|
Dragamesto
Astakos ( el, Αστακός, meaning "lobster") is a town and a former municipality in Aetolia-Acarnania, West Greece, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Xiromero, of which it is a municipal unit.Kallikratis law Greece Ministry of Interior The municipal unit has an area of 345.099 km2. It is located on a bay on the eastern shore of the , near the southern end of the . It takes its name from the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Greece
Western Greece Region ( el, Περιφέρεια Δυτικής Ελλάδας, translit=Periféria Dhitikís Elládhas, ) is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It comprises the western part of continental Greece and the northwestern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. It occupies an area of and its population is, according to the 2011 census, at 679,796 inhabitants. The capital of the Western Greece is Patras, the third-largest-city in the country with a population of about 280,000 inhabitants. The NUTS 2 code for the region of Western Greece is EL63. Administration The region of Western Greece was established in the 1987 administrative reform. With the 2010 Kallikratis plan, its powers and authority were redefined and extended. Along with Peloponnese and the Ionian Islands regions, it is supervised by the Decentralized Administration of Peloponnese, Western Greece and the Ionian Islands based at Patras. The region is based at Patras and is divided int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bampini
Bampini ( el, Μπαμπίνη) is a village located in the northern part of the municipal unit of Astakos in the western part of Aetolia-Acarnania, Greece. It is located on a hillside, 5 km southeast of Fyteies, 15 km northeast of Astakos, 23 km south of Amfilochia and 23 km west of Agrinio. Agriculture is the most important land use around Bampini. Historical population See also *List of settlements in Aetolia-Acarnania This is a list of settlements in Aetolia-Acarnania, Greece. * Achladokastro * Achyra * Aetopetra * Aetos * Afrato * Afroxylia * Agalianos * Agia Paraskevi * Agia Sofia * Agia Varvara * Agios Andreas * Agios Dimitrios * Agios Georgios * ... References External links *https://web.archive.org/web/20050328103757/http://www.akarnania.net/mpampini/greek/odip.htm (in Greek) {{Xiromero div Populated places in Aetolia-Acarnania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Ancient Acarnania
Acarnania is a region of western Greece. Below is a list of the cities that existed in Acarnania in ancient times.An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005. Cities *Alyzeia founded by CorinthiansAn Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen,2005,page 354 polis *Ambracia founded by Corinthians 650 BC polis * AmbrakosAn Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen,2005,page 352 pre Hellenistic fortress *Amphilochia *Anaktorion founded by Corinthians and Corcyrans 650 BC polis * Ancient Paleros or Palairos polis *Amphilochian Argos founded by Ambrakians polis *Astakos founded by CorinthiansAn Inventory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Settlements In Aetolia-Acarnania
This is a list of settlements in Aetolia-Acarnania, Greece. * Achladokastro * Achyra * Aetopetra * Aetos * Afrato * Afroxylia * Agalianos * Agia Paraskevi * Agia Sofia * Agia Varvara * Agios Andreas * Agios Dimitrios * Agios Georgios * Agios Ilias * Agios Konstantinos * Agios Nikolaos Trichonidos * Agios Nikolaos * Agios Thomas * Agios Vlasios * Agrampela * Agridi * Agrinio * Aitoliko * Akres * Alevrada * Amfilochia * Amorgianoi * Ampelaki * Ampelakiotissa * Ampelia * Amvrakia * Analipsi * Anavryti * Angelokastro * Ano Chora * Ano Kerasovo * Ano Koudouni * Ano Vasiliki * Anoixiatiko * Anthofyto * Antirrio * Arachova * Archontochori * Argyro Pigadi * Aspria * Astakos * Avarikos * Bampalio * Bampini * Chaliki Amvrakias * Chalkiopoulo * Chomori * Chouni * Chrysovergi * Chrysovitsa * Chrysovitsa * Dafni * Dafnias * Dendrochori * Diasellaki * Diplatanos * Dokimi * Dorvitsa * Drymonas * Drymos * Elaiofyto * Elatou * Elatovrysi * Elefthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dienekes
Dienekes or Dieneces ( el, Διηνέκης, from διηνεκής, Doric Greek: διανεκής "continuous, unbroken") was a Spartan soldier who fought and died at the Battle of Thermopylae in 480 BC. He was acclaimed the bravest of all the Greeks who fought in that battle. Herodotus (7.226) related the following anecdote about Dienekes: Herodotus also mentions that Dienekes said many other similar things which made him unforgotten. Plutarch in his " Sayings of the Spartans" also mentions this comment, but he attributes it to Leonidas I, Dienekes' general in the battle. According to Plutarch, when one of the soldiers complained to Leonidas that "Because of the arrows of the barbarians it is impossible to see the sun," Leonidas replied, "Won't it be nice, then, if we shall have shade in which to fight them?" The laconic phrase "then we will fight in the shade" was cited by Latin writers such as Cicero (''in umbra igitur pugnabimus'' ) and Valerius Maximus (''in umbra enim pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spartiate
A Spartiate (cf. its plural Spartiatae 'Spartans') �spärshēˈātē(z)or Spartiate �spärshēˌāt(from respectively the Latin and French forms corresponding to Classical- el, and pl. Σπᾰρτῐᾱ́ται) or ''Homoios'' (pl. ''Homoioi'' from respectively Classical- el, and Ὅμοιοι "those who are alike") was an elite full-citizen male of Sparta. Full citizen Spartiates were barred by law from work, and were supported by the other social classes of Spartan society. From a young age, male Spartiates were trained for battle and put through grueling challenges intended to craft them into fearless warriors. In battle, they had the reputation of being the best soldiers in Greece, and the strength of Sparta's hoplite forces let the city become the dominant state in Greece throughout much of the Classical period. Other city-states were reluctant to attack Sparta, even though it could muster a force of only about 8000 Spartiates during the zenith of its dominance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squire
In the Middle Ages, a squire was the shield- or armour-bearer of a knight. Use of the term evolved over time. Initially, a squire served as a knight's apprentice. Later, a village leader or a lord of the manor might come to be known as a "squire", and still later, the term was applied to members of the landed gentry. In contemporary American usage, "squire" is the title given to justices of the peace or similar local dignitaries. ''Squire'' is a shortened version of the word ''esquire'', from the Old French (modern French ), itself derived from the Late Latin ("shield bearer"), in medieval or Old English a ''scutifer''. The Classical Latin equivalent was ("arms bearer"). Knights in training The most common definition of ''squire'' refers to the Middle Ages. A squire was typically a young boy, training to become a knight. A boy became a page at the age of 7 then a squire at age 14. Squires were the second step to becoming a knight, after having served as a page. Boys s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ; grc, Μάχη τῶν Θερμοπυλῶν, label=Greek, ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lasting over the course of three days, it was one of the most prominent battles of both the second Persian invasion of Greece and the wider Greco-Persian Wars. The engagement at Thermopylae occurred simultaneously with the Battle of Artemisium: between July and September 480 BC. The second Persian invasion under Xerxes I was a delayed response to the failure of the first Persian invasion, which had been initiated by Darius I and ended in 490 BC by an Athenian-led Greek victory at the Battle of Marathon. By 480 BC, a decade after the Persian defeat at Marathon, Xerxes had amassed a massive land and naval force, and subsequently set out to conquer all of Greece. In response, the Athenian politician and general Themistocles proposed that the allie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
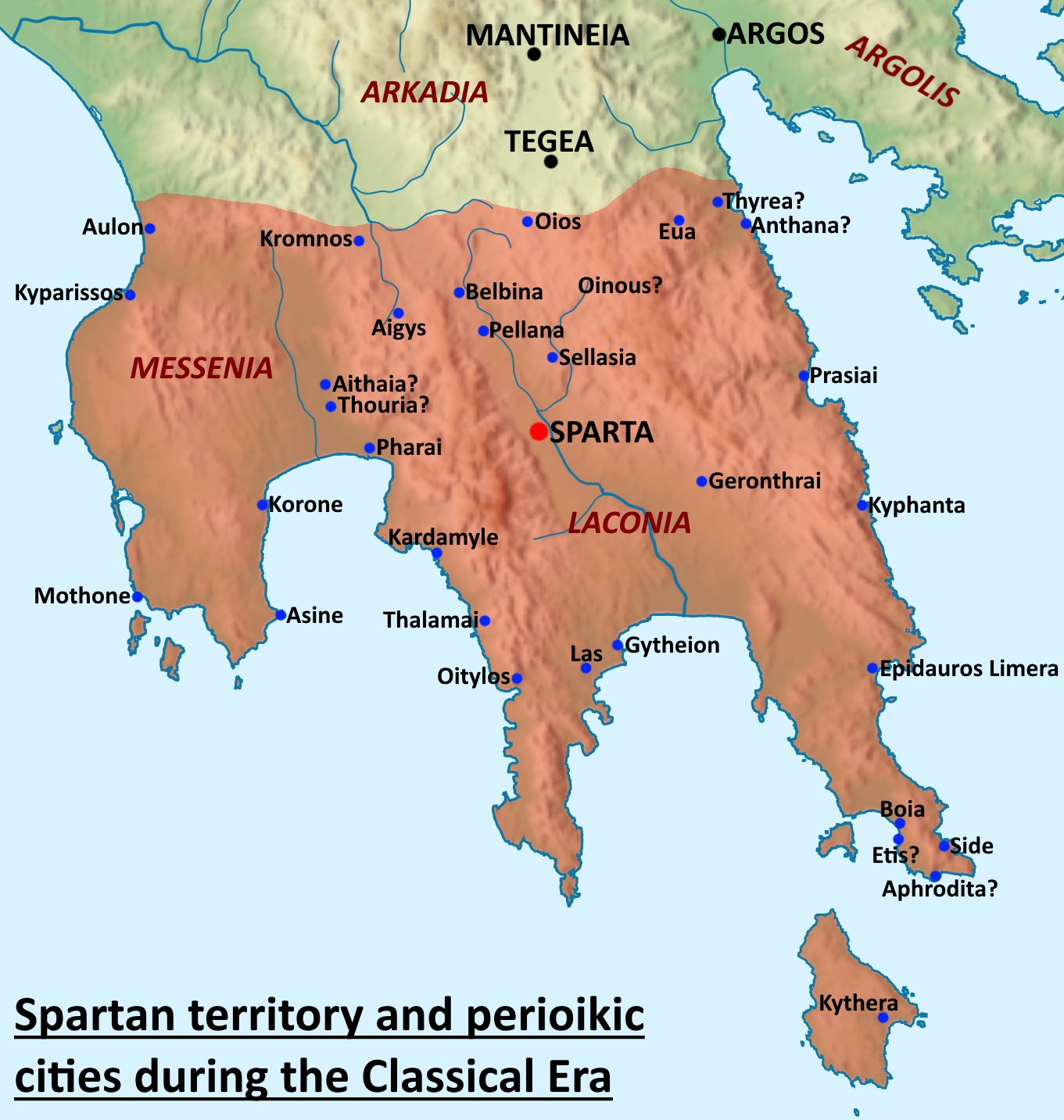
Perioikoi
The Perioeci or Perioikoi (, ) were the second-tier citizens of the ''polis'' of Sparta until 200 BC. They lived in several dozen cities within Spartan territories (mostly Laconia and Messenia), which were dependent on Sparta. The ''perioeci'' only had political rights in their own city, while the course of the Spartan state exclusively belonged to Spartan citizens, or Spartiates. The name ''perioeci'' roughly means "those dwelling around/nearby", deriving from , ''peri'', "around", and , ''oîkos'', "dwelling, house". ''Perioeci'' and Spartans were collectively called the ''Lakedaimonians''. They had a central role in the Spartan economy, controlling commerce and business, as well as being responsible for crafts and manufacturing, including producing the weapons and armour of the Spartan army, as the higher-ranking Spartan citizens considered all commercial and money-making activities to be unworthy of them. The ''perioeci'' were also the only people allowed to freely travel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argos, Peloponnese
Argos (; el, Άργος ; grc, label=Ancient Greek, Ancient and Katharevousa, Ἄργος ) is a city in Argolis, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, Greece and is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, and the oldest in Europe. It is the largest city in Argolis and a major center for the area. Since the 2011 local government reform it has been part of the municipality of Argos-Mykines, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 138.138 km2. It is from Nafplion, which was its historic harbour. A settlement of great antiquity, Argos has been continuously inhabited as at least a substantial village for the past 7,000 years. A resident of the city of Argos is known as an Argive ( , ; grc-gre, Ἀργεῖος). However, this term is also used to refer to those ancient Greeks generally who assaulted the city of Troy during the Trojan War; the term is more widely applied by the Home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gates Of Fire
''Gates of Fire'' is a 1998 historical fiction novel by Steven Pressfield that recounts the Battle of Thermopylae through Xeones, a perioikos (free but non-citizen inhabitant of Sparta) born in Astakos, and one of only three Greek survivors of the battle. ''Gates of Fire'' was on the Commandant of the Marine Corps' Reading list. It is taught at West Point, the United States Naval Academy, and at the Marine Corps The Basic School. The novel stresses the literary themes of fate and irony as well as the military themes of honor, duty, stoicism, and '' esprit de corps''. Plot summary The novel is narrated by Xeones, a perioikos and one of only three Greek survivors of the Battle of Thermopylae. His story is dictated to King Xerxes and transcribed by his court historian, Gobartes. At Thermopylae, the allied Greek nations deployed a small force of four thousand Greek heavy infantry against the invading Persian army of two million strong. Leading the Greeks was a small force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steven Pressfield
Steven Pressfield (born September 1, 1943) is an American author of historical fiction, non-fiction, and screenplays, including his 1995 novel ''The Legend of Bagger Vance'' and 2002 non-fiction book '' The War of Art''. Early life Pressfield was born in Port of Spain, Trinidad, in 1943, while his father was stationed there, in the Navy. Education Pressfield graduated from Duke University in 1965. In 1966, he joined the Marine Corps. Career Pressfield was an advertising copywriter, schoolteacher, tractor-trailer driver, bartender, oilfield roustabout, attendant in a mental hospital, fruit-picker in Washington state, and screenwriter. His struggles to make a living as an author, including the period when he was homeless and living out of the back of his car, are detailed in his 2002 book '' The War of Art''. Pressfield's first book, ''The Legend of Bagger Vance'', which was loosely based on the Bhagavad Gita, was published in 1995, and was made into a 2000 film of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |