|
Dortmund Stadthaus Station
Dortmund Stadthaus station is an important railway station of the inner city of Dortmund in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is located in the inner city at the junction of Ruhrallee (Bundesstraße 54, B54) and Märkischen Straße, near the Stadthaus, a municipal office building. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a German railway station categories, category 5 station. The above-ground section of the station is served by Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn line S4 (Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn), S 4 and the underground section is served by lines U41, U45, U47 and U49 of the Dortmund Stadtbahn. Significance Line S4 runs in the east–west direction from Unna to Dortmund-Luetgendortmund on above ground tracks through the station. The platforms are accessible by stairs and lifts. The underground section is served by lines U41, U45, U47 and U49, which run in a north–south direction. In addition, bus route 444 operated by the municipal bus company, Dortmunder Stadtwerke (''DSW21''), stops i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dortmund
Dortmund (; Westphalian nds, Düörpm ; la, Tremonia) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the eighth-largest city of Germany, with a population of 588,250 inhabitants as of 2021. It is the largest city (by area and population) of the Ruhr, Germany's largest urban area with some 5.1 million inhabitants, as well as the largest city of Westphalia. On the Emscher and Ruhr rivers (tributaries of the Rhine), it lies in the Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Region and is considered the administrative, commercial, and cultural center of the eastern Ruhr. Dortmund is the second-largest city in the Low German dialect area after Hamburg. Founded around 882,Wikimedia Commons: First documentary reference to Dortmund-Bövinghausen from 882, contribution-list of the Werden Abbey (near Essen), North-Rhine-Westphalia, Germany Dortmund became an Imperial Free City. Throughout the 13th to 14th centuries, it was the "chief city" of the Rhine, Westphali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
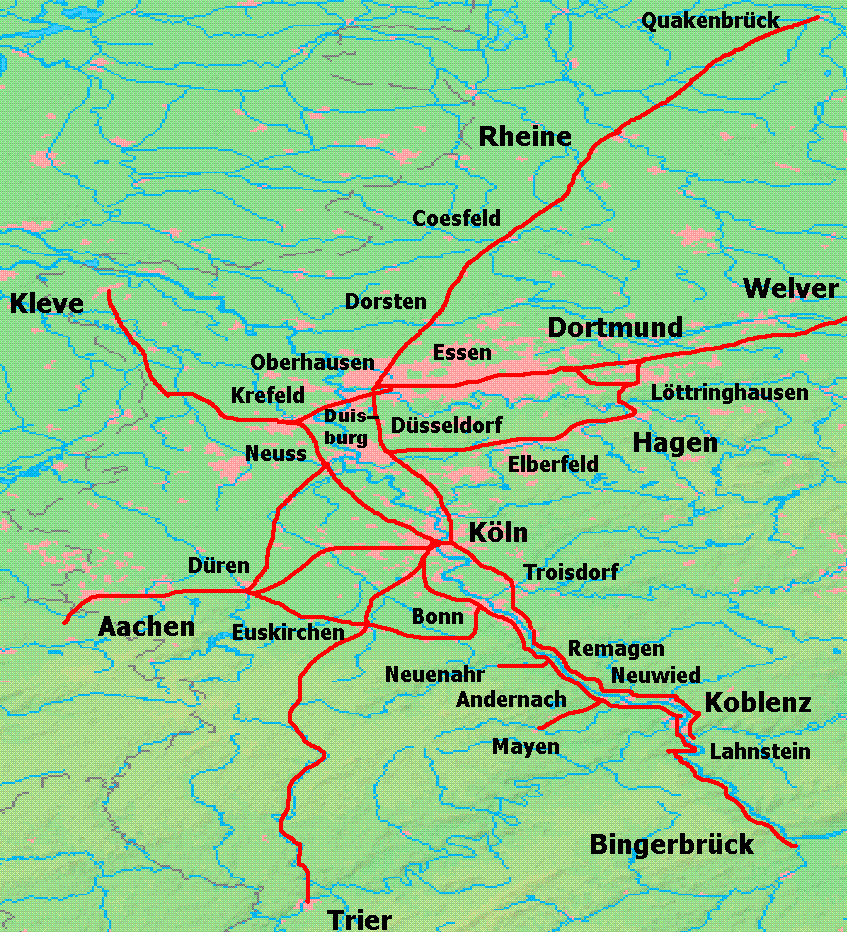
Rhenish Railway Company
The Rhenish Railway Company (German language, German: ''Rheinische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', RhE) was along with the Cologne-Minden Railway Company (CME) and the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company (BME) one of the railway companies that in the mid-19th century built the first railways in the Ruhr and large parts of today's North Rhine-Westphalia. Foundation The industrialists of the Rhineland and the Bergisches Land, then part of Prussia, sought to avoid paying the high tolls for using the Rhine imposed by the Netherlands and very early in its development, saw the possibility of the new means of transport, the railway. As early as the 1830s committees were established the cities of the Rhineland to promote proposals for building railways. Some of the members of the Cologne committee under David Hansemann (1790–1864)—a merchant and banker from Aachen—and the Aachen Committee favoured a railway line through Belgium to the seaport of Antwerp via Liege. Belgium, which had bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dortmund Möllerbrücke Station
Dortmund Möllerbrücke station is a transportation hub to the southwest of the inner city of Dortmund, near the Kreuzviertel (district) and West Park. A Dortmund Stadtbahn underground station is located next to the station. The station is named after the nearby Möller bridge (''Möllerbrücke'') and is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 5 station. The above ground section of the station is served by Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn line S 4 and the underground section is served by line U42 of the Dortmund Stadtbahn. It is located on the historic Ruhr line of the Rhenish Railway Company. History A block post was built on the site of today's S-Bahn station as early as 1910. There has been a tram stop at Dortmund Möllerbrücke since 1925. Trains have stopped since 26 May 1963. It was originally served by battery electric multiple units of class 515. It was served by Silberling carriages hauled by class 212 locomotives from 1980. Since 3 June 1984 x-Wagen (“x-cars”, a type of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dortmund-Lütgendortmund Station
Dortmund-Lütgendortmund station is a single-track, underground terminal station in the city of Dortmund in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The platform is accessible by stairs, escalator or lift. It was opened in 1993 at the end of an extension of Line S 4 trains of the Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn. Trains reverse here in order to return to Unna station. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 5 station. History The station was built as part of the extension of a fragment of the Rhenish Railway Company's Ruhr line, which opened in 1874. Line S 4 services commenced operation to the station on 23 May 1993. The nearest bus stop had been called ''Lütgendortmunder Markt'', but it was renamed ''Dortmund Lütgendortmund S-Bahn station''. Extension of the S 4 line from its current western end in the tunnel at Dortmund-Lütgendortmund was formerly planned to be implemented with a target of opening it in 2015. This would have included an extension of the single-track tunnel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DBAG Class 422 trains. The inner carriages are called Class 432. Following a timetable change in Dec ...
The Class 422 is a series of four-car electric multiple units that are a derivative of the DBAG Class 423. The two inner cars in the set are designated as Class 432 vehicles. History The units were commissioned by Deutsche Bahn in 2005. 78 units worth euro, €343 million were built by Bombardier Transportation and Alstom and delivered between March 2008 and October 2010. They are now used in such places as like on the Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn which operate in cities like Köln and Düsseldorf as well as the Ruhr area. Deutsche Bahn uses the units on the Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn network, unlike most S-Bahn Networks which use similar DBAG Class 423 The Deutsche Bahn Class 423 EMU is a light-weight articulated electric railcar for S-Bahn commuter networks in Germany. The train has similar dimensions to its predecessor, the Class 420 EMU, but is significantly lighter and has one large passe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DR Class 243
The DR Class 243 is a universal electric locomotive of the Deutsche Reichsbahn which is used for general rail service. Deutsche Bahn lists the locomotive as Class 143. The locomotives of class 143/243 still belong to the most successful class of German electric locomotives. Development Beginning in 1976, the Deutsche Reichsbahn of the GDR recommenced their railway electrification efforts in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis, which had also affected the Eastern Bloc countries. Prior to this, Deutsche Reichsbahn had mainly acquired Russian-built diesel locomotives, such as the class 120 and the DR Class 130 family, as the Soviet Union had been providing the GDR with inexpensive heavy oil and diesel fuel. '' VEB Lokomotivbau und Elektrotechnische Werke Hennigsdorf'', the only manufacturer of electric locomotives left in the GDR, was subsequently ordered to develop a modern lightweight, eight-wheel electric locomotive for both passenger and medium freight services, which was to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DB Class 111
The Baureihe 111 is a class of electric locomotives built for the Deutsche Bundesbahn, and now owned by Deutsche Bahn AG. History Class 111 is the successor of the Class 110 express '' Einheitslokomotive''. Since demand for fast electric locomotives was high even after production of the 110 ended, the Deutsche Bundesbahn (DB) decided to commission a new batch in the 1970s. The bogies were replaced with a different type, significantly improving the locomotive's behaviour at higher speeds. The driver's cab also was significantly improved by the ''DB-Einheitsführerstand'' (jointly developed by the ''Bundesbahn-Zentralamt München'' and Krauss-Maffei and designed under ergonomic aspects) that was first used for Class 111 locos and whose basic layout nowadays still forms part of the cab design found in many of DB's locomotives and control cars. For the first time, a digital cab car interface in addition to the then-standard conventional interface was used in new DB locomotives. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push–pull Train
Push–pull is a configuration for locomotive-hauled trains, allowing them to be driven from either end of the train, whether having a locomotive at each end or not. A push–pull train has a locomotive at one end of the train, connected via some form of remote control, such as multiple-unit train control, to a vehicle equipped with a control cab at the other end of the train. This second vehicle may be another locomotive, or an unpowered control car. In the UK and some other parts of Europe, the control car is referred to as a ''driving trailer'' (or driving van trailer/DVT where there is no passenger accommodation); in the US and Canada, they are called ''cab cars''. Train formation Locomotive at one end Historically, push–pull trains with steam power provided the driver with basic controls at the cab end along with a bell or other signalling code system to communicate with the fireman located in the engine itself in order to pass commands to adjust controls not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DB Class V 100
These DB Class V 100 diesel locomotives were produced in the late 1950s by the Deutsche Bundesbahn for non-electrified branch lines as a replacement for steam locomotives. The V 100 class was built in three different variants. Decommissioned locomotives were also used in Austria by the Austrian Federal Railways during the 1990s and early 2000s, where they were registered as ÖBB Class 2048 Class V 100.10 / Class 211 The Class V 100.10 was a diesel locomotive for light passenger and goods traffic on branch lines. It was developed in 1956 by the Bundesbahn Central Office in Munich together with the engineering works, Maschinenbau Kiel (MaK), for the Deutsche Bundesbahn. In the late autumn of 1958 the first six trials engines were delivered. Numbers V 100 001 to 005 were fitted with an 809 kW (1,100 HP) motor, but number V 100 006 was given a 993 kW (1,350 HP) motor. The latter formed the basis for the V 100.20, later DB Class 212. Number V 100 007 was built by MaK as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silberling
Silberling is the colloquial name for the n-coaches of the Deutsche Bundesbahn, a type of regional Passenger car (rail), passenger coach of which more than 5,000 units were built from 1958 to 1981. Nearly all of the coaches have undergone extensive modernisation – these modernised units are widely known as ''Mintling'', ''Grünling'' ("greenling") or ''Rotling'' ("redling") after their exterior colours. The term ''Buntling'' ("colourfulling") is used to denote refurbished Silberling coaches in general. Origin of the name The term ''Silberling'' derives from the coaches' stainless steel body which gave them a unique look during their term of service. Translated it means "silverling" in the English language. Historically, Silberling is a silver coin and widely known from the bible: the thirty pieces of silver (in the Bible translations into German, German Bible: "30 Silberlinge", Gospel of Matthew, Matthew 26,14) Judas Iscariot, Judas obtained for his treason. Technical data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DB Class ETA 150
The accumulator cars of Class ETA 150 (Class 515 from 1968) were German railbuses used extensively by Deutsche Bundesbahn (DB) for 40 years. The railcars were very comfortable to travel in because they were quiet (despite the typical Dc_motors#Noise, whine of their DC motors), rode well on the rails owing to the weight of the batteries, and were pollution-free (no smoke or fumes). They ran on both main and branch lines. They were very popular with passengers, who nicknamed them ''Akkublitz'' (''Battery Lightning''), ''Säurebomber'' (''Acid Bombers''), ''Steckdosen-Intercity (Deutsche Bahn), InterCity'' (''Socket InterCitys''), ''Taschenlampen-Express'' (''Pocket Torch Express''), or ''Biene Maja'' (''Maya the Bee'' – because of the sound they made when under way). History As a result of many years of favourable experience with this type of vehicle (the Prussian state railways had placed accumulator railcars in service as early as 1907 – these would later becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery Electric Multiple Unit
A battery electric multiple unit (BEMU), battery electric railcar or accumulator railcar is an electrically driven multiple unit or railcar whose energy is derived from rechargeable batteries driving the traction motors. Prime advantages of these vehicles is that they do not use fossil fuels such as coal or diesel fuel, emit no exhaust gases and do not require the railway to have expensive infrastructure like electric ground rails or overhead catenary. On the down side is the weight of the batteries, which raises the vehicle weight, and their range before recharging of between . Currently, battery electric units have a higher purchase price and running cost than petrol or diesel railcars. One or more charging stations are required along the routes they operate, unless operation is on a mixture of electrified and unelectrified track, with the batteries being charged from the electrified track. Battery technology has greatly improved over the past 20 years broadening the scope of u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |