|
Duomi Khan
Duomi Khan (多彌可汗) (died 646), personal name Bazhuo (拔灼), full regal name Jialijulixueshaduomi Khan (頡利俱利薛沙多彌可汗), was a khan of the Xueyantuo. After the death of his father, the Zhenzhu Khan Yi'nan, he disputed with and killed his older brother, Yemang (曵莽), and became khan in 645. Then, reversing his father's peaceful policy with the Tang Dynasty, Duomi Khan immediately started incursions into their territory. This drew a heavy response from Emperor Taizong of Tang, who sent the generals Qiao Shiwang (喬師望), Zhishi Sili (執失思力), and Li Daozong to defend. They proved too strong for Duomi Khan's attacks, so he fled. But he did not live long. He was betrayed by his own vassal, Huige, who rebelled and killed him. Under Yi'nan It is not known when Bazhuo was born, but it was known that he was not his father Yi'nan's oldest son—although throughout historical records, Yi'nan's oldest son was various referred to as Jialibi (頡利苾), Dad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
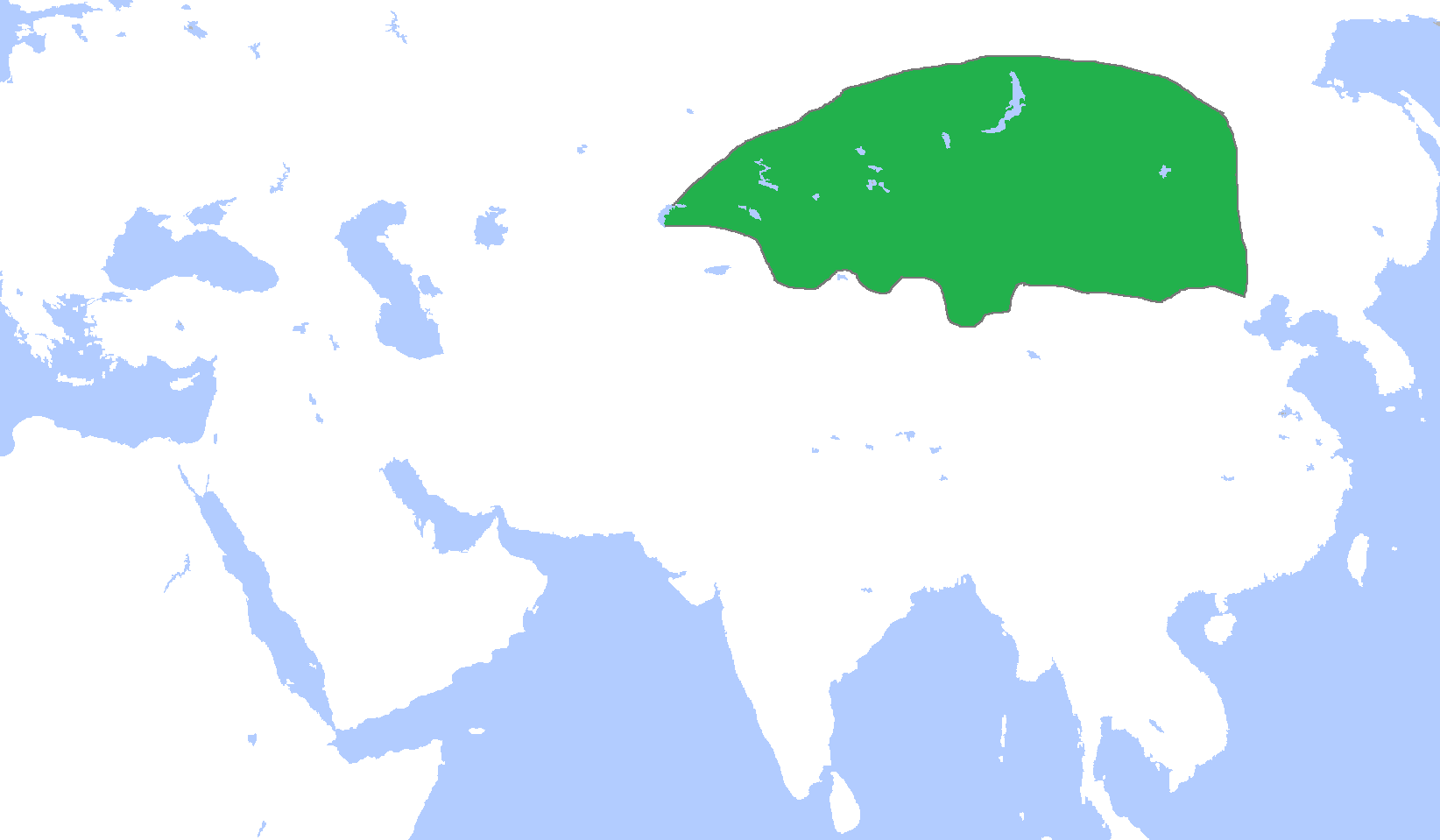
Xueyantuo
The Xueyantuo were an ancient Tiele people, Tiele tribe and khaganate in Northeast Asia who were at one point vassals of the Göktürks, later aligning with the Tang dynasty against the Eastern Turkic Khaganate, Eastern Göktürks. Names Xue ''Xue'' 薛 appeared earlier as ''Xinli'' 薪犁 in Sima Qian's Records of the Grand Historian, vol. 110 but were not referred to again until the 7th century. Peter B. Golden, Golden (2011) proposed that 薛 Xue's Old Turkic form ''Sir'' derived from Sanskrit ''Shri, Śrī'' "fortunate, auspicious" Yantuo The etymology of ''Yantuo'' 延陀 is much debated. It was first identified with ''Tarduš'', one of two divisions, besides ''Töliš'', of the short-lived Xueyantuo Qaghanate, by Western Orientalists (like Vilhelm Thomsen) who considered ''Töliš'' and ''Tarduš'' to be tribal names. The ethnonym is thus reconstructable as Syr-Tardush. However, Chinese scholars viewed ''Töliš'' and ''Tarduš'' as names of political organizations or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
646 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 646 ( DCXLVI) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 646 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Arab-Byzantine War: Alexandria is recaptured by the Muslim Arabs, after a Byzantine attempt (see 645) to retake Egypt fails, ending nearly 1,000 years of rule by Greco-Roman states in the city. * Gregory the Patrician, Byzantine exarch of Africa, begins a rebellion against Constans II, and proclaims himself emperor; the revolt finds broad support among the populace. Arabian Empire * Caliph Uthman ibn Affan founds the city of Jeddah (Saudi Arabia) on the coast of the Red Sea. He establishes a port for Muslim pilgrims making the required ''Hajj'' to Mecca. Africa * Battle of Nikiou: The Rashidun army (15,000 men) under Amr ibn al-'A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty People
Tang or TANG most often refers to: * Tang dynasty * Tang (drink mix) Tang or TANG may also refer to: Chinese states and dynasties * Jin (Chinese state) (11th century – 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (唐) before 8th century BC * Tang dynasty (唐; 618–907), a major Chinese dynasty * Later Tang (唐; 923–937), a state during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period * Southern Tang (唐; 937–975), a state during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period Food * Tang (drink mix), a brand name of instant fruit flavored drinks, produced by Mondelēz International * Guk, soup or stew in Korean cuisine, sometimes known as "tang" Places Europe * Tang, County Westmeath, a village in Ireland * Tang, North Yorkshire, a settlement in England Asia * Tang, Ardabil, a village in Ardabil Province, Iran * Tang, Badakhshan, a village in Afghanistan * Tang, a village in Bumthang District, Bhutan * Tang (唐镇), a town in Pudong, Shanghai, China * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xueyantuo Rulers
The Xueyantuo were an ancient Tiele tribe and khaganate in Northeast Asia who were at one point vassals of the Göktürks, later aligning with the Tang dynasty against the Eastern Göktürks. Names Xue ''Xue'' 薛 appeared earlier as ''Xinli'' 薪犁 in Sima Qian's Records of the Grand Historian, vol. 110 but were not referred to again until the 7th century. Golden (2011) proposed that 薛 Xue's Old Turkic form ''Sir'' derived from Sanskrit '' Śrī'' "fortunate, auspicious" Yantuo The etymology of ''Yantuo'' 延陀 is much debated. It was first identified with ''Tarduš'', one of two divisions, besides ''Töliš'', of the short-lived Xueyantuo Qaghanate, by Western Orientalists (like Vilhelm Thomsen) who considered ''Töliš'' and ''Tarduš'' to be tribal names. The ethnonym is thus reconstructable as Syr-Tardush. However, Chinese scholars viewed ''Töliš'' and ''Tarduš'' as names of political organizations or districts: for example, Cen Zhongmian viewed the Töliš-Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yitewushi Khan
Yitewushi Khan (伊特勿失可汗), personal name Duomozhi (咄摩支), was the last khan of Xueyantuo. Little is known about Duomozhi's background, other than that he was a nephew of Xueyantuo's greatest khan, the Zhenzhu Khan Yi'nan. In 646, during the reign of Yi'nan's son and successor, the Duomi Khan Bazhuo, Xueyantuo fell into a state of confusion due to a combination of attacks by the Tang dynasty, misrule by Bazhuo, and rebellions by the Huige. Bazhuo was killed in a Huige attack, and Xueyantuo forces collapsed. Some 70,000 people fled west and supported Duomozhi as the Yitewushi Khan. Under Duomozhi, they returned east to their old territory, but, with Huige having taken much of the old Xueyantuo territory, Duomozhi soon renounced the title of khan, sending an emissary to Tang to request permission to move to the area north of the Khangai Mountains. Emperor Taizong of Tang initially sent the official Cui Dunli to try to comfort Duomozhi, but at the same time was concerned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Huiyao
The ''Tang Huiyao'' () is an institutional history of Tang dynasty compiled by Wang Pu and presented it to Emperor Taizu of Song in 961. The book contains 100 volumes and 514 sections, it has an abundant content for the period before 846, and scarce material unobtainable from the ''Tongdian'', '' Old Book of Tang'', and '' New Book of Tang''. It combines the earlier ''Huiyao'' compiled by Su Mian, which covers the history of Tang to 779, and the ''Xu Huiyao'' by Yang Shaofu and others, which extended the coverage to 846. The compilation was finished by the early Song dynasty, with the addition of small amount of material after the reign of Emperor Xuānzong of Tang included by Wang Pu. References * Zhang, Zexian"Tang Huiyao" ("Institutional History of Tang") ''Encyclopedia of China The ''Encyclopedia of China'' () is the first large-entry modern encyclopedia in the Chinese language. The compilation began in 1978. Published by the Encyclopedia of China Publishing House, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Taizong's Campaign Against Xueyantuo
The Emperor Taizong of Tang (r. 626—649), the second emperor of the Tang dynasty, early in his reign, had allied with Xueyantuo, a vassal of the powerful Eastern Tujue ( Göktürk) Khanate, against Eastern Tujue, who Tang defeated in 630. Upon Eastern Tujue's defeat, Xueyantuo's Zhenzhu Khan Yi'nan took over Eastern Tujue's former territory, and while he was formally submissive to Tang, he was expanding his own strength. When Emperor Taizong tried to restore Eastern Tujue in 639 under the Qilibi Khan Ashina Simo (also known as Li Simo) to counteract the rise of Xueyantuo power, Xueyantuo engaged in multiple battles with the newly restored Eastern Tujue, in order to prevent this return. The major Tang general Li Shiji temporarily came to protect Eastern Tujue against Xueyantuo and defeated the Xueyantuo forces in 641. But in 644, with Emperor Taizong occupied with a campaign against Goguryeo, Xueyantuo forces launched a new campaign, defeated Eastern Tujue, forcing Ashina Simo to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khan (title)
Khan ''khan/qan''; tr, han; Azerbaijani: ''xan''; Ottoman: ''han''; Old Turkic: ''kan''; Chinese: 汗 ''hán''; Goguryeo: 皆 ''key''; Buyeo: 加 ''ka''; Silla: 干 ''kan''; Gaya: 旱 ''kan''; Baekje: 瑕 ''ke''; Manchu: ; Persian: خان; Punjabi: ਖ਼ਾਨ; Hindustani: ख़ान or ख़ां (Devanagari), or (Nastaleeq); Balochi: خان; Bulgarian: хан, ''khan''; Chuvash: хун, ''hun''; Arabic: خان; bn, খান or ) () is a historic Turko-Mongol title originating among nomadic tribes in the Central and Eastern Eurasian Steppe to refer to a chief or ruler. It first appears among the Rouran and then the Göktürks as a variant of khagan (sovereign, emperor) and implied a subordinate ruler. In the Seljuk Empire, it was the highest noble title, ranking above malik (king) and emir (prince). In the Mongol Empire it signified the ruler of a horde (''ulus''), while the ruler of all the Mongols was the khagan or great khan. The title subsequently de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynasties and spanning almost 1400 years. The main text is arranged into 294 scrolls (''juan'' , equivalent to a chapter) totaling about 3 million Chinese characters. In 1065 AD, Emperor Yingzong of Song commissioned his official Sima Guang (1019–1086 AD) to lead a project to compile a universal history of China, and granted him funding and the authority to appoint his own staff. His team took 19 years to complete the work and in 1084 AD it was presented to Emperor Yingzong's successor Emperor Shenzong of Song. It was well-received and has proved to be immensely influential among both scholars and the general public. Endymion Wilkinson regards it as reference quality: "It had an enormous influence on later Chinese historical wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huige
The Uyghur Khaganate (also Uyghur Empire or Uighur Khaganate, self defined as Toquz-Oghuz country; otk, 𐱃𐰆𐰴𐰕:𐰆𐰍𐰕:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, Toquz Oγuz budun, Tang-era names, with modern Hanyu Pinyin: or ) was a Turkic empire that existed for about a century between the mid 8th and 9th centuries. They were a tribal confederation under the Orkhon Uyghur () nobility, referred to by the Chinese as the ''Jiu Xing'' ("Nine Clans"), a calque of the name ''Toquz Oghuz'' or ''Toquz Tughluq''. History Rise In 657, the Western Turkic Khaganate was defeated by the Tang dynasty, after which the Uyghurs defected to the Tang. Prior to this the Uyghurs had already shown an inclination towards alliances with the Tang when they fought with them against the Tibetan Empire and Turks in 627. In 742, the Uyghurs, Karluks, and Basmyls rebelled against the Second Turkic Khaganate. In 744, the Basmyls captured the Turk capital of Ötüken and killed the reigning Özmiş Khagan. Later t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |