|
Dugdale Glacier
Dugdale Glacier () is a glacier about long, draining northeast from the Admiralty Mountains into Robertson Bay on the north coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica. The geographical feature flows along the west side of Geikie Ridge before coalescing with Murray Glacier just west of Duke of York Island. It was charted by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1898–1900, under Carsten Borchgrevink, who named it for Frank Dugdale of Snitterfield, Stratford-on-Avon. The glacier lies situated on the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare Cape Adare is a prominent cape of black basalt forming the northern tip of the Adare Peninsula and the north-easternmost extremity of Victoria Land, East Antarctica. Description Marking the north end of Borchgrevink Coast and the west e .... References Glaciers of Pennell Coast {{PennellCoast-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of York Island, Antarctica
Duke of York Island is a mountainous ice-free island, long, lying in the southern part of Robertson Bay, Antarctica, along the northern coast of Victoria Land. It was first charted in 1899 by the British Antarctic Expedition, under Carsten Borchgrevink, who named it for the then Duke of York, later George V. This island lies situated within the borders known as the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare. Important Bird Area A 680 ha site comprising the whole island has been designated an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports a breeding colony of Adélie penguins, with an estimate of some 16,000 breeding pairs based on 2011 satellite imagery. Snow petrel The snow petrel (''Pagodroma nivea'') is the only member of the genus ''Pagodroma.'' It is one of only three birds that has been seen at the Geographic South Pole, along with the Antarctic petrel and the south polar skua, which have the most s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Williams
Cape Williams () is an ice-covered cape in Antarctica. It is the termination of Buell Peninsula at the east side of the terminus of Lillie Glacier at the lower ends of George Glacier and Zykov Glacier. The peninsula is 15 nautical miles (28 km) long and is situated at the extremity of the Pennell Coast portion of Victoria Land, lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare Cape Adare is a prominent cape of black basalt forming the northern tip of the Adare Peninsula and the north-easternmost extremity of Victoria Land, East Antarctica. Description Marking the north end of Borchgrevink Coast and the west e .... It was discovered in February 1911 when the Terra Nova of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, explored the area westward of Cape North, and it was named for William Williams, Chief Engine-room Artificer on the Terra Nova. Headlands of Victoria Land Pennell Coast {{VictoriaLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennell Coast
Pennell Coast is that portion of the coast of Antarctica between Cape Williams and Cape Adare. To the west of Cape Williams lies Oates Coast, and to the east and south of Cape Adare lies Borchgrevink Coast. Named by New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee (NZ-APC) in 1961 after Lieutenant Harry Pennell, Royal Navy, commander of the Terra Nova, the expedition ship of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13. Pennell engaged in oceanographic work in the Ross Sea during this period. In February 1911 he sailed along this coast in exploration and an endeavor to land the Northern Party led by Lieutenant Victor Campbell. The name is also used more loosely to refer to both the coast itself and the hinterland extending south to the watershed of the Southern Cross Mountains to the southeast and the Usarp Mountains to the west. Major features of the coast include the 250-kilometer long Rennick Glacier (one of Antarctica's largest glaciers), the Anare Mountains, and the norther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snitterfield
Snitterfield is a village and civil parish in the Stratford on Avon district of Warwickshire, England, less than to the north of the A46 road, from Stratford upon Avon, from Warwick and from Coventry. The population of the civil parish at the 2011 census was 1,226. History The early name of Snitterfield was "Snytenfeld", open field of snipe, "Feld", signifying a cleared stretch of land amid the Forest of Arden and "Snyten" referring to the snipe frequenting the meadows near the Sherbourne Brook which runs through the village. The earliest record of Snitterfield is on a map dated 1630 by John Speed and as late as 1814, Snitterfield was spelt as Snitfield. At the time of the Norman Conquest Snitefeld was held by Saxi who also possessed land at Walton, Charlecote, Bramcote, Dorsington and Werlavescote but by 1086 it was held by the Count of Meulan; "in Ferncombe hundred, Snitefeld. Saxi held it he was a free man. 4 hides. Land for 14 ploughs. In lordship 2; 10 slaves.11 vill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Dugdale
Frank or Franks may refer to: People * Frank (given name) * Frank (surname) * Franks (surname) * Franks, a medieval Germanic people * Frank, a term in the Muslim world for all western Europeans, particularly during the Crusades - see Farang Currency * Liechtenstein franc or frank, the currency of Liechtenstein since 1920 * Swiss franc or frank, the currency of Switzerland since 1850 * Westphalian frank, currency of the Kingdom of Westphalia between 1808 and 1813 * The currencies of the German-speaking cantons of Switzerland (1803–1814): ** Appenzell frank ** Argovia frank ** Basel frank ** Berne frank ** Fribourg frank ** Glarus frank ** Graubünden frank ** Luzern frank ** Schaffhausen frank ** Schwyz frank ** Solothurn frank ** St. Gallen frank ** Thurgau frank ** Unterwalden frank ** Uri frank ** Zürich frank Places * Frank, Alberta, Canada, an urban community, formerly a village * Franks, Illinois, United States, an unincorporated community * Franks, Missouri, United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carsten Borchgrevink
Carsten Egeberg Borchgrevink (1 December 186421 April 1934) was an Anglo-Norwegian polar explorer and a pioneer of Antarctic travel. He inspired Sir Robert Falcon Scott, Sir Ernest Shackleton, Roald Amundsen, and others associated with the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration. Borchgrevink began his exploring career in 1894 by joining a Norwegian whaling expedition, during which he became one of the first people to set foot on the Antarctic mainland. This achievement helped him to obtain backing for his ''Southern Cross'' expedition, which became the first to overwinter on the Antarctic mainland, and the first to visit the Great Ice Barrier since the expedition of Sir James Clark Ross nearly sixty years earlier. The expedition's successes were received with only moderate interest by the publicand by the British geographical establishment, whose attention was by then focused on Scott's upcoming ''Discovery'' expedition. Some of Borchgrevink's colleagues were critical of his lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Antarctic Expedition, 1898–1900
The ''Southern Cross'' Expedition, otherwise known as the British Antarctic Expedition, 1898–1900, was the first British venture of the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, and the forerunner of the more celebrated journeys of Robert Falcon Scott and Ernest Shackleton. The brainchild of the Anglo-Norwegian explorer Carsten Borchgrevink, it was the first expedition to over-winter on the Antarctic mainland, the first to visit the Great Ice Barrier—later known as the Ross Ice Shelf—since Sir James Clark Ross's groundbreaking expedition of 1839 to 1843, and the first to effect a landing on the Barrier's surface. It also pioneered the use of dogs and sledges in Antarctic travel. The expedition was privately financed by the British magazine publisher Sir George Newnes. Borchgrevink's party sailed in the , and spent the southern winter of 1899 at Cape Adare, the northwest extremity of the Ross Sea coastline. Here they carried out an extensive programme of scientific observations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
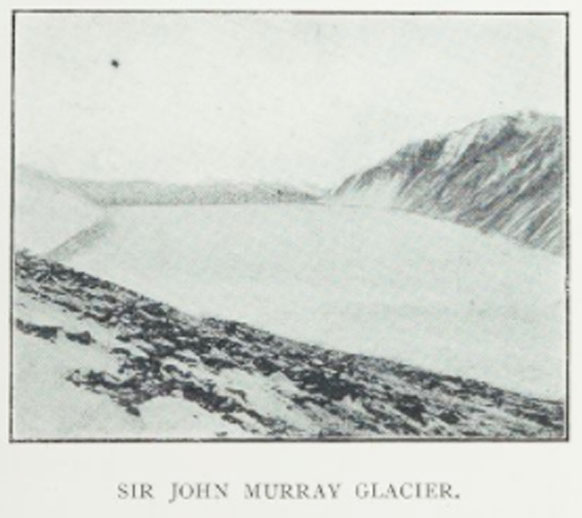
Murray Glacier
Murray Glacier () is a valley glacier, long, draining seaward along the east side of Geikie Ridge in the Admiralty Mountains. Its terminus coalesces with that of Dugdale Glacier where both glaciers discharge into Robertson Bay along the north coast of Victoria Land. First charted by the British Antarctic Expedition 1898-1900, under Carsten Borchgrevink, who named this feature for Sir John Murray of the Challenger Expedition The ''Challenger'' expedition of 1872–1876 was a scientific program that made many discoveries to lay the foundation of oceanography. The expedition was named after the naval vessel that undertook the trip, . The expedition, initiated by Wil ..., 1872–76. References Glaciers of Pennell Coast {{PennellCoast-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geikie Ridge
Robertson Bay is a large, roughly triangular bay that indents the north coast of Victoria Land between Cape Barrow (Antarctica), Cape Barrow and Cape Adare. Discovered in 1841 by Captain James Clark Ross, Royal Navy, who named it for Dr. John Robertson (surgeon), John Robertson, Surgeon on HMS Terror (1813), HMS ''Terror''. See also *Nameless Glacier Bays of Victoria Land Pennell Coast {{VictoriaLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |