|
Duboisia Santeng
''Duboisia santeng'' or Dubois' antelope is an extinct antelope-like bovid that was endemic to Indonesia during the Pleistocene. It went extinct during the Ionian stage of the Pleistocene, about 750.000 years ago. ''Duboisia santeng'' was first described by the Dutch paleoanthropologist and geologist Eugène Dubois in 1891.Christine Hertler/ Yan Rizal (2005): Excursion guide to the Pleistocene Hominid sites in Central and East Java, JW Goethe University, Frankfurt, Germany/ ITB, Bandung, Indonesia The species is most closely related to the modern Nilgai-antelope (''Boselaphus tragocamelus'') and the Four-horned antelope (''Tetracerus quadricornis''). ''Antilope modjokertensis'' is a junior synonym for ''Duboisia santeng''.Fossil Bovidae from the Malay archipelago and the Punjab by Dr. D. A. Hooijer, Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie, Leiden Description It was a small to middle-sized antelope, with body mass estimates ranging from 32 kg to 84 kg, with an average va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugène Dubois
Marie Eugène François Thomas Dubois (; 28 January 1858 – 16 December 1940) was a Dutch paleoanthropologist and geologist. He earned worldwide fame for his discovery of ''Pithecanthropus erectus'' (later redesignated ''Homo erectus''), or "Java Man". Although hominid fossils had been found and studied before, Dubois was the first anthropologist to embark upon a purposeful search for them. Life and work MEFT. Dubois was born and raised in the village of Eijsden, Limburg, where his father, Jean Joseph Balthazar Dubois, an immigrant from Thimister-Clermont, Liège, Belgium, was an apothecary, later the mayor. Interested in all phenomena of the world of nature, Eugène explored the "caves" ("''grotten''", actually underground limestone mines) of Mount Saint Peter and amassed collections of plant parts, stones, insects, shells, and animal skulls. From age 12-13 on, he attended school in the Limburg city of Roermond, boarding with a family there and then he dropped out. In Roermon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinil Fauna
The Trinil Fauna is a biostratigraphic faunal assemblage composed from several Javanese sites by Ralph von Koenigswald. Von Koenigswald assigned the early hominid fossils Java Man Java Man (''Homo erectus erectus'', formerly also ''Anthropopithecus erectus'', ''Pithecanthropus erectus'') is an early human fossil discovered in 1891 and 1892 on the island of Java (Dutch East Indies, now part of Indonesia). Estimated to be b ... to the Trinil Fauna after discovering the main fossil of Java Man, a skullcap catalogued as " Trinil 2", in the same geological horizon. References Works cited * See also * Trinil H. K. Fauna {{Prehistoric Asia 1891 archaeological discoveries East Java Prehistoric Indonesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Mammals Of Asia
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinil Dog
''Mececyon trinilensis'', the Trinil dog, is an extinct canid species that lived in Indonesia during the Pleistocene. Description The body size of ''Mececyon trinilensis'' been estimated to be about 22 kg. This size is the result of insular dwarfism. Habitat and ecology ''Mececyon trinilensis'' is endemic to the island of Java. It was part of the Pleistocene Trinil Fauna The Trinil Fauna is a biostratigraphic faunal assemblage composed from several Javanese sites by Ralph von Koenigswald. Von Koenigswald assigned the early hominid fossils Java Man Java Man (''Homo erectus erectus'', formerly also ''Anthropopit ... of Java. Other animals of this Faunal assemblage were '' Bos palaesondaicus'', the Indian muntjac, Indian muntjak (''Muntiacus muntjak''), ''Bubalus palaeokerabau'', the Dubois santeng and ''Stegodon trigonocephalus''. Other predators of the Trinil Fauna were the Trinil tiger (''Panthera tigris trinilensis'') and the leopard cat (''Prionailurus bengalens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinil Tiger
''Panthera tigris trinilensis'', known as the Trinil tiger, is an extinct tiger subspecies dating from about 1.2 million years ago that was found at the locality of Trinil, Java, Indonesia. The fossil remains are now stored in the Dubois Collection of the National Museum of Natural History in Leiden, the Netherlands. Although these fossils have been found on Java, the Trinil tiger is probably not a direct ancestor of the Javan tiger. The Trinil tiger probably became extinct 50,000 years ago. The Bali tiger was also not closely related to the Trinil because of their time differences. It lived in Indonesia, particularly in Java and Trinil, and according to some zoologists, it could be the ancestor of all known Indonesian subspecies. Perhaps, East Asia was a center of the origin of Pantherinae. The oldest tiger fossils found in Early Pleistocene Java show that about two million years ago, tigers were already quite common in East Asia. However, the glacial and interglacial climatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
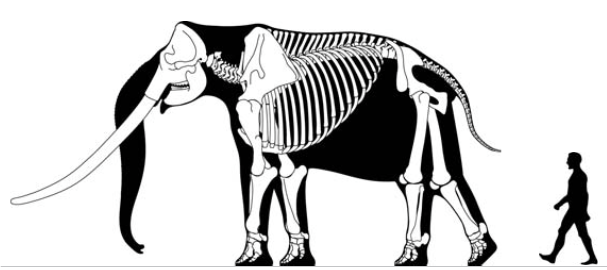
Stegodon
''Stegodon'' ("roofed tooth" from the Ancient Greek words , , 'to cover', + , , 'tooth' because of the distinctive ridges on the animal's molars) is an extinct genus of proboscidean, related to elephants. It was originally assigned to the family Elephantidae along with modern elephants but is now placed in the extinct family Stegodontidae. Like elephants, ''Stegodon'' had teeth with plate-like lophs that are different from those of more primitive proboscideans like gomphotheres and mastodons. The oldest fossils of the genus are found in Late Miocene strata in Asia, likely originating from the more archaic ''Stegolophodon,'' shortly afterwards migrating into Africa. While the genus became extinct in Africa during the Pliocene, ''Stegodon'' remained widespread in Asia until the end of the Pleistocene. Morphology Size Some species of ''Stegodon'' were amongst the largest proboscideans. ''S. zdanskyi'' is known from an old male (50-plus years old) from the Yellow River that is tall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubalus Palaeokerabau
''Bubalus palaeokerabau'' is an extinct species of water buffalo that was endemic to Java Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mos ... during the Late Pleistocene. ''B. palaeokerabau'' can be distinguished from more recent domestic water buffalo introduced to Java by their larger size and their extremely long horns, which can be around long from tip to tip. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q108083546 Prehistoric bovids Pleistocene even-toed ungulates Pleistocene mammals of Asia Pleistocene extinctions Extinct animals of Indonesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Muntjac
The Indian muntjac or the common muntjac (''Muntiacus muntjak''), also called the southern red muntjac and barking deer, is a deer species native to South and Southeast Asia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List. In popular local language, it is known as ''Kaakad'' or ''Kakad'' (काकड़) This muntjac has soft, short, brownish or grayish hair, sometimes with creamy markings. It is among the smallest deer species. It is an omnivore and eats grass, fruit, shoots, seeds, bird eggs, and small animals, and occasionally scavenges on carrion. Its calls sound like barking, often when frightened by a predator, hence the common name "barking deer". Males have canines, short antlers that usually branch just once near the base, and a large postorbital scent gland used to mark territories. Name The species was formerly classified as '. Characteristics The Indian muntjac has a short but very soft, thick, dense coat that is more dense in cooler regions. Its face is dar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bos Palaesondaicus
''Bos palaesondaicus'' occurred on Pleistocene Java (Indonesia) and belongs to the Bovinae subfamily. It has been described by the Dutch paleoanthropologist Eugène Dubois in 1908.Dubois, E. (1908). Das Geologische Alter der Kendengoder TrinilFauna. Tijdschr. Kon. Ned. Aardr. Gen., ser. 2, vol. 25, pp. 12351270, pl. 39. The holotype of ''Bos palaesondaicus'' is a skull from Trinil. This species In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ... is the likely ancestor to the banteng (''Bos javanicus'').Hooijer, D.A. (1958a). Fossil Bovidae from the Malay archipelago and the Punjab, Zoologische Verhandelingen van de Museum Leiden 38:1–112.Hooijer, D. A. (1958b). Sexual differences in the skull of fossil and recent banteng. Mammalia 22:73-75. References Bovines Extinct a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junior Synonym
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anoa
Anoa, also known as dwarf buffalo and ''sapiutan'', are two species of the genus '' Bubalus'' endemic to the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia: the mountain anoa (''Bubalus quarlesi'') and the lowland anoa (''Bubalus depressicornis''). Both live in undisturbed rainforest and are similar in appearance to miniature water buffaloes, weighing . Both species of anoa have been classified as endangered since the 1960s and the populations continue to decrease. Fewer than 5,000 animals of each species likely remain. Reasons for their decline include hunting for hides, horns and meat by the local peoples and loss of habitat due to the advancement of settlement. Currently, hunting is the more serious factor in most areas. Anoa are most closely allied to the larger Asian buffaloes, showing the same reversal of the direction of the hair on their backs. The horns are peculiar for their upright direction and comparative straightness, although they have the same triangular section as in ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
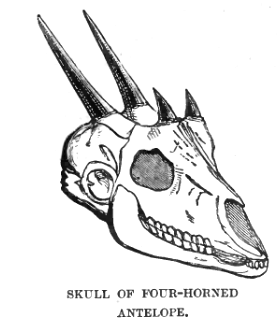
Four-horned Antelope
The four-horned antelope (''Tetracerus quadricornis''), or ''chousingha'', is a small antelope found in India and Nepal. Its four horns distinguish it from most other bovids, which have two horns (with a few exceptions, such as the Jacob sheep). The sole member of the genus ''Tetracerus'', the species was first described by French zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1816. Three subspecies are recognised. The four-horned antelope stands nearly at the shoulder and weighs nearly . Slender with thin legs and a short tail, the four-horned antelope has a yellowish brown to reddish coat. One pair of horns is located between the ears, and the other on the forehead. The posterior horns are always longer than the anterior horns, which might be mere fur-covered studs. While the posterior horns measure , the anterior ones are long. The four-horned antelope is diurnal (active mainly during the day). Though solitary by nature, four-horned antelopes may form loose groups of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |