|
Distance Sampling
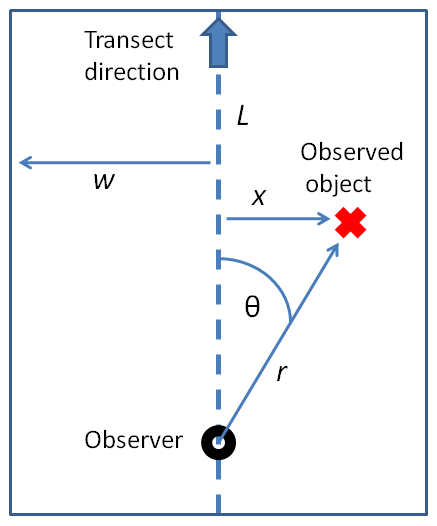
Distance sampling is a widely used group of closely related methods for estimating the density and/or abundance of populations. The main methods are based on line transects or point transects.Buckland, S. T., Anderson, D. R., Burnham, K. P. and Laake, J. L. (1993). ''Distance Sampling: Estimating Abundance of Biological Populations''. London: Chapman and Hall. In this method of sampling, the data collected are the distances of the objects being surveyed from these randomly placed lines or points, and the objective is to estimate the average density of the objects within a region. Basic line transect methodology A common approach to distance sampling is the use of line transects. The observer traverses a straight line (placed randomly or following some planned distribution). Whenever they observe an object of interest (e.g., an animal of the type being surveyed), they record the distance from their current position to the object (''r''), as well as the angle of the detection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Population Density
Population density (in agriculture: Standing stock (other), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopulation Density Geography.about.com. March 2, 2011. Retrieved on December 10, 2011. Biological population densities Population density is population divided by total land area, sometimes including seas and oceans, as appropriate. Low densities may cause an extinction vortex and further reduce fertility. This is called the Allee effect after the scientist who identified it. Examples of the causes of reduced fertility in low population densities are: * Increased problems with locating sexual mates * Increased inbreeding Human densities Population density is the number of people per unit of area, usually transcribed as "per square kilometre" or square mile, and which may include or exclude, for example, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Exponential Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution or negative exponential distribution is the probability distribution of the distance between events in a Poisson point process, i.e., a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate; the distance parameter could be any meaningful mono-dimensional measure of the process, such as time between production errors, or length along a roll of fabric in the weaving manufacturing process. It is a particular case of the gamma distribution. It is the continuous analogue of the geometric distribution, and it has the key property of being memoryless. In addition to being used for the analysis of Poisson point processes it is found in various other contexts. The exponential distribution is not the same as the class of exponential families of distributions. This is a large class of probability distributions that includes the exponential distribution as one of its members, but also includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Environmental Statistics
Environment statistics is the application of statistical methods to environmental science. It covers procedures for dealing with questions concerning the natural environment in its undisturbed state, the interaction of humanity with the environment, and urban environments. The field of environmental statistics has seen rapid growth in the past few decades as a response to increasing concern over the environment in the public, organizational, and governmental sectors. The United Nations' Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics (FDES) defines the scope of environment statistics as follows: The scope of environment statistics covers biophysical aspects of the environment and those aspects of the socioeconomic system that directly influence and interact with the environment. The scope of environment, social and economic statistics overlap. It is not easy – or necessary – to draw a clear line dividing these areas. Social and economic statistics that describe proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
R (programming Language)
R is a programming language for statistical computing and Data and information visualization, data visualization. It has been widely adopted in the fields of data mining, bioinformatics, data analysis, and data science. The core R language is extended by a large number of R package, software packages, which contain Reusability, reusable code, documentation, and sample data. Some of the most popular R packages are in the tidyverse collection, which enhances functionality for visualizing, transforming, and modelling data, as well as improves the ease of programming (according to the authors and users). R is free and open-source software distributed under the GNU General Public License. The language is implemented primarily in C (programming language), C, Fortran, and Self-hosting (compilers), R itself. Preprocessor, Precompiled executables are available for the major operating systems (including Linux, MacOS, and Microsoft Windows). Its core is an interpreted language with a na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
University Of St Andrews
The University of St Andrews (, ; abbreviated as St And in post-nominals) is a public university in St Andrews, Scotland. It is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, oldest of the four ancient universities of Scotland and, following the universities of University of Oxford, Oxford and University of Cambridge, Cambridge, the third-oldest university in the English-speaking world. St Andrews was founded in 1413 when the Avignon Pope, Avignon Antipope Benedict XIII issued a papal bull to a small founding group of Augustinians, Augustinian clergy. Along with the universities of University of Glasgow, Glasgow, University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, and University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, St Andrews was part of the Scottish Enlightenment during the 18th century. St Andrews is made up of a variety of institutions, comprising three colleges — United College, St Andrews, United College (a union of St Salvator's and St Leonard's Colleges), St Mary's College, St Andrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Distance Sampling Rounding To Zero
