|
Divisia Index
A Divisia index is a theoretical construct to create index number series for continuous-time data on prices and quantities of goods exchanged. The name comes from François Divisia who first proposed and formally analyzed the indexes in 1926, and discussed them in related 1925 and 1928 works. The Divisia index is designed to incorporate quantity and price changes over time from subcomponents that are measured in different units, such as labor hours and equipment investment and materials purchases, and to summarize them in a time series that summarizes the changes in quantities and/or prices. The resulting index number series is unitless, like other index numbers. In practice, economic data are not measured in continuous time. Thus, when a series is said to be a Divisia index, it usually means the series follows a procedure that makes a close analogue in discrete time periods, usually the Törnqvist index procedure or the Fisher Ideal Index procedures.Diewert, W.E. 1993The early hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index (economics)
In Statistics, Economics and Finance, an index is a statistical measure of change in a representative group of individual data points. These data may be derived from any number of sources, including company performance, prices, productivity, and employment. Economic indices track economic health from different perspectives. Influential global financial indices such as the Global Dow, and the NASDAQ Composite track the performance of selected large and powerful companies in order to evaluate and predict economic trends. The Dow Jones Industrial Average and the S&P 500 primarily track U.S. markets, though some legacy international companies are included. The consumer price index tracks the variation in prices for different consumer goods and services over time in a constant geographical location and is integral to calculations used to adjust salaries, bond interest rates, and tax thresholds for inflation. The GDP Deflator Index, or real GDP, measures the level of prices of all- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Divisia
François Divisia (1889–1964) was a French economist most noted for the Divisia index A Divisia index is a theoretical construct to create index number series for continuous-time data on prices and quantities of goods exchanged. The name comes from François Divisia who first proposed and formally analyzed the indexes in 1926, and d ... and the Divisia monetary aggregates index. Notable publications * Divisia, F. (1925) L'indice monétaire et la théorie de la monnaie. ''Revue d'écon. polit.'', XXXIX, Nos. 4, 5, 6: 842-61, 980-1008, 1121-51. * Divisia, F. (1926) L'indice monétaire et la théorie de la monnaie. ''Revue d'écon. polit.'', LX, No. 1: 49-81. * Divisia, F. (1928) ''L'économie rationnelle'', Paris: Gaston Doin et Cie. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Divisia, F. French economists Fellows of the Econometric Society Presidents of the Econometric Society 1889 births 1964 deaths Place of birth missing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New Palgrave Dictionary Of Economics
''The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics'' (2018), 3rd ed., is a twenty-volume reference work on economics published by Palgrave Macmillan. It contains around 3,000 entries, including many classic essays from the original Inglis Palgrave Dictionary, and a significant increase in new entries from the previous editions by the most prominent economists in the field, among them 36 winners of the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel. Articles are classified according to ''Journal of Economic Literature'' (''JEL'') classification codes. ''The New Palgrave'' is also available in a hyperlinked online version. Online content is added to the 2018 edition, and a 4th edition under the editorship of J. Barkley Rosser Jr., Esteban Pérez Caldentey, and Matías Vernengo will be published in the future. The first edition was titled ''The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'' (1987), was and edited by John Eatwell, Murray Milgate, and Peter Newman, as a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Törnqvist Index
In economics, the Törnqvist index is a price or quantity index. In practice, Törnqvist index values are calculated for consecutive periods, then these are strung together, or "'' chained''". Thus, the core calculation does not refer to a single base year. Computation The price index for some period is usually normalized to be 1 or 100, and that period is called "base period." A Törnqvist or Törnqvist-Theil price index is the weighted geometric mean of the price relatives using arithmetic averages of the value shares in the two periods as weights. The data used are prices and quantities in two time-periods, (t-1) and (t), for each of ''n'' goods which are indexed by ''i''. If we denote the price of item ''i'' at time t-1 by p_, and, analogously, we define q_ to be the quantity purchased of item ''i'' at time t, then, the Törnqvist price index P_t at time t can be calculated as follows: :\frac = \prod_^\left(\frac\right)^ The denominators in the exponent are the sums of to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
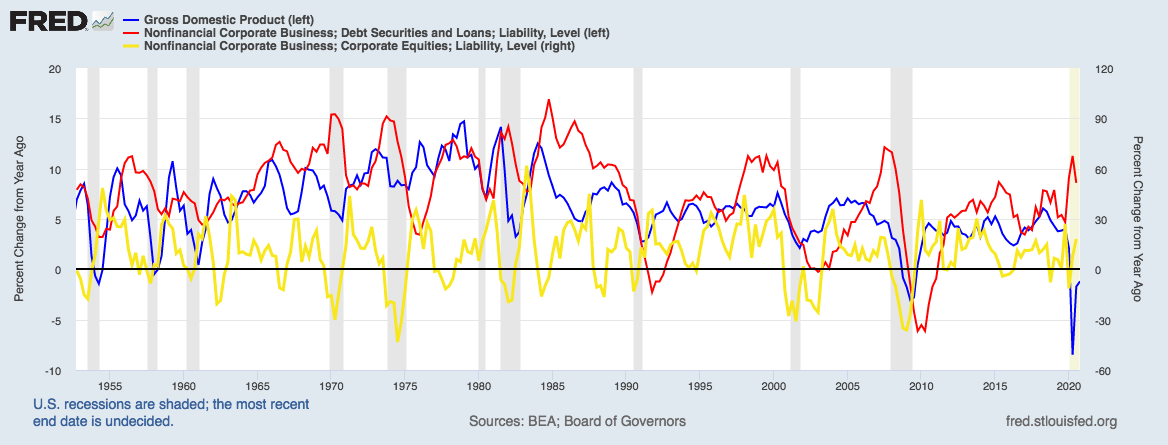
Volume Index
A volume index or quantity index is a numerical time series measure designed to help compare how the production of some class of goods and/or services, taken as a whole, differs between time periods or geographical locations. Compare price index. As compared to a price index, a volume index takes into account price changes and reflects the level of production without inflation. Volume or quantity indexes can be constructed by year-to-year chaining just as price indexes can be. See also * Gross domestic product Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ... References External referencesOECD glossary entry Business indices {{econ-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the English Government's banker, and still one of the bankers for the Government of the United Kingdom, it is the world's eighth-oldest bank. It was privately owned by stockholders from its foundation in 1694 until it was nationalised in 1946 by the Attlee ministry. The Bank became an independent public organisation in 1998, wholly owned by the Treasury Solicitor on behalf of the government, with a mandate to support the economic policies of the government of the day, but independence in maintaining price stability. The Bank is one of eight banks authorised to issue banknotes in the United Kingdom, has a monopoly on the issue of banknotes in England and Wales, and regulates the issue of banknotes by commercial banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland. The Bank's Monetary Policy Committee has devolved responsibility for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divisia Monetary Aggregates Index
In econometrics and official statistics, and particularly in banking, the Divisia monetary aggregates index is an index of money supply. It uses Divisia index methods. Background The monetary aggregates used by most central banks (notably the US Federal Reserve) are simple-sum indexes in which all monetary components are assigned the same weight: :M_=\sum_^x_, in which x_ is one of the n monetary components of the monetary aggregate M_. The summation index implies that all monetary components contribute equally to the money total, and it views all components as dollar-for-dollar perfect substitutes. It has been argued that such an index does not weight such components in a way that properly summarizes the services of the quantities of money. There have been many attempts at weighting monetary components within a simple-sum aggregate. An index can rigorously apply microeconomic- and aggregation-theoretic foundations in the construction of monetary aggregates. That approach to mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William A
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Indicators
An economic indicator is a statistic about an economic activity. Economic indicators allow analysis of economic performance and predictions of future performance. One application of economic indicators is the study of business cycles. Economic indicators include various indices, earnings reports, and economic summaries: for example, the unemployment rate, quits rate (quit rate in American English), housing starts, consumer price index (a measure for inflation), Inverted yield curve, consumer leverage ratio, industrial production, bankruptcies, gross domestic product, broadband internet penetration, retail sales, price index, and money supply changes. The leading business cycle dating committee in the United States of America is the private National Bureau of Economic Research. The Bureau of Labor Statistics is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the field of labor economics and statistics. Other producers of economic indicators includes the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
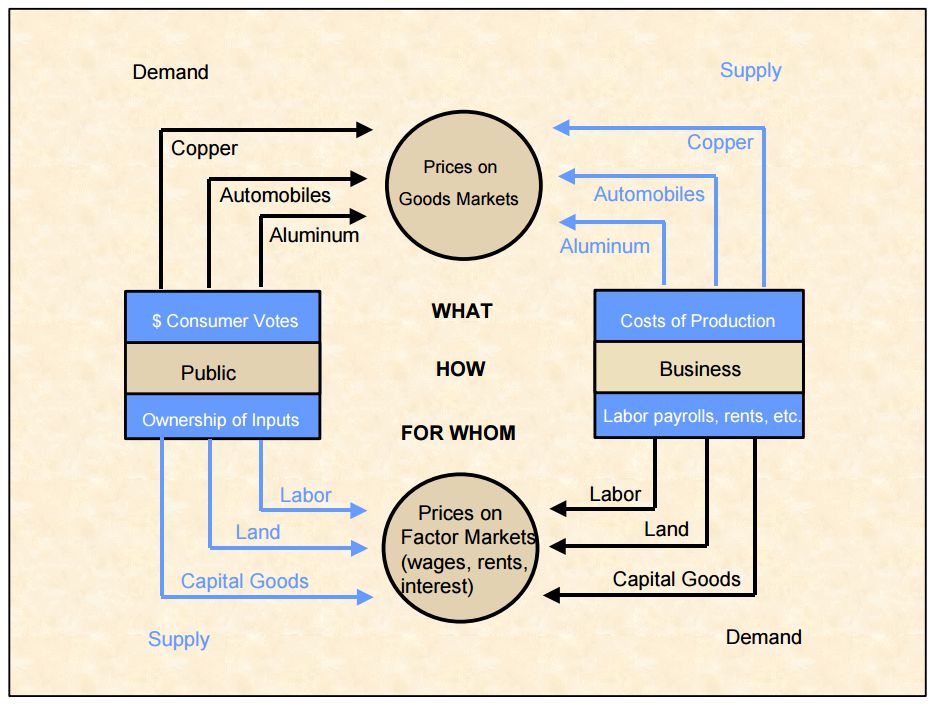
Price Index Theory
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in the commercial exchange, the payment for this product will likely be called its "price". However, if the product is "service", there will be other possible names for this product's name. For example, the graph on the bottom will show some situations A good's price is influenced by production costs, supply of the desired item, and demand for the product. A price may be determined by a monopolist or may be imposed on the firm by market conditions. Price can be quoted to currency, quantities of goods or vouchers. * In modern economies, prices are generally expressed in units of some form of currency. (More specifically, for raw materials they are expressed as currency per unit weight, e.g. euros per kilogram or Rands per KG.) * Although prices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |