|
Dislocation Of Hip In Animals
Dislocation of hip (coxofemoral luxation) may occur in domestic animals. It is a not rare condition, usually unilateral, in: * cattle, among others, after calving. * dogs, resulting from trauma or as a complication of hip dysplasia. The same illness also exists in human medicine. The condition can be observed after the forced traction of fetus while delivery, slip of animal on a floor. More commonly seen in animals with poor nutrient ration at end stage of gestation which results in osteoporosis of bones & joints due to which the acetabulum notch become shallow and femur comes out if it while delivery, ketonemia also has adverse effect on coxo-femoral luxation. Symptoms In dogs, it occurs mainly in an upwards and forwards direction. Hence, the affected leg is shortened, and the greater trochanter prominent. In cattle, it occurs mainly craniodorsally or caudoventrally, but other directions are possible. A typical stance is seen in craniodorsal luxations, with a shortened limb, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hip Dysplasia (canine)
In dogs, hip dysplasia is an abnormal formation of the hip socket that, in its more severe form, can eventually cause lameness and arthritis of the joints. It is a genetic (polygenic) trait that is affected by environmental factors. It is common in many dog breeds, particularly the larger breeds, and is the most common single cause of arthritis of the hips. During growth, both the ball (the head of the femur, or thighbone) and the socket in the pelvis (acetabulum) must grow at equal rates. In hip dysplasia, this uniform growth during puppyhood does not occur. The result is laxity (looseness) of the joint, followed by degenerative joint disease (DJD) or osteoarthritis (OA), which is the body's attempt to stabilize the loose hip joint. Overview Normal hip anatomy In the normal anatomy of the hip joint, the almost spherical end of the femur head (the caput, or caput ossis femoris) fits into the acetabulum (a concave socket located in the pelvis). The bony surfaces of the femur he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dislocation Of Hip
A hip dislocation is when the thighbone (femur) separates from the hip bone (pelvis). Specifically it is when the ball–shaped head of the femur (femoral head) separates from its cup–shaped socket in the hip bone, known as the acetabulum. The joint of the femur and pelvis (hip joint) is very stable, secured by both bony and soft-tissue constraints. With that, dislocation would require significant force which typically results from Major trauma, significant trauma such as from a motor vehicle collision or from a Falling (accident), fall from elevation. Hip dislocations can also occur following a hip replacement or from a developmental abnormality known as hip dysplasia. Hip dislocations are classified by fracture association and by the positioning of the dislocated femoral head. A posteriorly positioned head is the most common dislocation type. Hip dislocations are a medical emergency, requiring prompt placement of the femoral head back into the acetabulum (Reduction (orthoped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
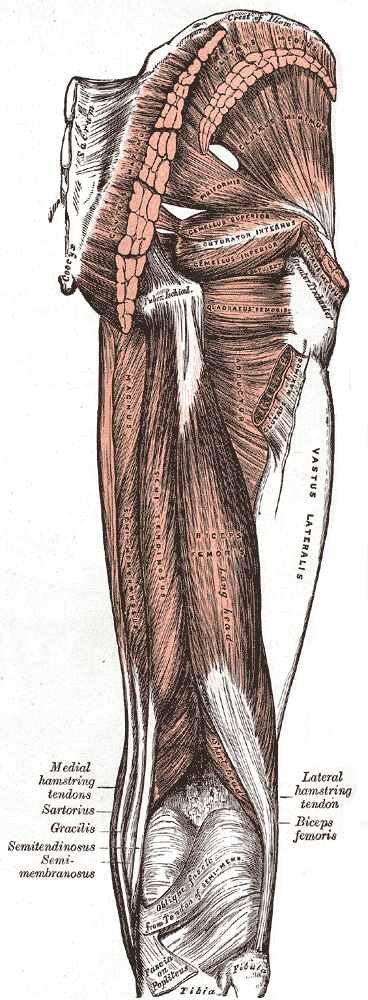
Greater Trochanter
The greater trochanter of the femur is a large, irregular, quadrilateral eminence and a part of the skeletal system. It is directed lateral and medially and slightly posterior. In the adult it is about 2–4 cm lower than the femoral head.Standring, Susan, editor. ''Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice''. Forty-First edition, Elsevier Limited, 2016, p. 1327. Because the pelvic outlet in the female is larger than in the male, there is a greater distance between the greater trochanters in the female. It has two surfaces and four borders. It is a traction epiphysis. Surfaces The ''lateral surface'', quadrilateral in form, is broad, rough, convex, and marked by a diagonal impression, which extends from the postero-superior to the antero-inferior angle, and serves for the insertion of the tendon of the gluteus medius. Above the impression is a triangular surface, sometimes rough for part of the tendon of the same muscle, sometimes smooth for the interposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |