|
Dissenting Gothic
Dissenting Gothic is an architectural style associated with English Dissenters - Protestants not affiliated with the Church of England. It is a distinctive style in its own right within Gothic Revival architecture that emerged primarily in Britain, its colonies and North America, during the 19th century. Definition In contrast to the pure copying of English Gothic architecture, English Gothic advocated for and promoted by some influential ecclesiologists during the early Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival period in Britain (most particularly by Augustus Welby Pugin and to an extent in the pages of the Cambridge Camden Society, Camden Society's quarterly journal ''The Ecclesiologist'' (1841–68)), Dissenting Gothic provided a less Anglo-centric interpretation of the Gothic style, and purposely introduced modernising elements to meet clients' needs. This primarily involved the interests of good design overriding historical purity to the Gothic style, with the role of the ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abney Park Chapel
Abney Park Chapel, is a Grade II Listed chapel, designed by William Hosking and built by John Jay that is situated in Europe's first wholly nondenominational cemetery, Abney Park Cemetery, London. Opened in May, 1840, it was the first nondenominational cemetery chapel in Europe (and probably the world – since the chapel at Mount Auburn was a later addition). It helped pioneer the early use of the Dissenting Gothic building style, and encouraged renewed interest in the careful blending of earlier styles. It was primarily the work of a small design team consisting of George Collison II (acting as client for the cemetery founders, with a passion for Mount Auburn Cemetery near Boston, and it is said, Beverley Minster which dominated the skyline in his ancestral town); William Hosking (architect and civil engineer with an interest in Egyptology, antiquities, and architectural writing and scholarship); the builder John Jay, and George Loddiges (botanical scientist and horticultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brick Gothic
Brick Gothic (german: Backsteingotik, pl, Gotyk ceglany, nl, Baksteengotiek) is a specific style of Gothic architecture common in Northeast and Central Europe especially in the regions in and around the Baltic Sea, which do not have resources of standing rock, but in many places many glacial boulders. The buildings are essentially built using bricks. Buildings classified as Brick Gothic (using a strict definition of the architectural style based on the geographic location) are found in Belgium (and the very north of France), Netherlands, Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Kaliningrad (former East Prussia), Denmark, Sweden and Finland. As the use of baked red brick arrived in Northwestern and Central Europe in the 12th century, the oldest such buildings are classified as the Brick Romanesque. In the 16th century, Brick Gothic was superseded by Brick Renaissance architecture. Brick Gothic is characterised by the lack of figurative architectural sculpture, wides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mill Hill Chapel
Mill Hill Chapel is a Unitarian church in Leeds, West Yorkshire, England. It is a member of the General Assembly of Unitarian and Free Christian Churches, the umbrella organisation for British Unitarians. The building, which stands in the centre of the city on City Square, was granted Grade II* listed status in 1963. History As early as 1674, only a dozen years after the Great Ejection, the Dissenters in Leeds had built a chapel on the main town square. One of the founders was the father of the historian Ralph Thoresby who guided the chapel toward the Dissenter movement which, at Mill Hill Chapel, would become Unitarianism. 18th century During the late 18th century, Mill Hill's sister chapel was the Independent Congregationalist Call Lane Chapel, Leeds. Many of Leeds's leading families such as George William Oates at Low Hall, Potternewton and the Dixon family of Gledhow Hall were heavily involved with both churches at this time. Some local gentry, such as Hans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Barry
Sir Charles Barry (23 May 1795 – 12 May 1860) was a British architect, best known for his role in the rebuilding of the Palace of Westminster (also known as the Houses of Parliament) in London during the mid-19th century, but also responsible for numerous other buildings and gardens. He is known for his major contribution to the use of Italianate architecture in Britain, especially the use of the Palazzo as basis for the design of country houses, city mansions and public buildings. He also developed the Italian Renaissance garden style for the many gardens he designed around country houses.Bisgrove, p. 179 Background and training Born on 23 May 1795Barry p. 4 in Bridge Street, Westminster (opposite the future site of the Clock Tower of the Palace of Westminster), he was the fourth son of Walter Edward Barry (died 1805), a stationer, and Frances Barry ''née'' Maybank (died 1798). He was baptised at St Margaret's, Westminster, into the Church of England, of which he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
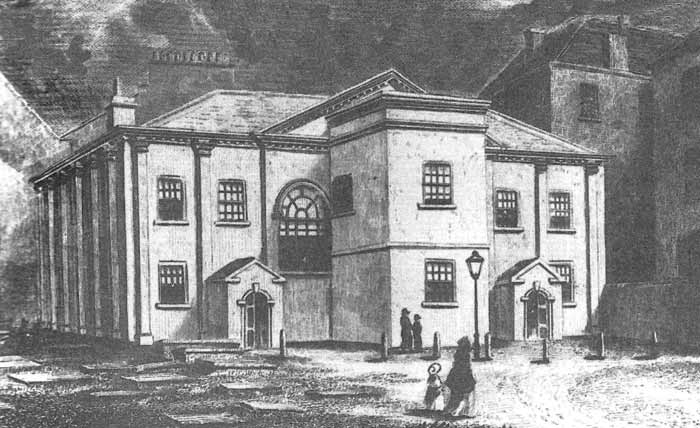
Upper Brook Street Chapel, Manchester
The Upper Brook Street Chapel, also known as the Islamic Academy, the Unitarian Chapel and the Welsh Baptist Chapel, is a former chapel with an attached Sunday School on the east side of Upper Brook Street, Chorlton-on-Medlock, Greater Manchester, England. It is said to be the first neogothic Nonconformist chapel, having been constructed for the British Unitarians between 1837 and 1839, at the very beginning of the reign of Queen Victoria. It was designed by Sir Charles Barry, later architect of the Palace of Westminster. A listed building since 3 October 1974 (currently Grade II*), it is owned by Manchester City Council and was on the Buildings at Risk Register, rated as "very bad". It was partially demolished in 2006. The Victorian Society placed the building on a list of ten most threatened buildings in England and Wales. It was restored and converted to student accommodation in 2017 by Buttress Architects. History Architecture The chapel was designed by Sir Charles Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Collison
George Collison (1772–1847) was an English Congregationalist and educator associated with Hackney Academy or Hackney College, which became part of New College London—itself part of the University of London. Early life Collison was born in Beverley, Yorkshire, on 6 January 1772, and became articled to a solicitor in Bridlington. Taking a keen interest in the local Independent Chapel, he became an early Sunday school teacher, and in 1792 decided to give up law and train full-time as a minister at Hoxton College near London. In 1797 he settled close to London in the village of Walthamstow in Essex to carry out pastoral duties, becoming the minister oMarsh Street Congregational Chapel in whose grounds he was buried in 1847. He undertook this ministerial role whilst also tutoring at Hoxton—until ill health led him to give up the latter in 1801. Detached from Hoxton, he was sought after by other educationalists, and was attracted to an offer to become the founding President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hosking
William Hosking (26 November 1800 – 2 August 1861) was an English writer, lecturer, and architect who had an important influence on the growth and development of London in Victorian times. He became the first Professor of Architecture at King's College London, and associated this discipline in a scholarly fashion with interests in town planning, civil engineering, history and antiquities. Early life Upbringing and early writings Hosking was born at Buckfastleigh in Devon, the son of a woolen manufacturer. In 1809 he emigrated with his parents to New South Wales (which joined the federation of Australia in 1901), where his father, whose business interests in Devon had been doing poorly, had accepted a government office. It was here that Hosking's architectural career began for he was apprenticed to a surveyor and builder. This profession continued to interest him when, in 1819, he returned to England to seek further training, becoming articled to a Wesleyan minister-turne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abney Park Chapel
Abney Park Chapel, is a Grade II Listed chapel, designed by William Hosking and built by John Jay that is situated in Europe's first wholly nondenominational cemetery, Abney Park Cemetery, London. Opened in May, 1840, it was the first nondenominational cemetery chapel in Europe (and probably the world – since the chapel at Mount Auburn was a later addition). It helped pioneer the early use of the Dissenting Gothic building style, and encouraged renewed interest in the careful blending of earlier styles. It was primarily the work of a small design team consisting of George Collison II (acting as client for the cemetery founders, with a passion for Mount Auburn Cemetery near Boston, and it is said, Beverley Minster which dominated the skyline in his ancestral town); William Hosking (architect and civil engineer with an interest in Egyptology, antiquities, and architectural writing and scholarship); the builder John Jay, and George Loddiges (botanical scientist and horticultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Chapel, Islington
Union Chapel is a working church, live entertainment venue and charity drop-in centre for the homeless in Islington, London, England. Built in the late 19th century in the Gothic revival style, the church is Grade I-listed. It is at the north end of Upper Street, near Highbury Fields. As a venue Union Chapel hosts live music, film, spoken word and comedy events. There are around 250 events per year. It was voted London's Best Live Music Venue by readers of '' Time Out'' magazine in 2002, 2012 and again in 2014. It has a reputation for great acoustics, thanks to its design. Margins Homelessness Project The Margins Project, based in the Union Chapel, provides a range of support services to people facing homelessness, crisis and isolation. It operates Monday & Wednesday drop-in that provides advice around accessing benefits, support showers and laundry facilities. There is also a Supported Employment Programme which provides opportunity for people who have experienced homelessne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Tabernacle
The Metropolitan Tabernacle is a large independent Reformed Baptist church in the Elephant and Castle in London. It was the largest non-conformist church of its day in 1861. The Tabernacle Fellowship have been worshipping together since 1650. Its first pastor was William Rider; other notable pastors and preachers include Benjamin Keach, John Gill, John Rippon and C. H. Spurgeon. The Tabernacle still worships and holds to its Biblical foundations and principles under its present pastor, Peter Masters. History The Tabernacle fellowship dates back to 1650, when the English Parliament banned independent Christian organisations from meeting together. This congregation braved persecution until 1688, when the Baptists were once again allowed to worship in freedom. At this point, the group built their first chapel, in the Tower Bridge area. In 1720, John Gill became pastor and served for 51 years. In 1771, John Rippon became pastor and served for 63 years. During these times, the chu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(cropped).jpg)

_(14758340366).jpg)
_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)