Distance is a numerical or occasionally qualitative measurement of how far apart objects, points, people, or ideas are. In physics or everyday usage, distance may refer to a physical length or an estimation based on other criteria (e.g. "two counties over"). The term is also frequently used metaphorically to mean a measurement of the amount of difference between two similar objects (such as statistical distance between probability distributions or edit distance between strings of text) or a degree of separation (as exemplified by distance between people in a social network). Most such notions of distance, both physical and metaphorical, are formalized in mathematics using the notion of a metric space. In the social sciences, distance can refer to a qualitative measurement of separation, such as social distance or psychological distance. Distances in physics and geometry The distance between physical locations can be defined in different ways in different contexts. Straight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Range Finder
A rangefinder (also rangefinding telemeter, depending on the context) is a device used to measure distances to remote objects. Originally optical devices used in surveying, they soon found applications in other fields, such as photography, the military, and space travel. They were especially useful for finding the range of a target, such as in naval gunnery and anti-aircraft artillery. The word ''telemeter'' is derived . Designs The first rangefinder telemeter was invented by James Watt in 1769 and put to use in 1771 in surveying canals. Watt called his instrument a micrometer, a term now used with a different meaning in engineering (the micrometer screw gauge). It consisted of two parallel hairs in the focal plane of a telescope eyepiece crossing an upright hair. At the point to be measured, two sliding targets on a surveyor's rod were adjusted to align with the hairs in the telescope. The distance to the rod could then be determined from the distance between the tar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dead Reckoning
In navigation, dead reckoning is the process of calculating the current position of a moving object by using a previously determined position, or fix, and incorporating estimates of speed, heading (or direction or course), and elapsed time. The corresponding term in biology, to describe the processes by which animals update their estimates of position or heading, is path integration. Advances in navigational aids that give accurate information on position, in particular satellite navigation using the Global Positioning System, have made simple dead reckoning by humans obsolete for most purposes. However, inertial navigation systems, which provide very accurate directional information, use dead reckoning and are very widely applied. Etymology Contrary to myth, the term "dead reckoning" was not originally used to abbreviate "deduced reckoning", nor is it a misspelling of the term "ded reckoning". The use of "ded" or "deduced reckoning" is not known to have appeared earlier th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Distance Sampling Observer Avoidance
Distance is a numerical or occasionally qualitative measurement of how far apart objects, points, people, or ideas are. In physics or everyday usage, distance may refer to a physical length or an estimation based on other criteria (e.g. "two counties over"). The term is also frequently used metaphorically to mean a measurement of the amount of difference between two similar objects (such as statistical distance between probability distributions or edit distance between strings of text) or a degree of separation (as exemplified by distance between people in a social network). Most such notions of distance, both physical and metaphorical, are formalized in mathematics using the notion of a metric space. In the social sciences, distance can refer to a qualitative measurement of separation, such as social distance or psychological distance. Distances in physics and geometry The distance between physical locations can be defined in different ways in different contexts. Straight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Overfitting
In mathematical modeling, overfitting is "the production of an analysis that corresponds too closely or exactly to a particular set of data, and may therefore fail to fit to additional data or predict future observations reliably". An overfitted model is a mathematical model that contains more parameters than can be justified by the data. In the special case where the model consists of a polynomial function, these parameters represent the degree of a polynomial. The essence of overfitting is to have unknowingly extracted some of the residual variation (i.e., the Statistical noise, noise) as if that variation represented underlying model structure. Underfitting occurs when a mathematical model cannot adequately capture the underlying structure of the data. An under-fitted model is a model where some parameters or terms that would appear in a correctly specified model are missing. Underfitting would occur, for example, when fitting a linear model to nonlinear data. Such a model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hermite Polynomials
In mathematics, the Hermite polynomials are a classical orthogonal polynomial sequence. The polynomials arise in: * signal processing as Hermitian wavelets for wavelet transform analysis * probability, such as the Edgeworth series, as well as in connection with Brownian motion; * combinatorics, as an example of an Appell sequence, obeying the umbral calculus; * numerical analysis as Gaussian quadrature; * physics, where they give rise to the eigenstates of the quantum harmonic oscillator; and they also occur in some cases of the heat equation (when the term \beginxu_\end is present); * systems theory in connection with nonlinear operations on Gaussian noise. * random matrix theory in Gaussian ensembles. Hermite polynomials were defined by Pierre-Simon Laplace in 1810, though in scarcely recognizable form, and studied in detail by Pafnuty Chebyshev in 1859. Chebyshev's work was overlooked, and they were named later after Charles Hermite, who wrote on the polynomials in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is a Expression (mathematics), mathematical expression consisting of indeterminate (variable), indeterminates (also called variable (mathematics), variables) and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and exponentiation to nonnegative integer powers, and has a finite number of terms. An example of a polynomial of a single indeterminate is . An example with three indeterminates is . Polynomials appear in many areas of mathematics and science. For example, they are used to form polynomial equations, which encode a wide range of problems, from elementary word problem (mathematics education), word problems to complicated scientific problems; they are used to define polynomial functions, which appear in settings ranging from basic chemistry and physics to economics and social science; and they are used in calculus and numerical analysis to approximate other functions. In advanced mathematics, polynomials are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |