|
Dulo
The Dulo clan was a ruling dynasty of the Bulgars. The origins of the Bulgars and Dulo clan are not known precisely, and there are many theories about their origin. It is generally considered that they – or at least the elite caste – were intimately related to the origin and activity of the Huns and Western Turkic Khaganate. Particularly, it is said that the Dulo descended from the rulers of Great Bulgaria, which was founded by Khan Asparuh's (681–701) father on the steppes of Ukraine. This state was a centralized monarchy from its inception, unlike previous Hunno-Turkic political entities, which were tribal confederations. The royal family and rulers of Old Great Bulgaria (632–668) and the first half of the First Bulgarian Empire (681–1018), in their prince lists ('' Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans'') claimed through Irnik, who was probably related to or was Attila's son Ernak himself, or at least of Attilid descent. During the pagan period, the succession of clan le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomadic equestrians in the Volga-Ural region, but some researchers say that their ethnic roots can be traced to Central Asia. During their westward migration across the Eurasian steppe, the Bulgar tribes absorbed other tribal groups and cultural influences in a process of ethnogenesis, including Iranian, Finnic and Hunnic tribes. Modern genetic research on Central Asian Turkic people and ethnic groups related to the Bulgars points to an affiliation with Western Eurasian populations. The Bulgars spoke a Turkic language, i.e. Bulgar language of Oghuric branch. They preserved the military titles, organization and customs of Eurasian steppes, as well as pagan shamanism and belief in the sky deity Tangra. The Bulgars became semi-sedentary durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attilid Dynasty
The Attilids were a leading dynasty of the Huns, a nomadic pastoralist people who confronted the Roman Empire during the decline of the Western Roman Empire, as well as the Eastern Roman Empire. They also often fought in alliance with both of these empires against the invading Germanic people. Origin The Attilids descended from Attila, the last sole ruler of the Hunnic Empire. Attila was of noble origin, the son of Mundzuk. His father was a brother of co-rulers of the Hunnic Empire Rugila and Octar, but never became king himself. He begat two sons by an unknown consort. His sons were Bleda and Attila, who succeeded their uncle Rugila as regents of the Empire. Rugila had become sole ruler after the death of his brother Octar in 430. History Attila and Bleda made a series of successful campaigns in the Balkans and Greece, capturing the major Roman cities up to arriving to Constantinople, where they destroyed the Roman forces around the city before forcing the Romans to pay an inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
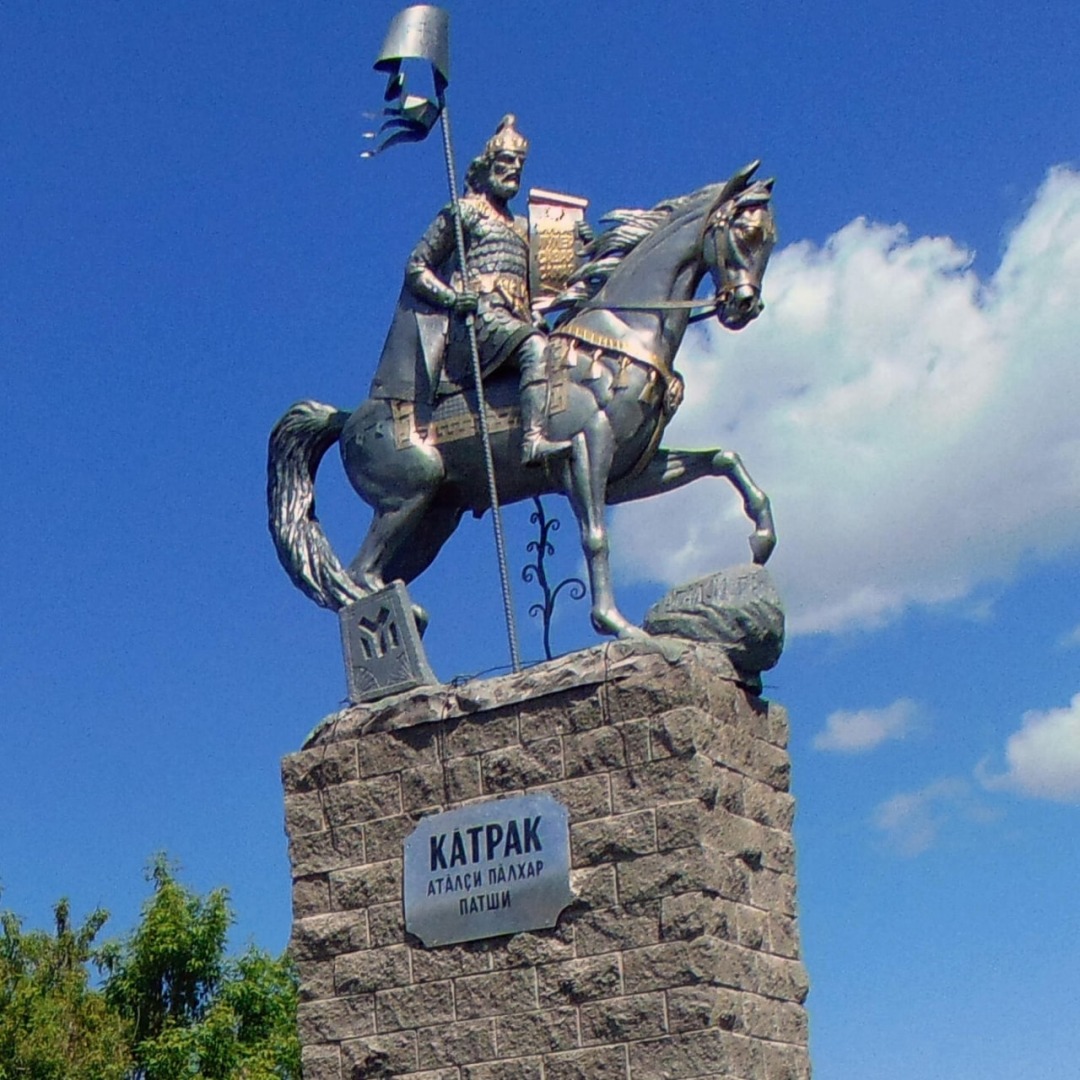
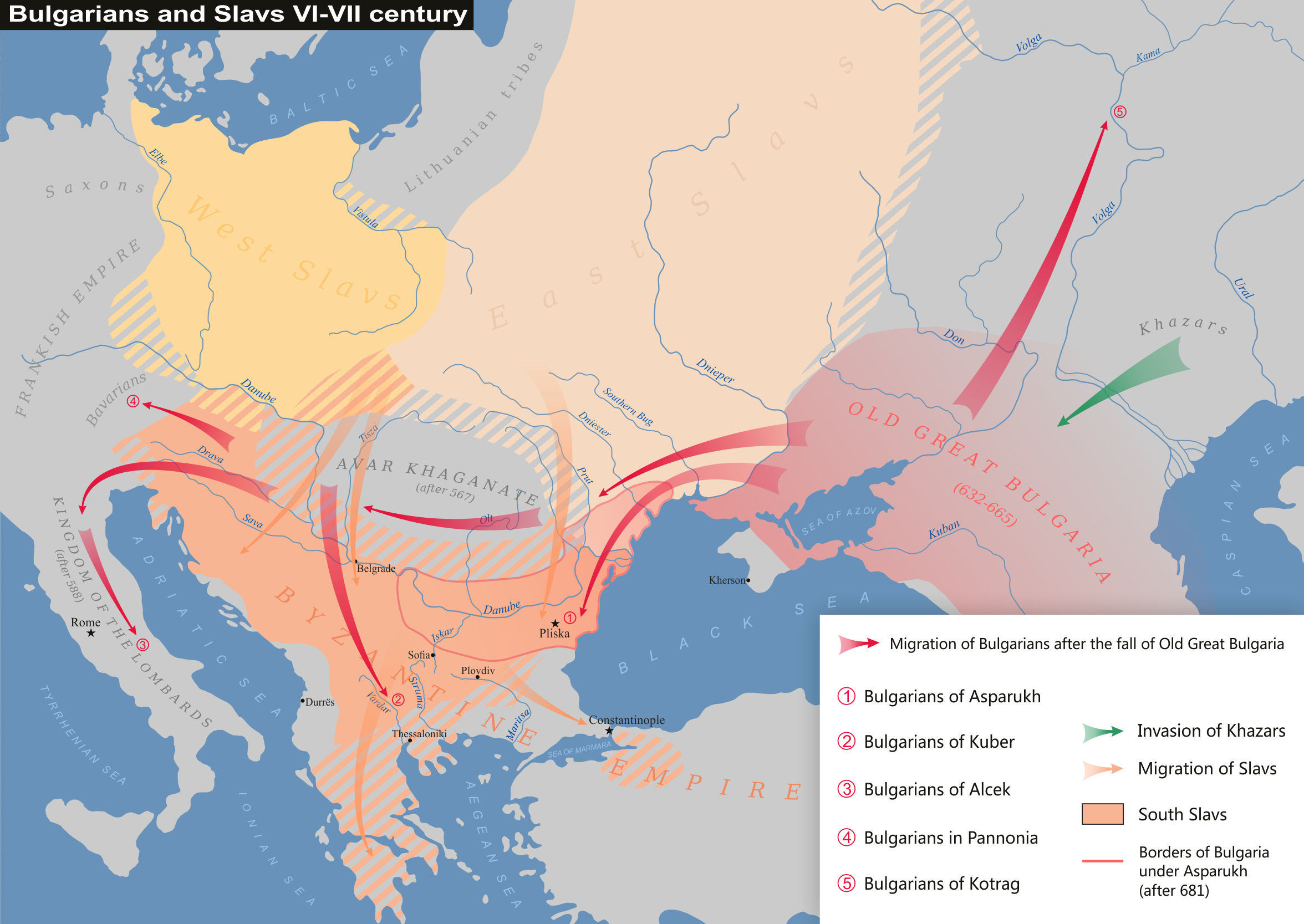
Kotrag
Kotrag was according to Nikephoros I of Constantinople a son of Kubrat of the Dulo clan of Bulgars. Following the death of his father, he began to extend the influence of his Bulgars to the Volga River. He is remembered as the founder of Volga Bulgaria. Honour * Kotrag Nunatak on Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica is named after Kotrag. * In the Republic of Chuvashia in the village of Shemursha on June 12, 2022, a monument was erected to the founder of the Volga Bulgaria - Kotrag Name The possible origin of the name of khan Kotrag from the Chuvash name ''Kătrak'' and ''Kătrashka'', which in translation means ''Curly'', a common pre-Christian name among the Chuvash. In the Kipchak languages The Kipchak languages (also known as the Kypchak, Qypchaq, Qypshaq or the Northwestern Turkic languages) are a sub-branch of the Turkic language family spoken by approximately 28 million people in much of Central Asia and Eastern Europe, spannin ..., the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
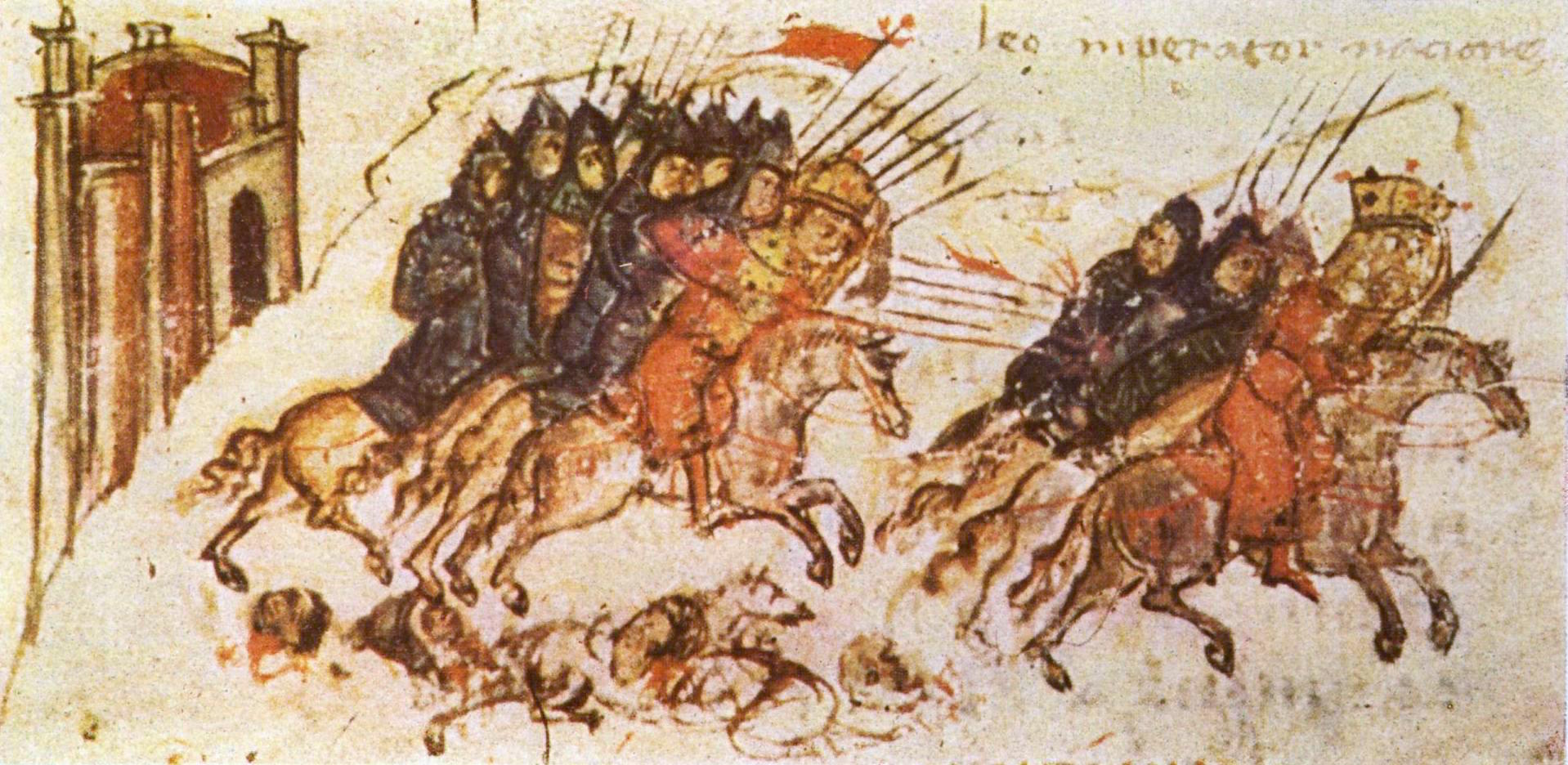
Asparukh Of Bulgaria
Asparuh (also ''Ispor''; bg, Аспарух, Asparuh or (rarely) bg, Исперих, Isperih) was а ruler of Bulgars in the second half of the 7th century and is credited with the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681. Early life The '' Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans'' states that Asparuh belonged to the Dulo clan and reigned for 61 years. This long period cannot be accepted as accurate due to chronological constraints, and may indicate the length of Asparuh's life. According to the chronology developed by Moskov, Asparuh would have reigned 668–695. Other chronologies frequently end his reign in 700 or 701 but cannot be reconciled with the testimony of the ''Namelist''. According to the Byzantine sources, Asparuh was a younger son of Kubrat, who had established a spacious state ("Great Bulgaria") in the steppes of modern Ukraine. Asparuh may have gained experience in politics and statesmanship during the long reign of his father, who probably died in 66 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuber
Kuber, (also Kouber or Kuver), was a Bulgar leader who, according to the ''Miracles of Saint Demetrius'', liberated a mixed Bulgar and Byzantine Christian population in the 670s, whose ancestors had been transferred from the Eastern Roman Empire to the Syrmia region in Pannonia by the Avars 60 years earlier.CurtaFine According to a scholarly theory, he was a son of Kubrat, brother of Khan Asparukh and member of the Dulo clan. Origins According to the Byzantine scholar, Theophanes the Confessor, Kubrat's (unnamed) fourth son, who left the Pontic steppes after his father's death around 642, became "the subject of the of the Avars in Avar Pannonia and remained there with his army". According to a scholarly theory, first proposed by the Bulgarian historian Vasil Zlatarski, Kuber was the fourth son of Kubrat, the Christian ruler of the Onogur Bulgars in the steppes north of the Black Sea. Kuber's story is continued in the second book of the ''Miracles of Saint Demetrius''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asparuh Of Bulgaria
Asparuh (also ''Ispor''; bg, Аспарух, Asparuh or (rarely) bg, Исперих, Isperih) was а ruler of Bulgars in the second half of the 7th century and is credited with the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681. Early life The '' Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans'' states that Asparuh belonged to the Dulo clan and reigned for 61 years. This long period cannot be accepted as accurate due to chronological constraints, and may indicate the length of Asparuh's life. According to the chronology developed by Moskov, Asparuh would have reigned 668–695. Other chronologies frequently end his reign in 700 or 701 but cannot be reconciled with the testimony of the ''Namelist''. According to the Byzantine sources, Asparuh was a younger son of Kubrat, who had established a spacious state ("Great Bulgaria") in the steppes of modern Ukraine. Asparuh may have gained experience in politics and statesmanship during the long reign of his father, who probably died in 665 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avitohol
Avitohol (153?–453?) is the first name in the '' Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans''. Little is known about him. According to the document he is from the Dulo clan and most probably was considered and respected as the forefather of the khans. Some researchers claim that Avitohol is Attila the Hun who was succeeded by his son Ernak or ''Irnik'' (the second name mentioned in the ''Nominalia''). Others suggests that Avitohol was a semi-legendary ruler who may have been either a descendant or an ancestor of Attila (see Dulo clan). Etymology The very name Avitohol, according to the interpretation of the economic historian Dobrev, done with the help of the Pamiric languages, means "Son of the Deer" (from Avi - deer, "Tohol" - child). This interpretation is rejected by the linguist-turkist Prof. Ivan Dobrev as insubstantial, because the word "tochol" is a relatively late Arabic loan (طفل, ifl"nursing") in the Pamiric languages. His proposed interpretation of the name is avit- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire ( cu, блъгарьско цѣсарьствиѥ, blagarysko tsesarystviye; bg, Първо българско царство) was a medieval Bulgar- Slavic and later Bulgarian state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh, moved south to the northeastern Balkans. There they secured Byzantine recognition of their right to settle south of the Danube by defeatingpossibly with the help of local South Slavic tribesthe Byzantine army led by Constantine IV. During the 9th and 10th century, Bulgaria at the height of its power spread from the Danube Bend to the Black Sea and from the Dnieper River to the Adriatic Sea and became an important power in the region competing with the Byzantine Empire. It became the foremost cultural and spiritual centre of south Slavic Europe throughout most of the Middle Ages. As the state solidified its position in the Balka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kubrat
Kubrat ( el, Κοβρᾶτος, Kούβρατος; bg, Кубрат ) was the ruler of the Onogur–Bulgars, credited with establishing the confederation of Old Great Bulgaria in ca. 632. His name derived from the Turkic words ''qobrat'' — "to gather", or ''qurt'', i.e. "wolf". Origin In the '' Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans'' Kubrat is mentioned as ''Kurt'' (), being a member of the Dulo clan and reigning for 60 years having succeeded Gostun of the Ermi clan. Bulgars were Turkic nomadic people, who participated in the 5th-century Hunnic confederation. Upon Attila's death, the tribes that later formed the Bulgars had retreated east into the Black Sea-Caspian Steppe. The western Bulgar tribes joined the Avar Khaganate, while the eastern Bulgars came under the Western Turkic Khaganate by the end of the 6th century. Theophanes the Confessor called him "king of the Onogundur Huns". Patriarch Nikephoros I (758–828) called Kubrat "lord of the Onuğundur" and "ruler of the O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernak
Ernak was the last known ruler of the Huns, and the third son of Attila. After Attila's death in 453 AD, his Empire crumbled and its remains were ruled by his three sons, Ellac, Dengizich and Ernak. He succeeded his older brother Ellac in 454 AD, and probably ruled simultaneously over Huns in dual kingship with his brother Dengizich, but in separate divisions in separate lands. Priscus, during his stay at Attila's court in 448 or 449 AD, recorded a personal occasion between Attila and Ernak. At a banquet Attila looked on him with serene eyes, while taking small account of his other sons. He was Attila's favorite son, because as a certain Hun explained to him, the Hunnic prophets prophesied his ''genos'' would fail, but would be restored by this son. Ernak has often been identified with ''Irnik'' from the Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans, who is noted as a descendant of the Dulo clan and leader of the Bulgars for 150 years, starting approximately from 437 AD. History The oldest bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batbayan
Batbayan ( bg, Батбаян) ruled the Khazarian Bulgars mentioned by Theophanes and Nicephorus after the Khazars defeated the Bulgars and Old Great Bulgaria disintegrated. There is a scholarly theory that he may have been the same person as Bezmer of the Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans who may have been also the first son of Kubrat. He was a member of the Dulo clan, who after Kubrat's death ruled Old Great Bulgaria, but his rule lasted only three years. Kevin Alan Brook Kevin () is the anglicized form of the Irish masculine given name (; mga, Caoimhghín ; sga, Cóemgein ; Latinized as ). It is composed of "dear; noble"; Old Irish and ("birth"; Old Irish ). The variant '' Kevan'' is anglicized from , a ... calls him Bayan.Kevin Alan Brook, The Jews of Khazaria, Edition 3, Rowman & Littlefield, 2018, , p. 15. Batbayan would have then ruled the Bulgars as a subject to the Khazar Khagan. Sources Year of birth unknown European royalty Bulgars {{Europe- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcek
Alcek or Alzeco was allegedly a son of Kubrat and led the Altsikurs to Ravenna that later settled in the villages of Gallo Matese, Sepino, Boiano and Isernia in the Matese mountains of southern Italy. Alzeco should not be confused with the Pannonian Bulgar leader Alciocus who joined the Wends before Alzeco was born. After the collapse of Old Great Bulgaria, some of the Bulgars, led by Alzeco, thought to be a son of Khan Kubrat, settled in the lands of the Longobard Kingdom. Paul the Deacon places a settlement in his history of the migration of the Bulgars in the area of the Duchy of Benevento. Under the leadership of Alzeco, the Bulgars (called "Vulgars" by Paul) came to Italy in Benevento, where they settled in the Molise region. Alciocus The earlier Khagan called Alciocus who was the leader of Bulgar hordes of the Avar Khanganate, is also known. The main source for these events is the medieval chronicle of Fredegar. In 631 Samo led a rebellion against the Pannonian Avars. Alcio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |