|
Dui (Bronze Vessel)
A ''dui'' is a type of Chinese ritual bronze vessel used in the late Zhou dynasty and the Warring States period of ancient China. It was a food container used as a ritual vessel. Most ''dui'' consist of two bowls supported on three legs. Form The ''dui'' is typically spherical in shape, possessing a half-domed bowl on bottom with a similarly shaped container fitting on top. Shapes vary from circular, ovular, or subcircular. Types from the late Eastern Zhou appear more spheroidal; containers become more ovular during the Spring and Autumn period; and transitioning from the late Spring and Autumn to the Warring States period, vessel types appear less round in shape, possessing a flattened lid paired with a rounded bowl. The vessel stands on either a single pedestal or is supported by three legs (similarly to the ''ding''). The three legs would permit heating of the food within. Each vessel sports two handles; either set or unfixed rings adorn the bottom portion of the ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Dui Vessel With Inlaid Geometric Cloud Pattern
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
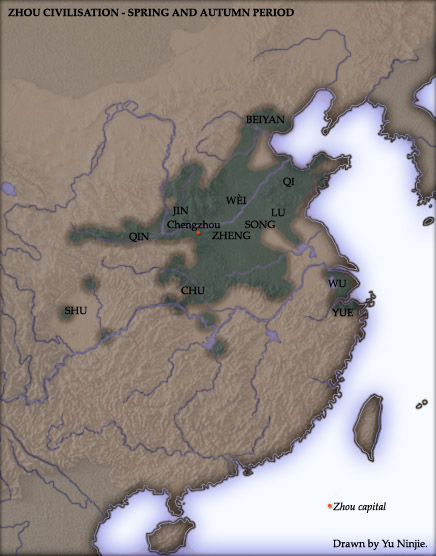
Eastern Zhou
The Eastern Zhou (; zh, c=, p=Dōngzhōu, w=Tung1-chou1, t= ; 771–256 BC) was a royal dynasty of China and the second half of the Zhou dynasty. It was divided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn and the Warring States. History In 770 BCE, the capital of the Zhou Kingdom was moved from Haojing (Chang'an County in Xi'an City) to Luoyi (known today as Luoyang, Henan Province). This brought about the beginning of the Eastern Zhou dynasty (as opposed to Western Zhou dynasty), so named due to Luoyi being situated to the east of Haojing. Over 25 kings reigned over the Eastern Zhou Dynasty, lasting 515 years in all. With the death of King You of Zhou, the last king of the Western Zhou Dynasty, ascended Crown Prince Yijiu was proclaimed the new king by the nobles from the states of Zheng, Lü, Qin and the Marquess of Shen. He was King Ping of Zhou. In the second year of his reign, he moved the capital east to Luoyi as Quanrong invaded Haojing, indicating the end of the Weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinzheng
Xinzheng () is a county-level city of Henan Province, China. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Zhengzhou, the provincial capital. The city has a population of 600,000 people and covers an area of , of which is urban. History Xinzheng is considered one of the birthplaces of the Chinese nation. More than 8000 years ago, neolithic people of Peiligang culture lived in the vicinity. The legendary Yellow Emperor was said to have been born in Xinzheng 5000 years ago. During the Zhou dynasty it was the capital of the state of Zheng and later, the state of Han, after the conquest of the former by the latter. It was the seat of government for the Qin dynasty, from about 221 BCE, which is considered the beginning of a unified China. The word ''qin'' (), which is pronounced similar to "chin", is thought to be the basis for the word "China." Historically, this prefecture was an integrated part of Zhengzhou. However, in 1994, the Henan Provincial Council authorized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Emperor
The Yellow Emperor, also known as the Yellow Thearch or by his Chinese name Huangdi (), is a deity ('' shen'') in Chinese religion, one of the legendary Chinese sovereigns and culture heroes included among the mytho-historical Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors and cosmological Five Regions' Highest Deities (). Calculated by Jesuit missionaries on the basis of Chinese chronicles and later accepted by the twentieth-century promoters of a universal calendar starting with the Yellow Emperor, Huangdi's traditional reign dates are 2697–2597 or 2698–2598 BC. Huangdi's cult became prominent in the late Warring States and early Han dynasty, when he was portrayed as the originator of the centralized state, as a cosmic ruler, and as a patron of esoteric arts. A large number of texts – such as the ''Huangdi Neijing'', a medical classic, and the '' Huangdi Sijing'', a group of political treatises – were thus attributed to him. Having waned in influence during most of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Wei Of Qi
King Wei of Qi (), whose personal name was Tian Yinqi (田因齊), was the king of the northern Chinese state of Qi during the Warring States period, when Qi was one of the most powerful states in China. He reigned from 356 to 320 BC. or according to another source from 378 to 343 BC. He was the first ruler of Qi to style himself "king". His successor was King Xuan of Qi. In the ''Intrigues of the Warring States'', the strategist Su Qin is quoted as telling the king of Qin: "Kings Wei and Xuan of Qi were the worthiest rulers of their age. Their power was great and their lands were broad. Their states were wealthy and their citizens capable. Their generals were aggressive and their troops strong." King Wei was judicious and measured in his actions toward his subordinates. At one point he was told repeatedly by his spies that one of his generals, Zhangzi, had surrendered to the enemy, Qin. King Wei refused to believe that Zhangzi had deserted. Sure enough, "a short while later it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The dynasty is divided into two periods: Northern Song and Southern Song. During the Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now Eastern China. The Southern Song (; 1127–1279) refers to the period after the Song lost control of its northern half to the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in the Jin–Song Wars. At that time, the Song court retreated south of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ding (vessel)
''Ding'' () are prehistoric and ancient Chinese cauldrons, standing upon legs with a lid and two facing handles. They are one of the most important shapes used in Chinese ritual bronzes. They were made in two shapes: round vessels with three legs and rectangular ones with four, the latter often called ''fangding''. They were used for cooking, storage, and ritual offerings to the gods or to ancestors. The earliest recovered examples are pre-Shang ceramic ding at the Erlitou site but they are better known from the Bronze Age, particularly after the Zhou deemphasized the ritual use of wine practiced by the Shang kings. Under the Zhou, the ding and the privilege to perform the associated rituals became symbols of authority. The number of permitted ding varied according to one's rank in the Chinese nobility: the Nine Ding of the Zhou kings were a symbol of their rule over all China but were lost by the first emperor, Shi Huangdi in the late 3rd century BCE. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives from the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'', a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 479 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius (551–479 BCE). During this period, the Zhou royal authority over the various feudal states eroded as more and more dukes and marquesses obtained ''de facto'' regional autonomy, defying the king's court in Luoyi and waging wars amongst themselves. The gradual Partition of Jin, one of the most powerful states, marked the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period. Background In 771 BCE, a Quanrong invasion in coalition with the states of Zeng and Shen — the latter polity being the fief of the grandfather of the disinherited crown prince Yijiu — destroyed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warring States Bronze Dui, Chu State
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular or irregular military forces. Warfare refers to the common activities and characteristics of types of war, or of wars in general. Total war is warfare that is not restricted to purely legitimate military targets, and can result in massive civilian or other non-combatant suffering and casualties. While some war studies scholars consider war a universal and ancestral aspect of human nature, others argue it is a result of specific socio-cultural, economic or ecological circumstances. Etymology The English word ''war'' derives from the 11th-century Old English words ''wyrre'' and ''werre'', from Old French ''werre'' (also ''guerre'' as in modern French), in turn from the Frankish *''werra'', ultimately deriving from the Proto-Germanic *''we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Ritual Bronze
Sets and individual examples of ritual bronzes survive from when they were made mainly during the Chinese Bronze Age. Ritual bronzes create quite an impression both due to their sophistication of design and manufacturing process, but also because of their remarkable durability. From around 1650 BCE, these elaborately decorated vessels were deposited as grave goods in the tombs of royalty and the nobility, and were evidently produced in very large numbers, with documented excavations finding over 200 pieces in a single royal tomb. They were produced for an individual or social group to use in making ritual offerings of food and drink to his or their ancestors and other deities or spirits. Such ceremonies generally took place in family temples or ceremonial halls over tombs. These ceremonies can be seen as ritual banquets in which both living and dead members of a family were supposed to participate. Details of these ritual ceremonies are preserved through early literary records ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warring States Bronze Dui 1
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular or irregular military forces. Warfare refers to the common activities and characteristics of types of war, or of wars in general. Total war is warfare that is not restricted to purely legitimate military targets, and can result in massive civilian or other non-combatant suffering and casualties. While some war studies scholars consider war a universal and ancestral aspect of human nature, others argue it is a result of specific socio-cultural, economic or ecological circumstances. Etymology The English word ''war'' derives from the 11th-century Old English words ''wyrre'' and ''werre'', from Old French ''werre'' (also ''guerre'' as in modern French), in turn from the Frankish *''werra'', ultimately deriving from the Proto-Germanic *''we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinan 2009 1156
Jinan (), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanization of Chinese, romanized as Tsinan, is the Capital (political), capital of Shandong province in East China, Eastern China. With a population of 9.2 million, it is the second-largest city in Shandong. The area of present-day Jinan has played an important role in the history of the region from the earliest beginnings of civilization and has evolved into a major national administrative, economic, and transportation hub. The city has held Sub-provincial city, sub-provincial administrative status since 1994. Jinan is often called the "City of Springs" for its famous 72 Artesian aquifer, artesian springs. Jinan is one of the top List of cities by scientific output, 40 cities in the world for scientific research as tracked by the Nature Index according to the Nature Index 2022 Science Cities. The city is home to List of universities and colleges in Shandong, several major universities, including Shandong University, Shangdong, Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_with_human_faces_02.jpg)

