|
Discrete Optimization
Discrete optimization is a branch of optimization in applied mathematics and computer science. As opposed to continuous optimization, some or all of the variables used in a discrete optimization problem are restricted to be discrete variables—that is, to assume only a discrete set of values, such as the integer An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative in ...s. Branches Three notable branches of discrete optimization are:. * combinatorial optimization, which refers to problems on graphs, matroids and other discrete structures * integer programming * constraint programming These branches are all closely intertwined however, since many combinatorial optimization problems can be modeled as integer programs (e.g. shortest path) or constraint programs, any constraint pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Optimization (mathematics)
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfields: discrete optimization and continuous optimization. Optimization problems arise in all quantitative disciplines from computer science and engineering to operations research and economics, and the development of solution methods has been of interest in mathematics for centuries. In the more general approach, an optimization problem consists of maxima and minima, maximizing or minimizing a Function of a real variable, real function by systematically choosing Argument of a function, input values from within an allowed set and computing the Value (mathematics), value of the function. The generalization of optimization theory and techniques to other formulations constitutes a large area of applied mathematics. Optimization problems Opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Applied Mathematics
Applied mathematics is the application of mathematics, mathematical methods by different fields such as physics, engineering, medicine, biology, finance, business, computer science, and Industrial sector, industry. Thus, applied mathematics is a combination of mathematical science and specialized knowledge. The term "applied mathematics" also describes the profession, professional specialty in which mathematicians work on practical problems by formulating and studying mathematical models. In the past, practical applications have motivated the development of mathematical theories, which then became the subject of study in pure mathematics where abstract concepts are studied for their own sake. The activity of applied mathematics is thus intimately connected with research in pure mathematics. History Historically, applied mathematics consisted principally of Mathematical analysis, applied analysis, most notably differential equations; approximation theory (broadly construed, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Continuous Optimization
Continuous optimization is a branch of optimization in applied mathematics. As opposed to discrete optimization, the variables used in the objective function are required to be continuous variables—that is, to be chosen from a set of real values between which there are no gaps (values from intervals of the real line). Because of this continuity assumption, continuous optimization allows the use of calculus Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations. Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the ... techniques. References Mathematical optimization {{Mathapplied-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
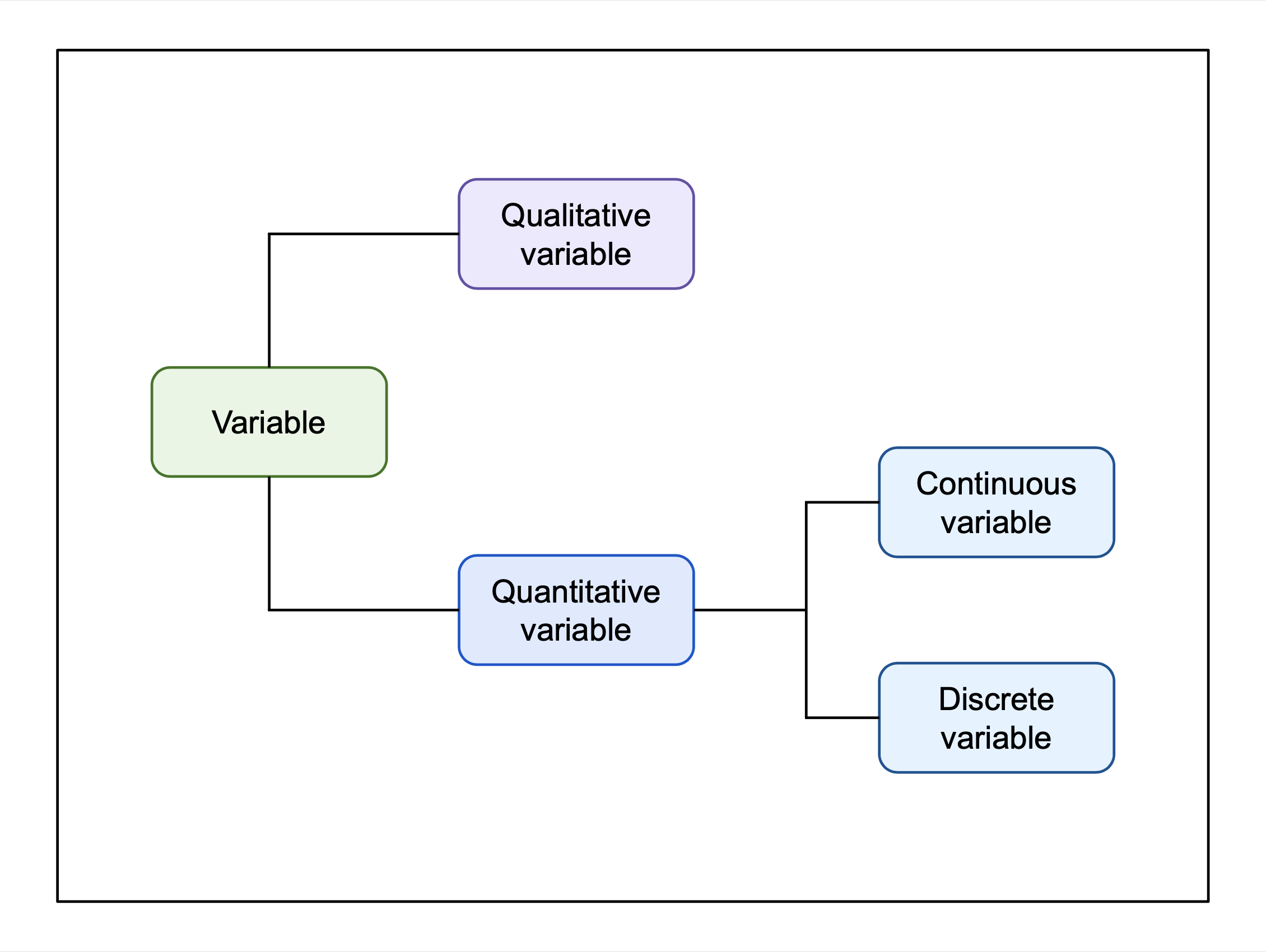
Variable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable (from Latin language, Latin ) is a Mathematical symbol, symbol, typically a letter, that refers to an unspecified mathematical object. One says colloquially that the variable ''represents'' or ''denotes'' the object, and that any valid candidate for the object is the value (mathematics), value of the variable. The values a variable can take are usually of the same kind, often numbers. More specifically, the values involved may form a Set (mathematics), set, such as the set of real numbers. The object may not always exist, or it might be uncertain whether any valid candidate exists or not. For example, one could represent two integers by the variables and and require that the value of the square of is twice the square of , which in algebraic notation can be written . A definitive proof that this relationship is impossible to satisfy when and are restricted to integer numbers isn't obvious, but it has been known since ancient times and has had a big ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Discrete Variable
In mathematics and statistics, a quantitative variable may be continuous or discrete. If it can take on two real values and all the values between them, the variable is continuous in that interval. If it can take on a value such that there is a non-infinitesimal gap on each side of it containing no values that the variable can take on, then it is discrete around that value. In some contexts, a variable can be discrete in some ranges of the number line and continuous in others. In statistics, continuous and discrete variables are distinct statistical data types which are described with different probability distributions. Continuous variable A continuous variable is a variable such that there are possible values between any two values. For example, a variable over a non-empty range of the real numbers is continuous if it can take on any value in that range. Methods of calculus are often used in problems in which the variables are continuous, for example in continuous optimi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Discrete Mathematics
Discrete mathematics is the study of mathematical structures that can be considered "discrete" (in a way analogous to discrete variables, having a bijection with the set of natural numbers) rather than "continuous" (analogously to continuous functions). Objects studied in discrete mathematics include integers, Graph (discrete mathematics), graphs, and Statement (logic), statements in Mathematical logic, logic. By contrast, discrete mathematics excludes topics in "continuous mathematics" such as real numbers, calculus or Euclidean geometry. Discrete objects can often be enumeration, enumerated by integers; more formally, discrete mathematics has been characterized as the branch of mathematics dealing with countable sets (finite sets or sets with the same cardinality as the natural numbers). However, there is no exact definition of the term "discrete mathematics". The set of objects studied in discrete mathematics can be finite or infinite. The term finite mathematics is sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative integers. The set (mathematics), set of all integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the set of natural numbers, the set of integers \mathbb is Countable set, countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fraction, fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , 5/4, and Square root of 2, are not. The integers form the smallest Group (mathematics), group and the smallest ring (mathematics), ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Combinatorial Optimization
Combinatorial optimization is a subfield of mathematical optimization that consists of finding an optimal object from a finite set of objects, where the set of feasible solutions is discrete or can be reduced to a discrete set. Typical combinatorial optimization problems are the travelling salesman problem ("TSP"), the minimum spanning tree problem ("MST"), and the knapsack problem. In many such problems, such as the ones previously mentioned, exhaustive search is not tractable, and so specialized algorithms that quickly rule out large parts of the search space or approximation algorithms must be resorted to instead. Combinatorial optimization is related to operations research, algorithm theory, and computational complexity theory. It has important applications in several fields, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, auction theory, software engineering, VLSI, applied mathematics and theoretical computer science. Applications Basic applications of combina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Graph (discrete Mathematics)
In discrete mathematics, particularly in graph theory, a graph is a structure consisting of a Set (mathematics), set of objects where some pairs of the objects are in some sense "related". The objects are represented by abstractions called ''Vertex (graph theory), vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') and each of the related pairs of vertices is called an ''edge'' (also called ''link'' or ''line''). Typically, a graph is depicted in diagrammatic form as a set of dots or circles for the vertices, joined by lines or curves for the edges. The edges may be directed or undirected. For example, if the vertices represent people at a party, and there is an edge between two people if they shake hands, then this graph is undirected because any person ''A'' can shake hands with a person ''B'' only if ''B'' also shakes hands with ''A''. In contrast, if an edge from a person ''A'' to a person ''B'' means that ''A'' owes money to ''B'', then this graph is directed, because owing mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Matroid
In combinatorics, a matroid is a structure that abstracts and generalizes the notion of linear independence in vector spaces. There are many equivalent ways to define a matroid Axiomatic system, axiomatically, the most significant being in terms of: independent sets; bases or circuits; rank functions; closure operators; and closed sets or ''flats''. In the language of partially ordered sets, a finite simple matroid is equivalent to a geometric lattice. Matroid theory borrows extensively from the terms used in both linear algebra and graph theory, largely because it is the abstraction of various notions of central importance in these fields. Matroids have found applications in geometry, topology, combinatorial optimization, network theory, and coding theory. Definition There are many Cryptomorphism, equivalent ways to define a (finite) matroid. Independent sets In terms of independence, a finite matroid M is a pair (E, \mathcal), where E is a finite set (called the ''gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Integer Programming
An integer programming problem is a mathematical optimization or feasibility program in which some or all of the variables are restricted to be integers. In many settings the term refers to integer linear programming (ILP), in which the objective function and the constraints (other than the integer constraints) are linear. Integer programming is NP-complete. In particular, the special case of 0–1 integer linear programming, in which unknowns are binary, and only the restrictions must be satisfied, is one of Karp's 21 NP-complete problems. If some decision variables are not discrete, the problem is known as a mixed-integer programming problem. Canonical and standard form for ILPs In integer linear programming, the ''canonical form'' is distinct from the ''standard form''. An integer linear program in canonical form is expressed thus (note that it is the \mathbf vector which is to be decided): : \begin & \underset && \mathbf^\mathrm \mathbf\\ & \text && A \mathbf \le \mathbf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |