|
Dolby Stereo
Dolby Stereo is a sound format made by Dolby Laboratories. It is a unified brand for two completely different basic systems: the Dolby SVA (stereo variable-area) 1976 system used with optical sound tracks on 35mm film, and Dolby Stereo 70mm noise reduction on 6-channel magnetic soundtracks on 70mm prints. Dolby SVA significantly improves the development of sound effects in films and theorization of sound design by Walter Murch. In 1982, it was adapted for home use as Dolby Surround when hi-fi capable consumer VCRs were introduced, and further improved in 1987 with the Dolby Pro Logic home decoding system. Dolby SVA Of the two, Dolby SVA is by far the more significant, bringing high-quality stereo sound within the reach of virtually every cinema. Though 6-track magnetic stereo had been used in Cinerama films since 1952, and Fox had introduced 4-track stereo magnetic sound as part of the CinemaScope system in 1953, the technology had proved to be expensive and unreliable. Exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolby Laboratories
Dolby Laboratories, Inc. (often shortened to Dolby Labs and known simply as Dolby) is an American company specializing in Noise reduction#In audio, audio noise reduction, Audio data compression, audio encoding/compression, spatial audio, and High-dynamic-range television, HDR imaging. Dolby licenses its technologies to consumer electronics manufacturers. History Dolby Labs was founded by Ray Dolby (1933–2013) in London, England, in 1965. In the same year, he invented the Dolby noise-reduction system, Dolby Noise Reduction system, a form of audio signal processing for reducing the background hissing sound on audio tape recordings. His first U.S. patent on the technology was filed in 1969, four years later. The method was first used by Decca Records in the UK. He moved the company headquarters to the United States (San Francisco, California) in 1976. The first product Dolby Labs produced was the Dolby 301 unit which incorporated Type A Dolby Noise Reduction, a compander-based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
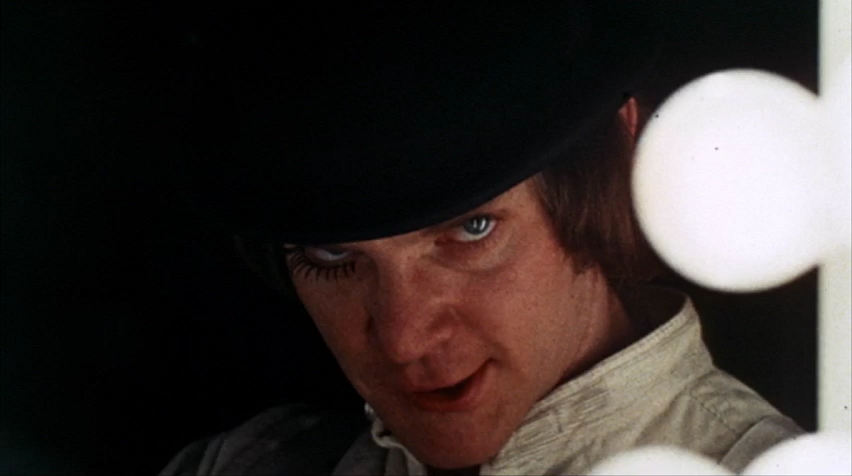
A Clockwork Orange (film)
''A Clockwork Orange'' is a 1971 dystopian crime film adapted, produced, and directed by Stanley Kubrick, based on Anthony Burgess's 1962 novel of the same name. It employs disturbing, violent images to comment on psychiatry, juvenile delinquency, youth gangs, and other social, political, and economic subjects in a dystopian near-future Britain. Alex (Malcolm McDowell), the central character, is a charismatic, antisocial delinquent whose interests include classical music (especially Beethoven), committing rape, theft, and ultra-violence. He leads a small gang of thugs, Pete (Michael Tarn), Georgie ( James Marcus), and Dim (Warren Clarke), whom he calls his ''droogs'' (from the Russian word друг, which is "friend", "buddy"). The film chronicles the horrific crime spree of his gang, his capture, and attempted rehabilitation via an experimental psychological conditioning technique (the "Ludovico Technique") promoted by the Minister of the Interior ( Anthony Sharp). Alex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CinemaScope
CinemaScope is an anamorphic lens series used, from 1953 to 1967, and less often later, for shooting widescreen films that, crucially, could be screened in theatres using existing equipment, albeit with a lens adapter. Its creation in 1953 by Spyros P. Skouras, the president of 20th Century Fox, marked the beginning of the modern anamorphic format in both principal 2.55:1, almost twice as wide as the previously common Academy format's 1.37:1 ratio. Although the technology behind the CinemaScope lens system was made obsolete by later developments, primarily advanced by Panavision, CinemaScope's anamorphic format has continued to this day. In film-industry jargon, the shortened form, 'Scope, is still widely used by both filmmakers and projectionists, although today it generally refers to any 2.35:1, 2.39:1, 2.40:1, or 2.55:1 presentation or, sometimes, the use of anamorphic lensing or projection in general. Bausch & Lomb won a 1954 Oscar for its development of the CinemaScope l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisztomania (film)
''Lisztomania'' is a 1975 British surreal biographical musical comedy film written and directed by Ken Russell about the 19th-century composer Franz Liszt. The screenplay is derived, in part, from the book ''Nélida'' by Marie d'Agoult (1848), about her affair with Liszt. Depicting the flamboyant Liszt as the first classical pop star, ''Lisztomania'' features contemporary rock star Roger Daltrey (of The Who) as Franz Liszt. The film was released the same year as ''Tommy'', which also starred Daltrey and was also directed by Russell. Rick Wakeman, from the progressive rock band Yes, composed the ''Lisztomania'' soundtrack, which included synthesiser arrangements of works by Liszt and Richard Wagner. He also appears in the film as Thor, the Nordic god of thunder. Daltrey and Russell wrote the lyrics for the soundtrack, and Daltrey provided vocals. Of the other rock celebrities appearing in the film, Ringo Starr appears as the Pope. The term Lisztomania was coined by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Russell
Henry Kenneth Alfred Russell (3 July 1927 – 27 November 2011) was a British film director, known for his pioneering work in television and film and for his flamboyant and controversial style. His films in the main were liberal adaptations of existing texts, or biographies, notably of composers of the Romantic music, Romantic era. Russell began directing for the BBC, where he made creative adaptations of composers' lives which were unusual for the time. He also directed many feature films independently and for Film studio, studios. Russell is best known for his Academy Awards, Oscar-winning film ''Women in Love (film), Women in Love'' (1969), ''The Devils (film), The Devils'' (1971), The Who's ''Tommy (1975 film), Tommy'' (1975), and the science fiction film ''Altered States'' (1980). Russell also directed several films based on the lives of classical music composers, such as Elgar (film), Elgar, Song of Summer, Delius, The Music Lovers, Tchaikovsky, Mahler (film), Mahler, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QS Regular Matrix
Quadraphonic Sound (originally called Quadphonic Synthesizer, and later referred to as RM or Regular Matrix) was a matrix 4-channel quadraphonic sound system for phonograph records. The system was based on technology created by Peter Scheiber, but further developed by engineer Ryosuke Ito of Sansui in the early 1970s. The technology was freely licensed and was adopted by many record labels including ABC, Advent, BluesWay, Candide, Command, Decca, Impulse, Longines, MCA, Passport, Pye, Turnabout and Vox. Hundreds of recordings using this format were released on vinyl LP records during the 1970s. RM (''Regular Matrix'') was often used a synonym for QS, but was actually a standard set by the Japanese governing body, which also embraced the QM (''Quadraphonic Matrix'', consisting of Stereo-4 and Dynaquad) and QX (''QuadXtra'', based on D.H. Cooper "Dual-Triphonic") matrix systems. The QS matrix has been found to offer the advantages of excellent diagonal separation and stereo c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sansui Electric
was a Japanese manufacturer of audio and video equipment. Headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, it was part of the Bermuda conglomerate (from 2011). The company was founded in Tokyo in 1947 by Kosaku Kikuchi, who had worked for a radio parts distributor in Tokyo before and during World War II. Due to the poor quality of radio parts Kikuchi had to deal with, he decided to start his private radio part manufacturer facility in December 1944 in Yoyogi, Tokyo. He picked transformers as his initial product line. Kikuchi's thought was "Even with higher prices, let's make the higher quality of products."tube-amps.net 2015-01-02, Sansui in Early Days retrieved 2020-04-23. In 1954 manufacturing Pre-Amp, Main-Amp kits, as well as finished amplifiers which used tubes, was started; in 1958 Sansui introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadraphonic
Quadraphonic (or quadrophonic and sometimes quadrasonic) sound – equivalent to what is now called 4.0 surround sound – uses four audio channels in which speakers are positioned at the four corners of a listening space. The system allows for the reproduction of sound signals that are (wholly or in part) independent of one another. Four channel quadraphonic surround sound can be used to recreate the highly realistic effect of a three-dimensional live concert hall experience in the home. It can also be used to enhance the listener experience beyond the directional limitations of ordinary two channel stereo sound. Quadraphonic audio was the earliest consumer product in surround sound. Since it was introduced to the public in the early 1970s many thousands of quadraphonic recordings have been made. Quadraphonic sound was a commercial failure when first introduced due to a variety of technical issues and format incompatibilities. Four channel audio formats can be more expensive to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RCA Photophone
RCA Photophone was the trade name given to one of four major competing technologies that emerged in the American film industry in the late 1920s for synchronizing electrically recorded audio to a motion picture image. RCA Photophone was an optical sound, "variable-area" film exposure system, in which the modulated area (width) corresponded to the waveform of the audio signal. The three other major technologies were the Warner Bros. Vitaphone sound-on-disc system, as well as two "variable-density" sound-on-film systems, Lee De Forest's Phonofilm, and Fox- Case's Movietone. When Joseph P. Kennedy and other investors merged Film Booking Offices of America (FBO) with the Keith-Albee-Orpheum theater chain and Radio Corporation of America, the resulting movie studio RKO Radio Pictures used RCA Photophone as their primary sound system. In March 1929, RKO released ''Syncopation'', the first film made in RCA Photophone. History and licensing In the early years following World War I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastman Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company (referred to simply as Kodak ) is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in analogue photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorporated in New Jersey. Kodak provides packaging, functional printing, graphic communications, and professional services for businesses around the world. Its main business segments are Print Systems, Enterprise Inkjet Systems, Micro 3D Printing and Packaging, Software and Solutions, and Consumer and Film. It is best known for photographic film products. Kodak was founded by George Eastman and Henry A. Strong on May 23, 1892. During most of the 20th century, Kodak held a dominant position in photographic film. The company's ubiquity was such that its " Kodak moment" tagline entered the common lexicon to describe a personal event that deserved to be recorded for posterity. Kodak began to struggle financially in the late 1990s, as a result of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMPTE
The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) (, rarely ), founded in 1916 as the Society of Motion Picture Engineers or SMPE, is a global professional association of engineers, technologists, and executives working in the media and entertainment industry. As an internationally recognized standards organization, SMPTE has published more than 800 technical standards and related documents for broadcast, filmmaking, digital cinema, audio recording, information technology (IT), and medical imaging. SMPTE also publishes the ''SMPTE Motion Imaging Journal'', provides networking opportunities for its members, produces academic conferences and exhibitions, and performs other industry-related functions. SMPTE membership is open to any individual or organization with an interest in the subject matter. In the US, SMPTE is a 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)3 non-profit charitable organization. History The Motion Picture and Television Engineers was founded in 1913 by Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Electric
The Western Electric Company was an American electrical engineering and manufacturing company officially founded in 1869. A wholly owned subsidiary of American Telephone & Telegraph for most of its lifespan, it served as the primary equipment manufacturer, supplier, and purchasing agent for the Bell System from 1881 to 1984 when it was dismantled. The company was responsible for many technological innovations as well as developments in industrial management. History In 1856, George Shawk, a craftsman and telegraph maker, purchased an electrical engineering business in Cleveland, Ohio. In January, 1869, Shawk had partnered with Enos M. Barton in the former Western Union repair shop of Cleveland, to manufacture burglar, fire alarms, and other electrical items. Both men were former Western Union employees. Shawk, was the Cleveland shop foreman and Barton, was a Rochester, New York telegrapher. During this Shawk and Barton partnership, one customer was an inventor sourcing parts an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)