|
Duodenal Adenocarcinoma
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the duodenum may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine. In humans, the duodenum is a hollow jointed tube about 25–38 cm (10–15 inches) long connecting the stomach to the middle part of the small intestine. It begins with the duodenal bulb and ends at the suspensory muscle of duodenum. Duodenum can be divided into four parts: the first (superior), the second (descending), the third (horizontal) and the fourth (ascending) parts. Structure The duodenum is a C-shaped structure lying adjacent to the stomach. It is divided anatomically into four sections. The first part of the duodenum lies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may be used instead of ileum. Its main function is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the jejunum. The ileum follows the duodenum and jejunum and is separated from the cecum by the ileocecal valve (ICV). In humans, the ileum is about 2–4 m long, and the pH is usually between 7 and 8 (neutral or slightly basic). ''Ileum ''is derived from the Greek word ''eilein'', meaning "to twist up tightly". Structure The ileum is the third and final part of the small intestine. It follows the jejunum and ends at the ileocecal junction, where the terminal ileum communicates with the cecum of the large intestine through the ileocecal valve. The ileum, along with the jejunum, is suspended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Omentum
The lesser omentum (small omentum or gastrohepatic omentum) is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach, and to the first part of the duodenum. The lesser omentum is usually divided into these two connecting parts: the hepatogastric ligament, and the hepatoduodenal ligament. Structure The lesser omentum is extremely thin, and is continuous with the two layers of peritoneum which cover respectively the antero-superior and postero-inferior surfaces of the stomach and first part of the duodenum. When these two layers reach the lesser curvature of the stomach and the upper border of the duodenum, they join and ascend as a double fold to the porta hepatis. To the left of the porta, the fold is attached to the bottom of the fossa for the ductus venosus, along which it is carried to the diaphragm, where the two layers separate to embrace the end of the esophagus. At the right border of the lesser omentum, the two layers are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatoduodenal Ligament
The hepatoduodenal ligament is the portion of the lesser omentum extending between the porta hepatis of the liver and the superior part of the duodenum. Running inside it are the following structures collectively known as the portal triad: * hepatic artery proper * portal vein * common bile duct Manual compression of the hepatoduodenal ligament during surgery is known as the Pringle manoeuvre. The cystoduodenal ligament is also found in the lesser omentum and is distinct from both the hepatoduodenal and hepatogastric ligaments. The cystoduodenal ligament is an abnormal peritoneal fold that attaches the duodenum to the gallbladder, representing a rare variation in the anatomy of the lesser sac and its foramen. Another variation sometimes present at the duodenal termination of the hepatoduodenal ligament is the duodenorenal ligament which passes to the front of the right kidney The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
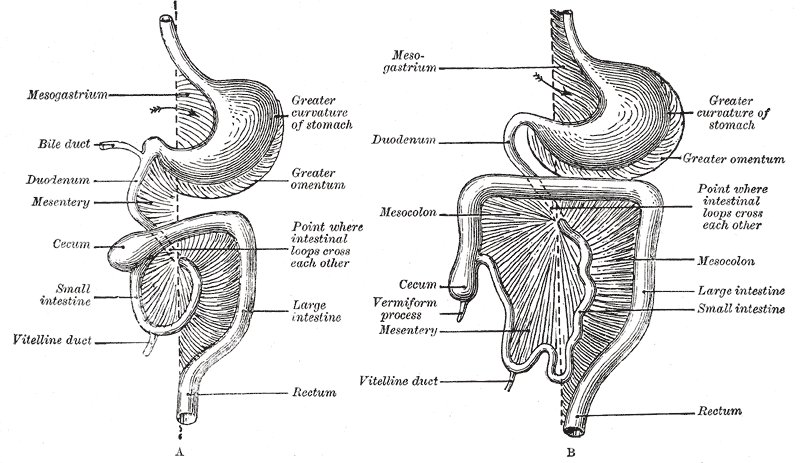
Mesentery
The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines, among other functions. The mesocolon was thought to be a fragmented structure, with all named parts—the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid mesocolons, the mesoappendix, and the mesorectum—separately terminating their insertion into the posterior abdominal wall. However, in 2012, new microscopic and electron microscopic examinations showed the mesocolon to be a single structure derived from the duodenojejunal flexure and extending to the distal mesorectal layer. Thus, the mesentery is an internal organ. Structure The mesentery of the small intestine arises from the root of the mesentery (or mesenteric root) and is the part connected with the structures in front of the vertebral column. The root is narrow, about 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumbar Vertebrae
The lumbar vertebrae are, in human anatomy, the five vertebrae between the rib cage and the pelvis. They are the largest segments of the vertebral column and are characterized by the absence of the foramen transversarium within the transverse process (since it is only found in the cervical region) and by the absence of facets on the sides of the body (as found only in the thoracic region). They are designated L1 to L5, starting at the top. The lumbar vertebrae help support the weight of the body, and permit movement. Human anatomy General characteristics The adjacent figure depicts the general characteristics of the first through fourth lumbar vertebrae. The fifth vertebra contains certain peculiarities, which are detailed below. As with other vertebrae, each lumbar vertebra consists of a ''vertebral body'' and a ''vertebral arch''. The vertebral arch, consisting of a pair of ''pedicles'' and a pair of ''laminae'', encloses the ''vertebral foramen'' (opening) and sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrae
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the vertebral column, backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxon, taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pylorus
The pylorus ( or ), or pyloric part, connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the ''pyloric antrum'' (opening to the body of the stomach) and the ''pyloric canal'' (opening to the duodenum). The ''pyloric canal'' ends as the ''pyloric orifice'', which marks the junction between the stomach and the duodenum. The orifice is surrounded by a sphincter, a band of muscle, called the ''pyloric sphincter''. The word ''pylorus'' comes from Greek πυλωρός, via Latin. The word ''pylorus'' in Greek means "gatekeeper", related to "gate" ( el, pyle) and is thus linguistically related to the word " pylon". Structure The pylorus is the furthest part of the stomach that connects to the duodenum. It is divided into two parts, the ''antrum'', which connects to the body of the stomach, and the ''pyloric canal'', which connects to the duodenum. Antrum The ''pyloric antrum'' is the initial portion of the pylorus. It is near the bottom of the stomach, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
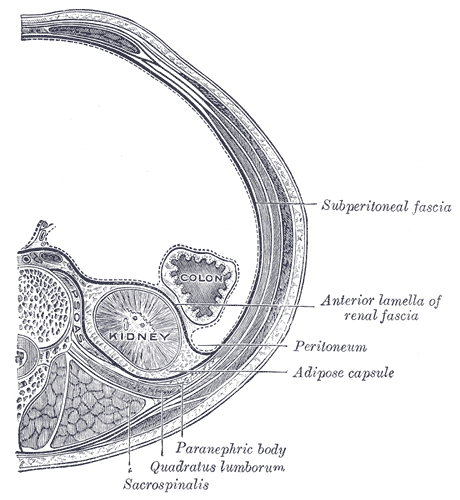
Retroperitoneal
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their anterior side only. Structures that are not suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and that lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall are classified as retroperitoneal. This is different from organs that are not retroperitoneal, which have peritoneum on their posterior side and are suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity. The retroperitoneum can be further subdivided into the following: *Perirenal (or perinephric) space *Anterior pararenal (or paranephric) space *Posterior pararenal (or paranephric) space Retroperitoneal structures Structures that lie behind the peritoneum are termed "retroperitoneal". Organs that were once suspended within the abdominal cavity by mesentery but migrated posterior to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. The abdominal cavity (the space bounded by the vertebrae, abdominal muscles, diaphragm, and pelvic floor) is different from the intraperitoneal space (located within the abdominal cavity but wrapped in peritoneum). The structures within the intraperitoneal space are called "intraperitoneal" (e.g., the stomach and intestines), the structures in the abdominal cavity that are located behind the intraperitoneal space are called "retroperitoneal" (e.g., the kidneys), and those structures below the intraperitoneal space are called "subp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |