|
Duncan Mackellar
Captain Duncan Mackellar (born c. 1789 in Kilmodan, Scotland), was a sea captain who later became a colonial settler in New South Wales, Australia. After a notable maritime career, including a daring escape from French capture in 1812, he visited Sydney in 1822 and decided to settle there. By 1829, he and his nephew, Duncan Mackellar, Junior, acquired substantial land near Braidwood. Mackellar developed a significant estate and was appointed a magistrate in 1833. Facing the end of convict transportation, he advocated for the importation of indentured labour. In 1836, he sold his land and returned to Scotland, where he published a guide on emigrating to Australia. Despite his brief stay, he is remembered as an early settler in the Braidwood district, commemorated by Mackellar Street and Duncan Street. Early life and maritime career Mackellar was born around 1789 in the parish of Kilmodan, Scotland. Known as Duncan Mackellar of Glendaruel, he was recognized as the head of the Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilmodan
Kilmodan is a civil parish situated on the Cowal Peninsula, in Argyll and Bute, in Scotland. It includes the valley of Glendaruel and surrounding areas, with Kilmodan Church located in the Clachan of Glendaruel. The alternative historical spelling, Kilmadan, is no longer used. The ''Imperial Gazetteer of Scotland'', c. 1857, has this to say about Kilmodan: Kilmadan (sometimes spelt Kilmodan) is a parish containing the postal station of Glendaruel in Cowal, Argyll. It is in the Presbytery (presbyterian church) of Dunoon and synod of Argyll. It is bounded by Loch Riddan, and by the parishes of Kilfinan, Strachur, Dunoon, and Inverchaolain. It consists chiefly of a glen, flanked by high hills, and extending southward; and is about long. The River Ruel traverses the upper part of the glen, and falls into the head of Loch Riddan. The extent of coast is upwards of three miles (5 km) and the scenery is of the grandest description. The most well-known native of the parish is Colin Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Darling
General Sir Ralph Darling, GCH (1772 – 2 April 1858) was a British Army officer who served as Governor of New South Wales from 1825 to 1831. He is popularly described as a tyrant, accused of torturing prisoners and banning theatrical entertainment. Local geographical features named after him include the Darling River and Darling Harbour in Sydney. Early career Darling seems to have been unique in the British Army of this period, as he progressed from an enlisted man to become a general officer with a knighthood. Born in Ireland, he was the son of a sergeant in the 45th Regiment of Foot who subsequently gained the unusual reward of promotion to officer rank as a lieutenant. Like most of the small number of former non-commissioned officers in this position, Lieutenant Darling performed only regimental administrative duties. He struggled to support his large family on a subaltern's pay. Ralph Darling enlisted at the age of fourteen as a private in his father's regiment, and ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Braidwood, New South Wales
The history of Braidwood, New South Wales in Australia dates back to the early nineteenth century. The historic nature of the town has been recognised with the listing of the entire town on the former Register of the National Estate on 21 October 1980 and the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 3 April 2006. History Early European settlement 1822–1839 Exploration Europeans first entered the upper Shoalhaven River basin in 1822 under instruction from the new Governor, Thomas Brisbane, to investigate the possibility of a track between the Limestone Plains and Batemans Bay. The reports of good country would have stimulated land selection in the area. Land The system of land grants available in the 1820s were attractive to settlers. A free grant of 640 acres of land (one square mile) was given to a selector for every £500 of money or stock held, with a limit of 2000 acres, shortly afterwards increased to 2560 (four square miles). Captain Duncan Mackellar, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Coghill (Australian Politician)
John Coghill (1785–1853) was an Australian politician and naval captain. He was the master of the ship '' Mangles'', which transported convicts to New South Wales from 1820 to 1826. After settling in New South Wales in 1826 he became a magistrate, and was based in Braidwood, where he built the Bedervale homestead. From 1843 to 1845 he was a member of the New South Wales Legislative Council. During 1841, he was in command of the convict road gang that built The Wool Road. In Braidwood, there is a wall plaque to his memory, in Anglican Church of St Andrew. Coghill Street is named after him. References External links Colonial Secretary's papers 1822-1877 State Library of Queensland- includes digitised letters written by Coghill to the Colonial Secretary of New South Wales Colonial or The Colonial may refer to: * Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology) Architecture * American colonial architecture * French Colonial * Spanish Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legislative Council Of New South Wales
The New South Wales Legislative Council, often referred to as the upper house, is one of the two chambers of the parliament of the Australian state of New South Wales. The other is the Legislative Assembly. Both sit at Parliament House in the state capital, Sydney. It is normal for legislation to be first deliberated on and passed by the Legislative Assembly before being considered by the Legislative Council, which acts in the main as a house of review. The Legislative Council has 42 members, elected by proportional representation in which the whole state is a single electorate. Members serve eight-year terms, which are staggered, with half the Council being elected every four years, roughly coinciding with elections to the Legislative Assembly. History The parliament of New South Wales is Australia's oldest legislature. It had its beginnings when New South Wales was a British colony under the control of the Governor, and was first established by the ''New South Wales Act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coolie
A coolie (also spelled koelie, kuli, khuli, khulie, cooli, cooly, or quli) is a term for a low-wage labourer, typically of South Asian or East Asian descent. The word ''coolie'' was first popularized in the 16th century by European traders across Asia, and by the 18th century would refer to migrant Indian indentured labourers, and by the 19th century during the British colonial era, would gain a new definition of the systematic transportation and employment of Asian laborers via employment contracts on sugar plantations that had been formerly worked by enslaved Africans. The word has had a variety of other implications and is sometimes regarded as offensive or a pejorative, depending upon the historical and geographical context; in India, its country of origin, it is still considered a derogatory slur. It is similar, in many respects, to the Spanish term peón, although both terms are used in some countries with different implications. The word originated in the 17th-centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombay, New South Wales
Bombay is a locality in the Queanbeyan–Palerang Regional Council, New South Wales, Australia. It is located about 14 km southwest of Braidwood on the western bank of the Shoalhaven River The Shoalhaven River is a perennial river that rises from the Southern Tablelands and flows into an open mature wave dominated barrier estuary near Nowra on the South Coast of New South Wales, Australia. Location and features The Shoalhaven .... At the , it had a population of 142. It has two areas of somewhat denser settlement described as "Bombay" (near Bombay creek) and "Little Bombay" (further north and near Little Bombay creek). It had a school in 1871 (when it was called "Little Bombay Half-Time School") and from 1873 to 1928, normally described as "Bombay Half-Time School" but sometimes as "Bombay Provisional School". References Localities in New South Wales Queanbeyan–Palerang Regional Council Southern Tablelands {{SouthernTablelands-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cronyism
Cronyism is the spoils system practice of partiality in awarding jobs and other advantages to friends or trusted colleagues, especially in politics and between politicians and supportive organizations. For example, cronyism occurs when appointing "cronies" to positions of authority regardless of their qualifications. This is in contrast to a ''meritocracy'', in which appointments are made based on merit. Politically, "cronyism" is derogatorily used to imply buying and selling favors, such as votes in legislative bodies, as doing favors to organizations, giving desirable ambassadorships to exotic places, etc. Cronyism is a specific form of favoritism. Etymology The word "crony" first appeared in 17th-century London, according to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' and is believed to be derived from the Greek word ''chronios'' (χρόνιος), meaning "long term". A less likely but oft-quoted source is the supposed Irish term ''Comh-Roghna'', which translates as "close pals", o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepotism
Nepotism is an advantage, privilege, or position that is granted to relatives and friends in an occupation or field. These fields may include but are not limited to, business, politics, academia, entertainment, sports, fitness, religion, and other activities. The term originated with the assignment of nephews to important positions by Catholic popes and bishops. Nepotism has been criticized since the ancient times by several philosophers, including Aristotle, Valluvar, and Confucius, condemning it as both evil and unwise. Origins The term comes from Italian word ''nepotismo'',"Nepotism." Dictionary.com. Retrieved 20 June 2013. which is based on Latin root ''nepos'' meaning nephew. Since the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world. The EIC had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three Presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British army at the time. The operations of the company had a profound effect on the global balance of trade, almost single-handedly reversing the trend of eastward drain of Western bullion, seen since Roman times. Originally chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies", the company rose to account for half of the world's trade duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Of New South Wales
The Colony of New South Wales was a colony of the British Empire from 1788 to 1901, when it became a State of the Commonwealth of Australia. At its greatest extent, the colony of New South Wales included the present-day Australian states of New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria, Tasmania, and South Australia, the Northern Territory as well as New Zealand. The first "responsible" self-government of New South Wales was formed on 6 June 1856 with Sir Stuart Alexander Donaldson appointed by Governor Sir William Denison as its first Colonial Secretary. History Formation On 18 January 1788, the First Fleet led by Captain Arthur Phillip founded the first British settlement in Australian history as a penal colony. Having set sail on 13 May 1787, Captain Arthur Phillip assumed the role of governor of the settlement upon arrival. On 18 January 1788, the first ship of the First Fleet, HMS ''Supply'', with Phillip aboard, reached Botany Bay. However, Botany Bay was found to be unsuita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clydesdale (1819 Ship)
The ship ''Clydesdale'' was launched at Bay of Quick, Greenock in 1819. She sailed as an East Indiaman under a licence from the British East India Company (EIC). She was condemned at Mauritius circa June 1827 as unseaworthy while homeward bound from Bengal. Career The partnership of R. & A. Carsewell commenced building vessels in 1816. ''Clydesdale'', at 584 tons (bm), was the largest vessel they launched. R & A Carsewell launched ''Clydesdale'' in July 1819, for the East India trade. In 1813 the British East India Company (EIC) had lost its monopoly on the trade between India and Britain. British ships were then free to sail to India or the Indian Ocean under a licence from the EIC. In December 1819 the following advertisement appeared. ''Clydesdale'' did not sail until February. ''Clydesdale'' first appeared in ''Lloyd's Register'' (''LR'') in the supplemental pages in 1819. ''Lloyd's Register'' reported that ''Clydesdale'', M'Kellar, master, sailed for Kolkatta, Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


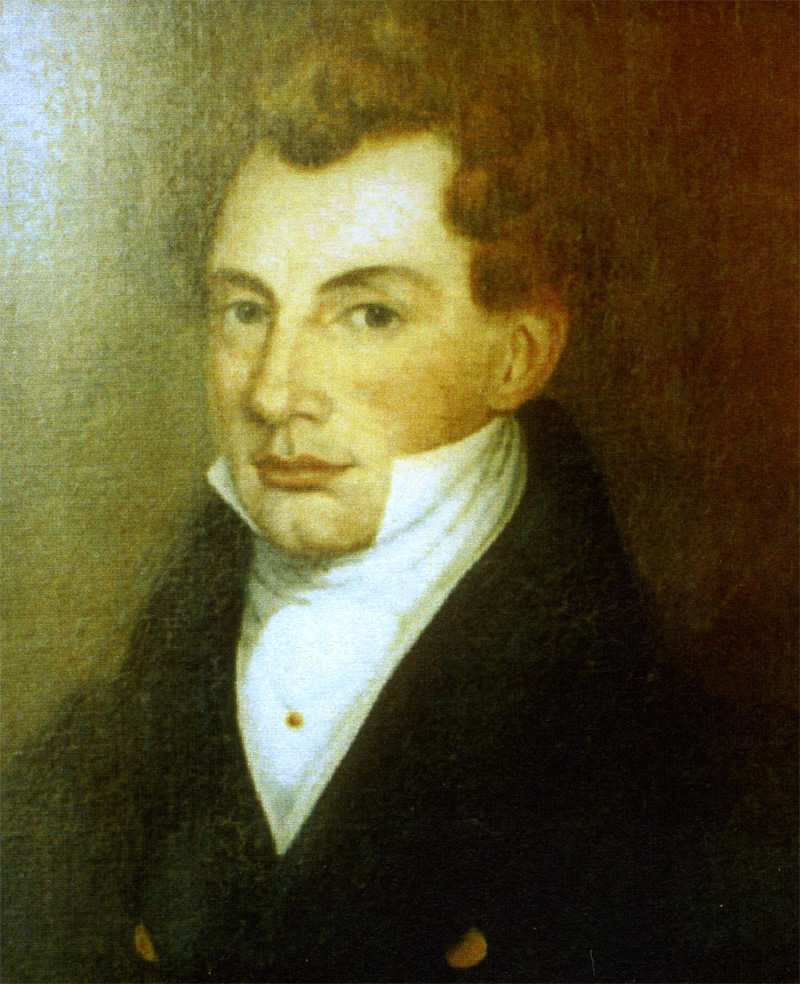

.jpg)


