|
Domsiah
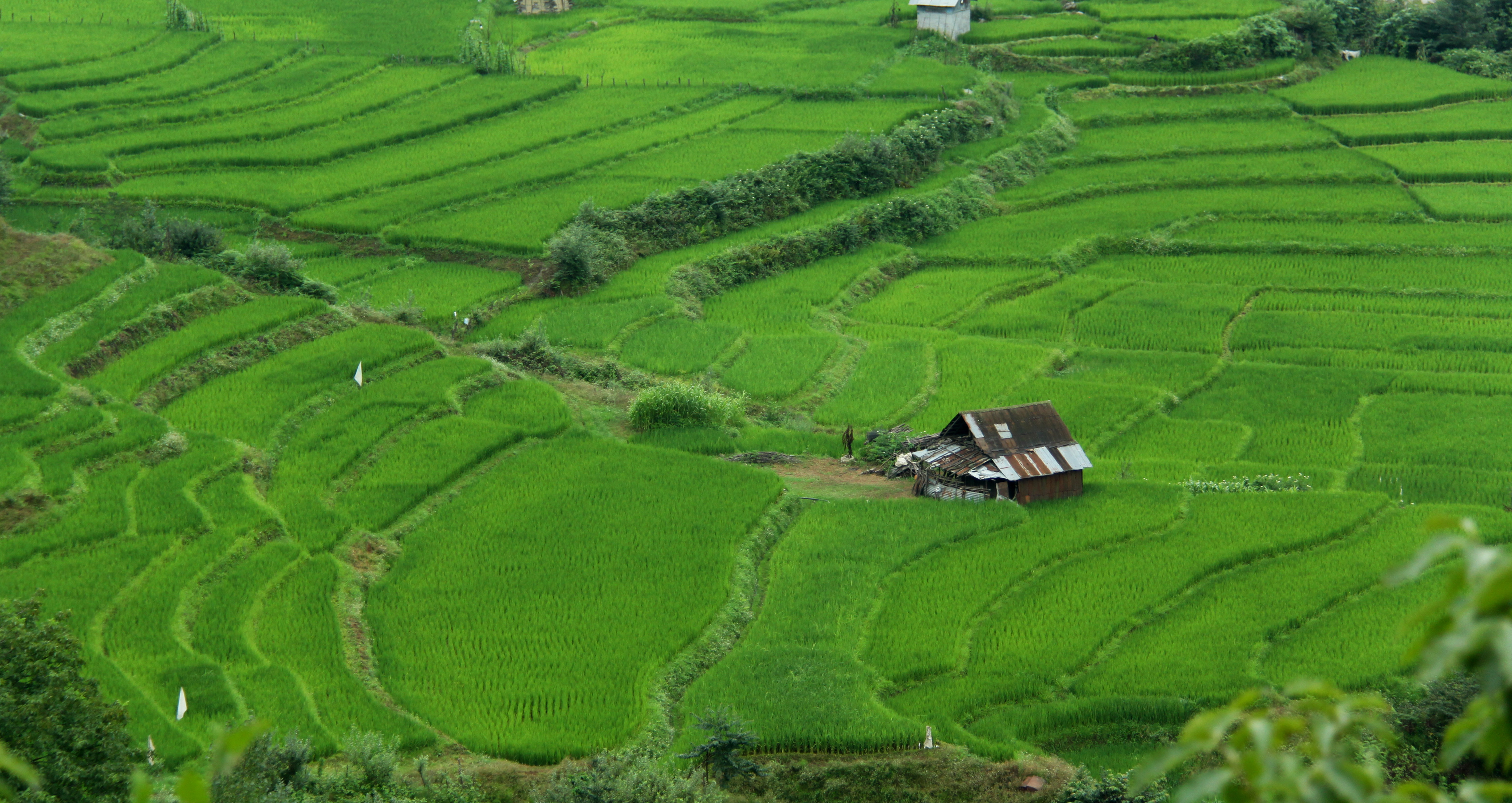
Domsiah ( fa, دم سیاه; also spelled domesiah) is an Iranian variety of rice. It is a long-grain rice, with a black spot on one end, which gives it the name, which is Persian meaning "black end". It is cultivated mainly in the Gilan province of Iran. Domsiah rice is related to basmati rice. Domsiah is especially valued for its aroma, which is more expressed than other basmati-type rices, and for its ability to end up as a fluffy, flaky and very light but tasty substance as basis for other ingredients of a meal. Research is trying to develop High Yielding Varieties (HYV) which could eventually replace Domsiah and help farmers obtain 5-7 tons per hectare; however, on the Iranian market quality goes before quantity so farmers can earn more money by cultivating Domsiah yielding only 2 - 2.5 tons per hectare. Researchers and scientists have not succeeded in bringing forth varieties which are resistant to fungi and stem borer and still have the aroma of Domsiah and the other rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basmati
Basmati, , is a variety of long, slender-grained aromatic rice which is traditionally grown in India, Pakistan, and Nepal.Big money in "specialty rices" Food and Agriculture Organization, United Nations (2002) , India accounted for 65% of the international trade in basmati rice, while Pakistan accounted for the remaining 35%. Many countries use domestically grown basmati rice crops; however, basmati is geographically exclusive to certain districts of India and Pakistan. According to the Indian Government agency APEDA, a rice variety is eligible to be called basmati if it has a minimum average precooked milled rice length of and average precooked milled rice breadth of up to , among other parameters. ...
|
Rice Varieties
This is a list of rice cultivars, also known as rice varieties. There are several species of grain called rice. Asian rice (''Oryza sativa)'' is most widely known and most widely grown, with two major subspecies (''indica'' and ''japonica'') and over 40,000 varieties. Also included in this list are varieties of African rice (''Oryza glaberrima'') and wild rice (genus ''Zizania''). Rice may vary in genetics, grain length, color, thickness, stickiness, aroma, growing method, and other characteristics, leading to many cultivars. For instance, over nine major rice cultivars exist to make sake alone. The two subspecies of Asian rice, indica and japonica, can generally be distinguished by length and stickiness. Indica rice is long-grained and unsticky, while japonica is short-grained and glutinous. Rice can also be divided based on processing type into the two broad categories of brown and white. Brown rice is whole grain, with only the inedible hull of the seed removed, while white r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Cuisine
Iranian cuisine () refers to the culinary practices of Iran. Due to the historically common usage of the term "Persia" to refer to Iran in the Western world,Yarshater, EhsaPersia or Iran, Persian or Farsi, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) it is alternatively known as Persian cuisine, despite Persians being only one of a multitude of Iranian ethnic groups who have contributed to Iran's culinary traditions. The cuisine of Iran has made extensive contact throughout its history with the cuisines of its neighbouring regions, including Caucasian cuisine, Central Asian cuisine, Greek cuisine, Levantine cuisine, Mesopotamian cuisine, Russian cuisine and Turkish cuisine. Aspects of Iranian cuisine have also been significantly adopted by Indian cuisine and Pakistani cuisine through various historical Persianate sultanates that flourished during Muslim rule on the Indian subcontinent, with the most notable and impactful of these polities being the Mughal Empire. Typical Iran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima ''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown in West Africa around 3,000 years ago. In agriculture, it has largely been replaced by higher-yielding Asian r ...'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera ''Zizania (genus), Zizania'' and ''Porteresia'', both wild and domesticated, although the term may also be used for primitive or uncultivated varieties of ''Oryza''. As a cereal, cereal grain, domesticated rice is the most widely consumed staple food for over half of the world's World population, human population,Abstract, "Rice feeds more than half the world's population." especially in Asia and Africa. It is the agricultural commodity with the third-highest worldwide production, after sugarcane and maize. Since sizable portions of sugarcane and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian (), also known by its endonym Farsi (, ', ), is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964) and Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate history in the cultural sphere of Greater Iran. It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in the Persian alphabet, a derivation of the Arabic script, and within Tajikistan in the Tajik alphabet, a der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmenistan to the north, by Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and by the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. It covers an area of , making it the 17th-largest country. Iran has a population of 86 million, making it the 17th-most populous country in the world, and the second-largest in the Middle East. Its largest cities, in descending order, are the capital Tehran, Mashhad, Isfahan, Karaj, Shiraz, and Tabriz. The country is home to one of the world's oldest civilizations, beginning with the formation of the Elamite kingdoms in the fourth millennium BC. It was first unified by the Medes, an ancient Iranian people, in the seventh century BC, and reached its territorial height in the sixth century BC, when Cyrus the Great fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
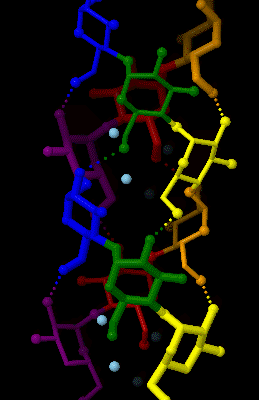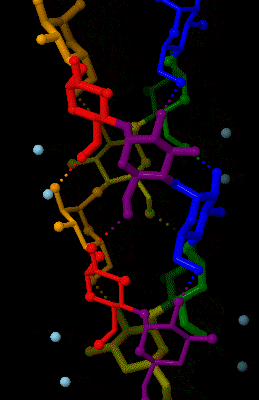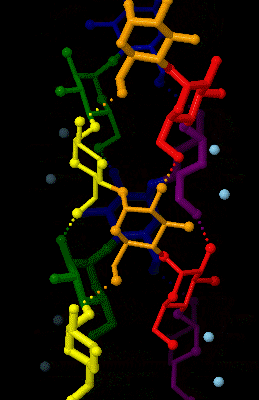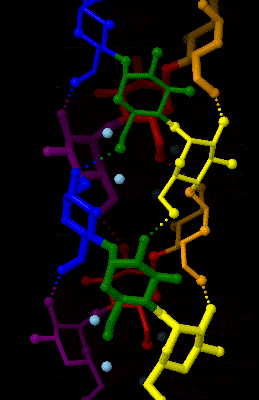
Amylose
Amylose is a polysaccharide made of α-D-glucose units, bonded to each other through α(1→4) glycosidic bonds. It is one of the two components of starch, making up approximately 20–30%. Because of its tightly packed helical structure, amylose is more resistant to digestion than other starch molecules and is therefore an important form of resistant starch. Structure Amylose is made up of α(1→4) bound glucose molecules. The carbon atoms on glucose are numbered, starting at the aldehyde (C=O) carbon, so, in amylose, the 1-carbon on one glucose molecule is linked to the 4-carbon on the next glucose molecule (α(1→4) bonds). The structural formula of amylose is pictured at right. The number of repeated glucose subunits (n) is usually in the range of 300 to 3000, but can be many thousands. There are three main forms of amylose chains can take. It can exist in a disordered amorphous conformation or two different helical forms. It can bind with itself in a double helix (A or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oryza Sativa
''Oryza sativa'', commonly known as Asian rice or indica rice, is the plant species most commonly referred to in English as ''rice''. It is the type of farmed rice whose cultivars are most common globally, and was first domesticated in the Yangtze River basin in China 13,500 to 8,200 years ago. ''Oryza sativa'' belongs to the genus '' Oryza'' of the grass family Poaceae. With a genome consisting of 430 Mbp across 12 chromosomes, it is renowned for being easy to genetically modify and is a model organism for the botany of cereals. Classification ''Oryza sativa'' contains two major subspecies: the sticky, short-grained ''japonica'' or ''sinica'' variety, and the nonsticky, long-grained ' rice variety. ''Japonica'' was domesticated in the Yangtze Valley 9–6,000 years ago, and its varieties can be cultivated in dry fields (it is cultivated mainly submerged in Japan), in temperate East Asia, upland areas of Southeast Asia, and high elevations in South Asia, while ''indica'' w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture In Iran
Roughly one-third of Iran's total surface area is suited for farmland, but because of poor soil and lack of adequate water distribution in many areas, most of it is not under cultivation. Only 12% of the total land area is under cultivation (arable land, orchards and vineyards) but less than one-third of the cultivated area is irrigated; the rest is devoted to dryland farming. Some 92 percent of agricultural products depend on water. The western and northwestern portions of the country have the most fertile soils. Iran's food security index stands at around 96 percent. 3% of the total land area is used for grazing and small fodder production. Most of the grazing is done on mostly semi-dry rangeland in mountain areas and on areas surrounding the large deserts ("Dasht's") of Central Iran. The non-agricultural surface represents 53% of the total area of Iran, as follows: * Abb. 39% of the country is covered by deserts, salt flats ("kavirs") and bare-rock mountains, not suited for agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)