|
Document Type Definition
A document type definition (DTD) is a set of ''markup declarations'' that define a ''document type'' for an SGML-family markup language ( GML, SGML, XML, HTML). A DTD defines the valid building blocks of an XML document. It defines the document structure with a list of validated elements and attributes. A DTD can be declared inline inside an XML document, or as an external reference. XML uses a subset of SGML DTD. , newer XML namespace-aware schema languages (such as W3C XML Schema and ISO RELAX NG) have largely superseded DTDs. A namespace-aware version of DTDs is being developed as Part 9 of ISO DSDL. DTDs persist in applications that need special publishing characters, such as the XML and HTML Character Entity References, which derive from larger sets defined as part of the ISO SGML standard effort. Associating DTDs with documents A DTD is associated with an XML or SGML document by means of a document type declaration (DOCTYPE). The DOCTYPE appears in the syntactic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SGML
The Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML; ISO 8879:1986) is a standard for defining generalized markup languages for documents. ISO 8879 Annex A.1 states that generalized markup is "based on two postulates": * Declarative: Markup should describe a document's structure and other attributes rather than specify the processing that needs to be performed, because it is less likely to conflict with future developments. * Rigorous: In order to allow markup to take advantage of the techniques available for processing, markup should rigorously define objects like programs and databases. DocBook SGML and LinuxDoc are examples which used SGML tools. Standard versions SGML is an ISO standard: "ISO 8879:1986 Information processing – Text and office systems – Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML)", of which there are three versions: * Original ''SGML'', which was accepted in October 1986, followed by a minor Technical Corrigendum. * ''SGML (ENR)'', in 1996, resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XHTML
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages. It mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated. While HTML, prior to HTML5, was defined as an application of Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML), a flexible markup language framework, XHTML is an application of XML, a more restrictive subset of SGML. XHTML documents are well-formed and may therefore be parsed using standard XML parsers, unlike HTML, which requires a lenient HTML-specific parser. XHTML 1.0 became a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) recommendation on 26 January 2000. XHTML 1.1 became a W3C recommendation on 31 May 2001. The standard known as XHTML5 is being developed as an XML adaptation of the HTML5 specification. Overview XHTML 1.0 is "a reformulation of the three HTML 4 document types as applications of XML 1.0". The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) also continues to maintai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
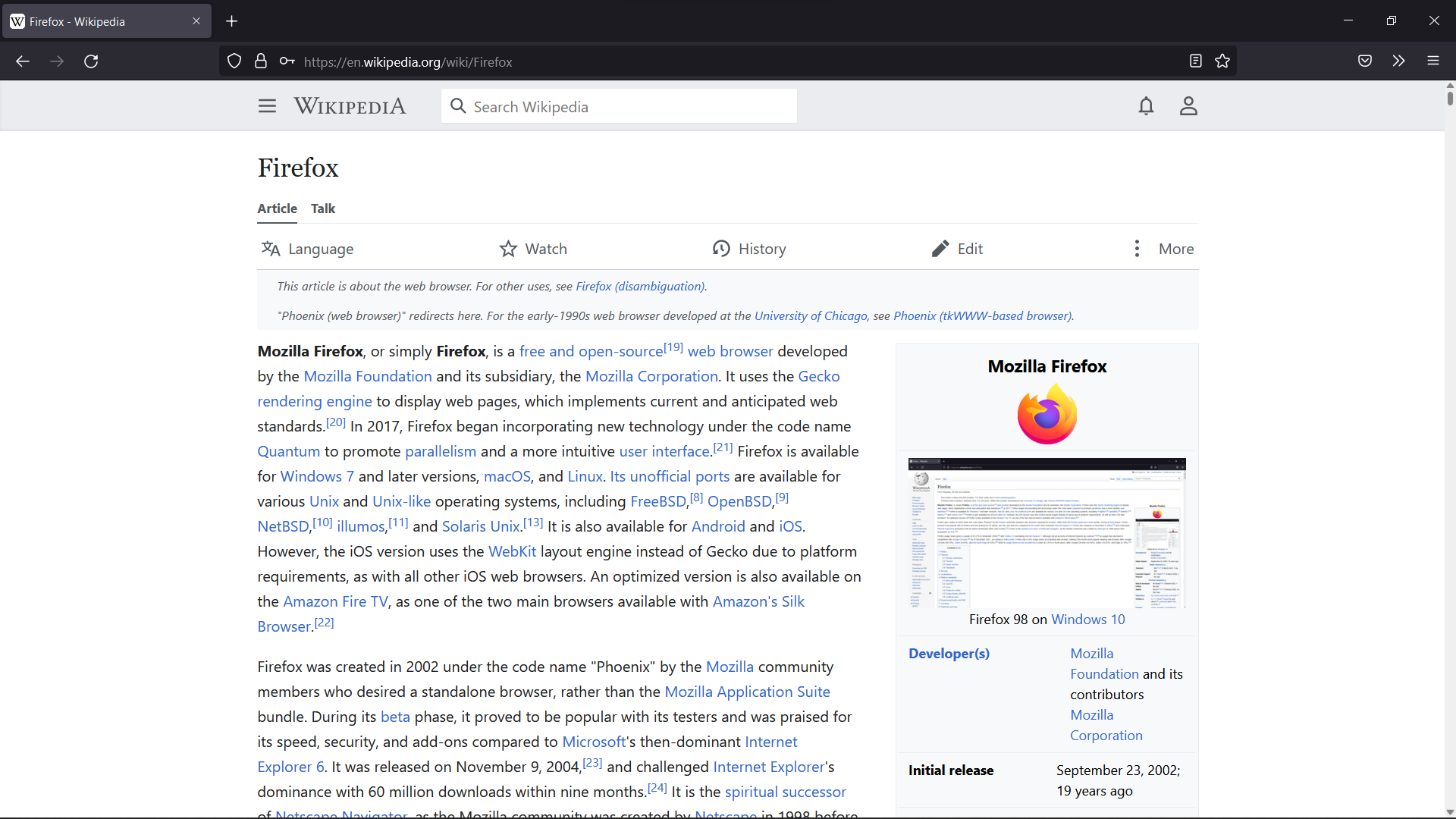
Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current and anticipated web standards. In November 2017, Firefox began incorporating new technology under the code name "Quantum" to promote parallelism and a more intuitive user interface. Firefox is available for Windows 7 and later versions, macOS, and Linux. Its unofficial ports are available for various Unix and Unix-like operating systems, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, illumos, and Solaris Unix. It is also available for Android and iOS. However, as with all other iOS web browsers, the iOS version uses the WebKit layout engine instead of Gecko due to platform requirements. An optimized version is also available on the Amazon Fire TV as one of the two main browsers available with Amazon's Silk Browser. Firefox was created in 2002 under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer (formerly Microsoft Internet Explorer and Windows Internet Explorer, commonly abbreviated IE or MSIE) is a series of graphical user interface, graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft which was used in the Microsoft Windows, Windows line of operating systems (in Windows 11, Windows Server Insider Build 22463 and Windows Server Insider Build 25110, it is replaced by the Chromium (web browser), Chromium version of Microsoft Edge). Starting in 1995, It was first released as part of the add-on package Microsoft Plus!, Plus! for Windows 95 that year. Later versions were available as free downloads, or in-service packs, and included in the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) service releases of Windows 95 and later versions of Windows. Microsoft spent over per year on Internet Explorer in the late 1990s, with over 1,000 people involved in the project by 1999. New feature development for the browser was discontinued in 2016 in favor of new browser Microsoft Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. In 2020, an estimated 4.9 billion people used a browser. The most used browser is Google Chrome, with a 65% global market share on all devices, followed by Safari with 18%. A web browser is not the same thing as a search engine, though the two are often confused. A search engine is a website that provides links to other websites. However, to connect to a website's server and display its web pages, a user must have a web browser installed. In some technical contexts, browsers are referred to as user agents. Function The purpose of a web browser is to fetch content from the World Wide Web or from local storage and display it on a user's device. This process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XML Declaration
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The World Wide Web Consortium's XML 1.0 Specification of 1998 and several other related specifications—all of them free open standards—define XML. The design goals of XML emphasize simplicity, generality, and usability across the Internet. It is a textual data format with strong support via Unicode for different human languages. Although the design of XML focuses on documents, the language is widely used for the representation of arbitrary data structures such as those used in web services. Several schema systems exist to aid in the definition of XML-based languages, while programmers have developed many application programming interfaces (APIs) to aid the processing of XML data. Overview The main purpose of XML is serialization, i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIME Type
A media type (also known as a MIME type) is a two-part identifier for file formats and format contents transmitted on the Internet. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority, Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is the official authority for the standardization and publication of these classifications. Media types were originally defined in Request for Comments (MIME) Part One: Format of Internet Message Bodies (Nov 1996) in November 1996 as a part of the ''MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)'' specification, for denoting type of email message content and attachments; hence the original name, ''MIME type''. Media types are also used by other internet protocols such as HTTP and document file formats such as HTML element, HTML, for similar purposes. Naming A media type consists of a ''type'' and a ''subtype'', which is further structured into a ''tree''. A media type can optionally define a ''suffix'' and ''parameters'': : As of November 1996, the registered types wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macro (computer Science)
In computer programming, a macro (short for "macro instruction"; ) is a rule or pattern that specifies how a certain input should be mapped to a replacement output. Applying a macro to an input is known as macro expansion. The input and output may be a sequence of lexical tokens or characters, or a syntax tree. Character macros are supported in software applications to make it easy to invoke common command sequences. Token and tree macros are supported in some programming languages to enable code reuse or to extend the language, sometimes for domain-specific languages. Macros are used to make a sequence of computing instructions available to the programmer as a single program statement, making the programming task less tedious and less error-prone. (Thus, they are called "macros" because a "big" block of code can be expanded from a "small" sequence of characters.) Macros often allow positional or keyword parameters that dictate what the conditional assembler program generates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fragment Identifier
In computer hypertext, a URI fragment is a character string (computer science), string of character (computing), characters that refers to a resource (computer science), resource that is subordinate to another, primary resource. The primary resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), and the fragment identifier points to the subordinate resource. The fragment identifier introduced by a hash mark # is the optional last part of a Uniform Resource Locator, URL for a document. It is typically used to identify a portion of that document. The generic syntax is specified in RFC ((3986))The number sign, hash-mark separator in URIs is not part of the fragment Identifier Basics In URIs, a hash mark # introduces the optional fragment near the end of the URL. The generic RFC 3986 syntax for URIs also allows an optional query string, query part introduced by a question mark ?. In URIs with a query and a fragment, the fragment follows the query. Query parts depend on the URI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backus–Naur Form
In computer science, Backus–Naur form () or Backus normal form (BNF) is a metasyntax notation for context-free grammars, often used to describe the syntax of languages used in computing, such as computer programming languages, document formats, instruction sets and communication protocols. It is applied wherever exact descriptions of languages are needed: for instance, in official language specifications, in manuals, and in textbooks on programming language theory. Many extensions and variants of the original Backus–Naur notation are used; some are exactly defined, including extended Backus–Naur form (EBNF) and augmented Backus–Naur form (ABNF). Overview A BNF specification is a set of derivation rules, written as ::= __expression__ where: * is a ''nonterminal'' (variable) and the __expression__ consists of one or more sequences of either terminal or nonterminal symbols; * means that the symbol on the left must be replaced with the expression on the right. * mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notation Declarations
In linguistics and semiotics, a notation is a system of graphics or symbols, characters and abbreviated expressions, used (for example) in artistic and scientific disciplines to represent technical facts and quantities by convention. Therefore, a notation is a collection of related symbols that are each given an arbitrary meaning, created to facilitate structured communication within a domain knowledge or field of study. Standard notations refer to general agreements in the way things are written or denoted. The term is generally used in technical and scientific areas of study like mathematics, physics, chemistry and biology, but can also be seen in areas like business, economics and music. Written communication Writing systems * Phonographic writing systems, by definition, use symbols to represent components of auditory language, i.e. speech, which in turn refers to things or ideas. The two main kinds of phonographic notational system are the alphabet and the syllabary. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entity Declarations
An entity is something that Existence, exists as itself, as a subject or as an object, actually or potentially, concretely or abstractly, physically or not. It need not be of material existence. In particular, abstractions and legal fictions are usually regarded as entities. In general, there is also no presumption that an entity is Life, animate, or present. The term is broad in scope and may refer to animals; natural features such as mountains; inanimate objects such as tables; numbers or sets as symbols written on a paper; human contrivances such as laws, corporations and academic disciplines; or supernatural beings such as gods and spirits. The adjectival form is ''entitative''. Etymology The word ''entity'' is derived from the Latin ''entitas'', which in turn derives from the Latin ''ens'' meaning "being" or "existing" (compare English ''essence''). ''Entity'' may hence literally be taken to mean "thing which exists". In philosophy Ontology is the study of concepts of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |