and-white
Black-and-white (B&W or B/W) images combine black and white in a continuous spectrum, producing a range of shades of grey. Media The history of various visual media began with black and white, and as technology improved, altered to color. However, there are exceptions to this rule, including black-and-white fine art photography, as well as many film motion pictures and art film(s). Photography Contemporary use Since the late 1960s, few mainstream films have been shot in black-and-white. The reasons are frequently commercial, as it is difficult to sell a film for television broadcasting if the film is not in color. 1961 was the last year in which the majority of Hollywood films were released in black and white. Computing In computing terminology, ''black-and-white'' is sometimes used to refer to a binary image consisting solely of pure black pixels and pure white ones; what would normally be called a black-and-white image, that is, an image containing shades of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filter (optics)
An optical filter is a device that selectively transmits light of different wavelengths, usually implemented as a glass plane or plastic device in the optical path, which are either dyed in the bulk or have interference coatings. The optical properties of filters are completely described by their frequency response, which specifies how the magnitude and phase of each frequency component of an incoming signal is modified by the filter. Filters mostly belong to one of two categories. The simplest, physically, is the absorptive filter; then there are interference or dichroic filters. Many optical filters are used for optical imaging and are manufactured to be transparent; some used for light sources can be translucent. Optical filters selectively transmit light in a particular range of wavelengths, that is, colours, while absorbing the remainder. They can usually pass long wavelengths only (longpass), short wavelengths only (shortpass), or a band of wavelengths, blocking both l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipack Color
In bipack color photography for motion pictures, two strips of black-and-white 35 mm film, running through the camera emulsion to emulsion, are used to record two regions of the color spectrum, for the purpose of ultimately printing the images, in complementary colors, superimposed on one strip of film. The result is a multicolored projection print that reproduces a useful but limited range of color by the subtractive color method. Bipack processes became commercially practical in the early 1910s when Kodak introduced duplitized film print stock, which facilitated making two-color prints. Bipack photography was, from about 1935 to 1950, the most economical means of 35 mm natural color cinematography available, used when color was wanted but the budget could not bear the much higher cost of three-strip Technicolor or the less well-known alternative three-color processes sometimes available outside the US. After 1950, when economical "monopack" color negative and print stocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Processing
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image into a visible image, makes this permanent and renders it insensitive to light.Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. All processes based upon the gelatin silver process are similar, regardless of the film or paper's manufacturer. Exceptional variations include instant films such as those made by Polaroid and thermally developed films. Kodachrome required Kodak's proprietary K-14 process. Kodachrome film production ceased in 2009, and K-14 processing is no longer available as of December 30, 2010. Ilfochrome materials use the dye destruction process. Deliberately using the wrong process for a film is known as cross processing. Common processes All photographic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complementary Color
Complementary colors are pairs of colors which, when combined or mixed, cancel each other out (lose hue) by producing a grayscale color like white or black. When placed next to each other, they create the strongest contrast for those two colors. Complementary colors may also be called "opposite colors". Which pairs of colors are considered complementary depends on the color theory one uses: *Modern color theory uses either the RGB additive color model or the CMY subtractive color model, and in these, the complementary pairs are red– cyan, green–magenta, and blue–yellow. *In the traditional RYB color model, the complementary color pairs are red–green, yellow–purple, and blue–orange. *Opponent process theory suggests that the most contrasting color pairs are red–green and blue–yellow. *The black-white color pair is common to all the above theories. In different color models Traditional color model The traditional color wheel model dates to the 18th century an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeutic") and industrial radiography. Similar techniques are used in airport security (where "body scanners" generally use backscatter X-ray). To create an image in conventional radiography, a beam of X-rays is produced by an X-ray generator and is projected toward the object. A certain amount of the X-rays or other radiation is absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition. The X-rays that pass through the object are captured behind the object by a detector (either photographic film or a digital detector). The generation of flat two dimensional images by this technique is called projectional radiography. In computed tomography (CT scanning) an X-ray source and its associated detectors rotate around the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_Town_window.png)