|
Dudley Railway Station
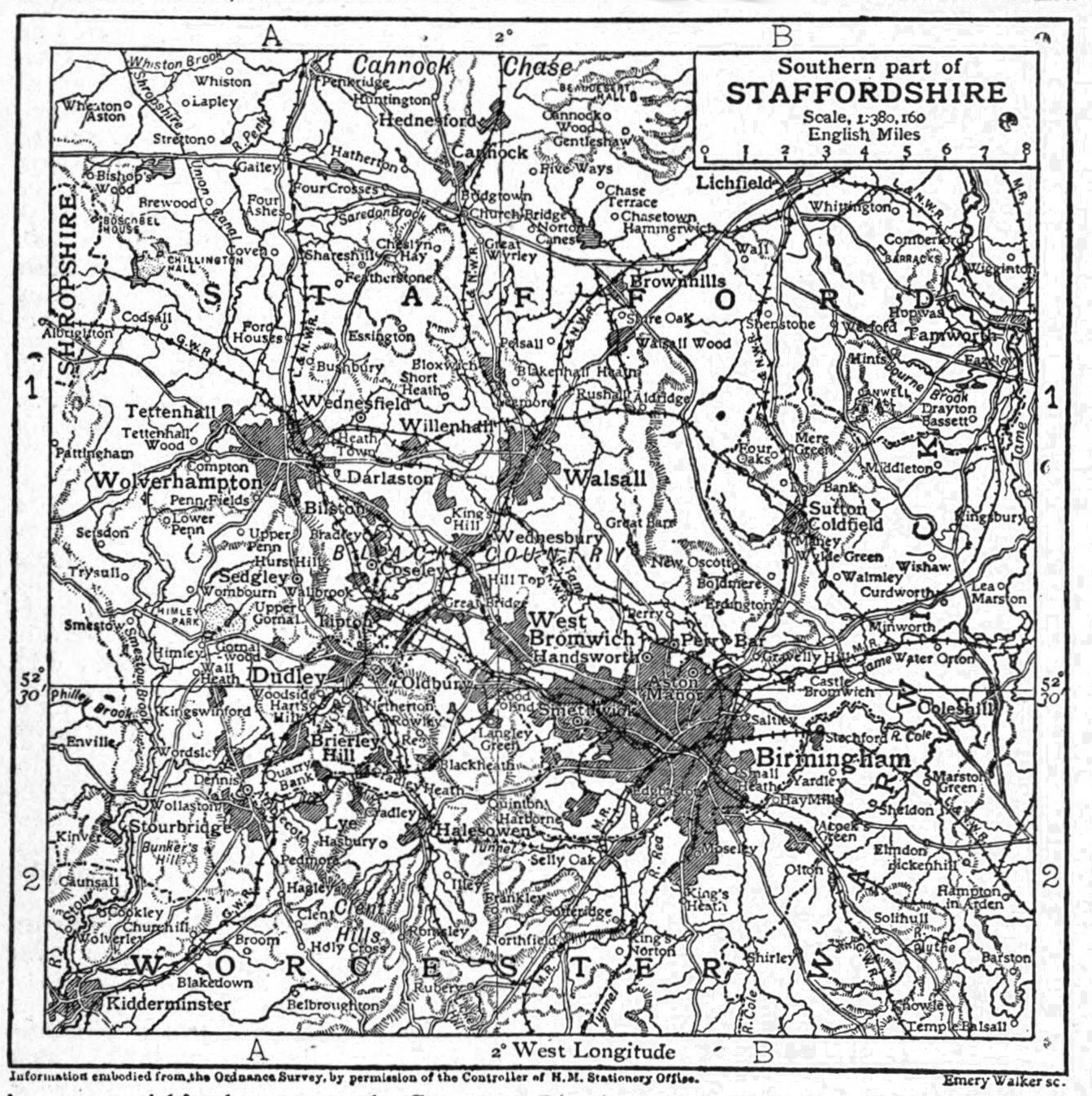
Dudley Railway Station was a railway station in Dudley, West Midlands, England, built where the Oxford-Worcester-Wolverhampton Line and the South Staffordshire Line diverged to Wolverhampton and Walsall and Lichfield respectively. History The station was built as a collaboration between the Oxford, Worcester and Wolverhampton Railway (which was soon to fall into the hands of the Great Western Railway, and the London and North Western Railway (which had taken control of the South Staffordshire Railway – the company that had constructed the line from Lichfield, via Walsall, to Dudley). The latter eventually became part of the London, Midland and Scottish Railway. The station was completed in 1860. A racecourse had been situated just north of the station until the mid-1840s when it was closed to make way for the railway, but its name was revived during the 1980s when Racecourse Colliery, a model colliery, was opened on the site as part of the Black Country Living Museum. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autotrain
The Autotrain was a type of passenger train used in the early 20th century, where the steam locomotive could be remotely controlled from the rear of the train. This meant that the engine would not have to run-around at the end of a journey before returning. These trains were also known as motor trains or railmotors at the time, but the term railmotor is now used to refer to trains where the steam engine was integrated into the coach. A driving cab in the rearmost coach (known as an autocoach or auto trailer) has controls to allow the driver to operate the regulator, brake and whistle when driving the train 'in reverse'. The fireman would remain on the engine in order to stoke the fire and to take off the brakes, as the driver could only apply them. Autotrains could operate with one or two coaches: either with the locomotive at the front or rear of the formation, or sandwiched between the two driving coaches. Autotrains were being used by most rail companies in Great Britain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Country
The Black Country is an area of the West Midlands county, England covering most of the Metropolitan Boroughs of Dudley, Sandwell and Walsall. Dudley and Tipton are generally considered to be the centre. It became industrialised during its role as one of the birth places of the Industrial Revolution across the English Midlands with coal mines, coking, iron foundries, glass factories, brickworks and steel mills, producing a high level of air pollution. The name dates from the 1840s, and is believed to come from the soot that the heavy industries covered the area in, although the 30-foot-thick coal seam close to the surface is another possible origin. The road between Wolverhampton and Birmingham was described as "one continuous town" in 1785. Extent The Black Country has no single set of defined boundaries. Some traditionalists define it as "the area where the coal seam comes to the surface – so West Bromwich, Coseley, Oldbury, Blackheath, Cradley Heath, Old Hill, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge tourist line). Passengers replaced freight as the main source of business, and one-third of the network was closed by the Beeching cuts of the 1960s in an effort to reduce rail subsidies. On privatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blowers Green Railway Station
Blowers Green railway station was a station on the Oxford-Worcester-Wolverhampton Line in Dudley, West Midlands, England. History It was opened in 1878 by the Great Western Railway intending to serve the growing communities of Woodside and Netherton. Soon after opening, it was renamed Dudley Southside & Netherton. It was opened immediately north of Netherton station which it replaced. Three railways/routes served the station - originally the Oxford, Worcester and Wolverhampton Railway and the South Staffordshire Railway, which later became the Great Western Railway and London, Midland and Scottish Railway (through amalgamation of the London and North Western Railway) respectively. There were also services from Dudley to Old Hill along this route as part of GWR's service. The junction to Old Hill diverged between here and Harts Hill. The line had reasonable passenger usage until about the early 1880s, when it began to slump at several stations, leading to the line becoming a lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merry Hill Shopping Centre
Merry Hill (formerly Westfield Merry Hill and The Merry Hill Shopping Centre) is a large shopping complex in Brierley Hill near Dudley, England. It was developed between 1985 and 1990, with several subsequent expansion and renovation projects. The centre is anchored by Marks & Spencer, Primark, Asda, Next and formerly Debenhams. The centre has over 200 shops, a retail park, cinema, food hall and ten-thousand parking spaces. Adjacent to the main shopping mall is a marina called The Waterfront accommodating a number of bars, restaurants, the studios of Black Country Radio, and the Headquarters and Control Room of West Midlands Ambulance Service. The Dudley No.1 Canal passes through The Waterfront and along the edge of the shopping centre before descending to Delph Locks. The centre's original developers and owners were Richardson Developments but it has had a number of other owners including Chelsfield, Mountleigh, Westfield Group and Intu Properties. Merry Hill is curren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dudley Port Railway Station
Dudley Port railway station serves the Dudley Port and Great Bridge areas of Tipton, West Midlands, England, Situated on the Stour Valley Line, the station is operated by West Midlands Railway. Upper Level station History The station opened in 1852. The line had passenger usage until about the early 1880s, when it began to slump at several stations, leading to the line becoming a largely freight only operation in 1887. It would remain open for goods traffic, which was considerable at this time, as the district had become highly industrialised in the then heyday of the Black Country's industrial past. As the local industry declined and road transport became more common, the station entered a post-World War II decline. Despite the name, and being located just north-east of the town centre of Dudley (which has not had its own railway station since 1964), Dudley Port station is not actually situated within the boundaries of the Borough of Dudley, but rather in the adjacent San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wednesbury Great Western Street Tram Stop
Wednesbury Great Western Street is a tram stop in Wednesbury, Sandwell, England. It was opened on 31 May 1999 and is situated on Midland Metro Line 1. The stop is next to the Midland Metro tram depot. The stop and depot are on the site of the old Wednesbury Central railway station, which closed in 1972, though the section of railway on which the tram stop currently stands remained open to goods trains until 1992. The stop is overlooked by a statue of Sleipnir, Odin's mythical eight-legged horse, by Steve Field, commissioned by Altram, the company that built the metro. Services Mondays to Fridays, Midland Metro services in each direction between Birmingham and Wolverhampton run at six to eight-minute intervals during the day, and at fifteen-minute intervals during the evenings and on Sundays. They run at eight minute intervals on Saturdays. South Staffordshire Line The South Staffordshire Line which is currently closed, is crossed over by the Midland Metro. Wednesbury Grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Midlands Metro
The West Midlands Metro (originally named Midland Metro) is a light-rail/tram system in the county of West Midlands, England. Opened on 30 May 1999, it currently consists of a single route, Line 1, which operates between the cities of Birmingham and Wolverhampton via the towns of Bilston, West Bromwich and Wednesbury, running on a mixture of reopened disused railway line (the Birmingham Snow Hill to Wolverhampton Low Level Line) and on-street running in urban areas. The line originally terminated at Birmingham Snow Hill station but, with extensions opened in 2015, 2019 and 2022, now runs via Birmingham city centre to terminate at Edgbaston. A further extension in Wolverhampton was scheduled to open in 2022, but has been pushed back to 2023. The system is owned by the public body Transport for West Midlands, and operated through Midland Metro Ltd, a company wholly owned by the West Midlands Combined Authority. An extension to Wolverhampton railway station is scheduled to op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dudley Freightliner Terminal
Dudley Freightliner Terminal was opened on the site of Dudley railway station in November 1967, as one of Freightliner's first rail terminals. It was an instant financial success and by 1981 was one of the most profitable Freightliner terminals in Britain, but Freightliner announced plans to close it and transfer the staff to the less successful Birmingham terminal. These plans were shelved in 1983 but resurfaced in 1986, with the terminal finally closing in September 1989. Trains continued to pass the site of the Freightliner terminal until the Wednesbury to Round Oak section of the South Staffordshire Line and Oxford, Worcester & Wolverhampton line closed in March 1993. History The station platform became the depot platform, but with no buildings save for the odd shed. A concrete strip was built over one of the Tipton Five Ways lines to act as a footing for a large gantry crane that had its other footing on the old platform. The old signal box was at the Blower's Green end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beeching Axe
The Beeching cuts (also Beeching Axe) was a plan to increase the efficiency of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain. The plan was outlined in two reports: ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the Major Railway Trunk Routes'' (1965), written by Richard Beeching and published by the British Railways Board. The first report identified 2,363 stations and of railway line for closure, amounting to 55% of stations, 30% of route miles, and 67,700 British Rail positions, with an objective of stemming the large losses being incurred during a period of increasing competition from road transport and reducing the rail subsidies necessary to keep the network running. The second report identified a small number of major routes for significant investment. The 1963 report also recommended some less well-publicised changes, including a switch to the now-standard practice of containerisation for rail freight, and the replacement of some services wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham Snow Hill Railway Station
Birmingham Snow Hill is a railway station in Birmingham City Centre, England. It is one of the three main city-centre stations in Birmingham, along with and . Snow Hill was once the main station of the Great Western Railway in Birmingham and, at its height, it rivalled New Street station with competitive services to destinations including , , , Wales and South West England. The station has been rebuilt several times since the first station at Snow Hill, a temporary wooden structure, was opened in 1852; it was rebuilt as a permanent station in 1871 and then rebuilt again on a much grander scale during 1906–1912. The electrification of the main line from London to New Street in the 1960s saw New Street favoured over Snow Hill, most of whose services were withdrawn in the late 1960s. This led to the station's eventual closure in 1972 and its demolition five years later. After fifteen years of closure, a new Snow Hill station, the present incarnation, was built; it reopened in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





.jpg)