|
Djurleite
Djurleite is a copper sulfide mineral of secondary origin with formula Cu31S16 that crystallizes with monoclinic-prismatic symmetry. It is typically massive in form, but does at times develop thin tabular to prismatic crystals. It occurs with other supergene minerals such as chalcocite, covellite and digenite in the enriched zone of copper orebodies. It is a member of the chalcocite group, and very similar to chalcocite, Cu2S, in its composition and properties, but the two minerals can be distinguished from each other by x-ray powder diffraction. Intergrowths and transformations between djurleite, digenite and chalcocite are common.Pósfai, M. & Buseck, P. R. (1994): Djurleite, digenite, and chalcocite: Intergrowths and transformations. American Mineralogist, 79, 308-315 Many of the reported associations of digenite and djurleite, however, identified by powder diffraction, could be anilite and djurleite, as anilite transforms to digenite during grinding. Djurleite was named for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digenite
Digenite is a copper sulfide mineral with formula: Cu9S5. Digenite is a black to dark blue opaque mineral that crystallizes with a trigonal - hexagonal scalenohedral structure. In habit it is usually massive, but does often show pseudo-cubic forms. It has poor to indistinct cleavage and a brittle fracture. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 to 3 and a specific gravity of 5.6. It is found in copper sulfide deposits of both primary and supergene occurrences. It is typically associated with and often intergrown with chalcocite, covellite, djurleite, bornite, chalcopyrite and pyrite. The type locality is Sangerhausen, Thuringia, Germany, in copper slate deposits. Occurrence Digenite occurs in the transitional zone of supergene oxidation of primary sulfide ore deposits, at the interface between the upper and lower saprolite ore zones. It is rarely an important mineral for copper ores, as it is more usually replaced by chalcocite further up in the weathering profile, and is a minor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digenite
Digenite is a copper sulfide mineral with formula: Cu9S5. Digenite is a black to dark blue opaque mineral that crystallizes with a trigonal - hexagonal scalenohedral structure. In habit it is usually massive, but does often show pseudo-cubic forms. It has poor to indistinct cleavage and a brittle fracture. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 to 3 and a specific gravity of 5.6. It is found in copper sulfide deposits of both primary and supergene occurrences. It is typically associated with and often intergrown with chalcocite, covellite, djurleite, bornite, chalcopyrite and pyrite. The type locality is Sangerhausen, Thuringia, Germany, in copper slate deposits. Occurrence Digenite occurs in the transitional zone of supergene oxidation of primary sulfide ore deposits, at the interface between the upper and lower saprolite ore zones. It is rarely an important mineral for copper ores, as it is more usually replaced by chalcocite further up in the weathering profile, and is a minor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Sulfide
Copper sulfides describe a family of chemical compounds and minerals with the formula CuxSy. Both minerals and synthetic materials comprise these compounds. Some copper sulfides are economically important ores. Prominent copper sulfide minerals include Cu2S (chalcocite) and CuS (covellite). In the mining industry, the minerals bornite or chalcopyrite, which consist of mixed copper-iron sulfides, are often referred to as "copper sulfides". In chemistry, a "binary copper sulfide" is any binary chemical compound of the elements copper and sulfur. Whatever their source, copper sulfides vary widely in composition with 0.5 ≤ Cu/S ≤ 2, including numerous non-stoichiometric compounds. Known copper sulfides The naturally occurring mineral binary compounds of copper and sulfur are listed below. Investigations of covellite (CuS) indicate that there are other metastable Cu-S phases still to be fully characterised. * CuS2, villamaniniteWells A.F. (1984) ''Structural Inorganic Chemistr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supergene (geology)
In ore deposit geology, supergene processes or enrichment are those that occur relatively near the surface as opposed to deep hypogene processes. Supergene processes include the predominance of meteoric water circulation (i.e. water derived from precipitation) with concomitant oxidation and chemical weathering. The descending meteoric waters oxidize the primary (hypogene) sulfide ore minerals and redistribute the metallic ore elements. Supergene ''enrichment'' occurs at the base of the oxidized portion of an ore deposit. Metals that have been leached from the oxidized ore are carried downward by percolating groundwater, and react with hypogene sulfides at the supergene-hypogene boundary. The reaction produces secondary sulfides with metal contents higher than those of the primary ore. This is particularly noted in copper ore deposits where the copper sulfide minerals chalcocite (Cu2S), covellite (CuS), digenite (Cu18S10), and djurleite (Cu31S16) are deposited by the descending surfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covellite
Covellite (also known as covelline) is a rare copper sulfide mineral with the formula CuS. This indigo blue mineral is commonly a secondary mineral in limited abundance and although it is not an important ore of copper itself, it is well known to mineral collectors. The mineral is generally found in zones of secondary enrichment ( supergene) of copper sulfide deposits. Commonly found as coatings on chalcocite, chalcopyrite, bornite, enargite, pyrite, and other sulfides, it often occurs as pseudomorphic replacements of other minerals. The first records are from Mount Vesuvius, formally named in 1832 after N. Covelli. Composition Covellite belongs to the binary copper sulfides group, which has the formula CuxSy and can have a wide-ranging copper/sulfur ratio, from 1:2 to 2:1 (Cu/S). However, this series is by no means continuous and the homogeneity range of covellite CuS is narrow. Materials rich in sulfur CuSx where x~ 1.1- 1.2 do exist, but they exhibit " superstructures", a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anilite
Anilite ( IMA symbol: Ani) is a mineral with the chemical formula CuS. It is named for its type locality, the Ani Mine in Akita Prefecture. on mindat.org
Mindat.org is a non-commercial online database, claiming to be the largest mineral database and mineralogy, mineralogical reference website on the Internet. It is used by professional mineralogists, geologists, and amateur mineral collecting, mi ...
References External links Anilite data sheet [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geerite
Geerite is a copper sulfide mineral with the chemical formula Cu8S5. The mineral is named after the original collector, Adam Geer, of Utica, New York, US. Crystallography Geerite is in the crystal class . This means that the crystal could be inverted and then rotated by 120 degrees to return to its original position. The optical class of geerite is unknown. Geerite is anisotropic which means that it will show interference colors when it is rotated in cross polarized light and that the mineral has different properties in different directions Discovery and occurrence It was first described in 1980 for an occurrence as thin coatings or platelets replacing sphalerite in the type locality in De Kalb Township, Saint Lawrence County, New York. It also occurs in a magnetite– chromite a serpentinite-hosted deposit in Eretria, Greece. It occurs associated with spionkopite, sphalerite, tetrahedrite, chalcopyrite, malachite, azurite, brochantite, chrysocolla, cervantite, stibiconite, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomorph
In mineralogy, a pseudomorph is a mineral or mineral compound that appears in an atypical form (crystal system), resulting from a substitution process in which the appearance and dimensions remain constant, but the original mineral is replaced by another. The name literally means "false form". Terminology for pseudomorphs is "''replacer'' after ''original''", as in ''brookite'' after ''rutile''. Substitution pseudomorph An infiltration pseudomorph, or substitution pseudomorph is a pseudomorph in which one mineral or other material is replaced by another. The original shape of the mineral remains unchanged, but color, hardness, and other properties change to those of the replacing mineral. An example of this process is the replacement of wood by silica (quartz or opal) to form petrified wood in which the substitution may be so perfect as to retain the original cellular structure of the wood. An example of mineral-to-mineral substitution is replacement of aragonite twin crystal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
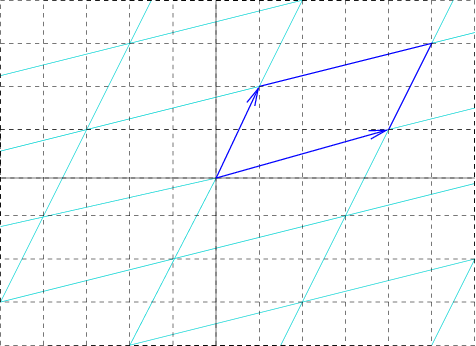
Unit Cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector, for example) does not necessarily have unit size, or even a particular size at all. Rather, the primitive cell is the closest analogy to a unit vector, since it has a determined size for a given lattice and is the basic building block from which larger cells are constructed. The concept is used particularly in describing crystal structure in two and three dimensions, though it makes sense in all dimensions. A lattice can be characterized by the geometry of its unit cell, which is a section of the tiling (a parallelogram or parallelepiped) that generates the whole tiling using only translations. There are two special cases of the unit cell: the primitive cell and the conventional cell. The primitive cell is a unit cell corresponding to a single lattice point, it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphism (materials Science)
In materials science, polymorphism describes the existence of a solid material in more than one form or crystal structure. Polymorphism is a form of isomerism. Any crystalline material can exhibit the phenomenon. Allotropy refers to polymorphism for chemical elements. Polymorphism is of practical relevance to pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, pigments, dyestuffs, foods, and explosives. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure (the inversion point) to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." According to McCrone, polymorphs are "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." Materials with two polymorphs are called dimorphic, with three polymorphs, trimorphic, etc. Examples Many compounds exhibit polymorphism. It has been claimed that "every compound has different polymorphic forms, and that, in general, the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)