|
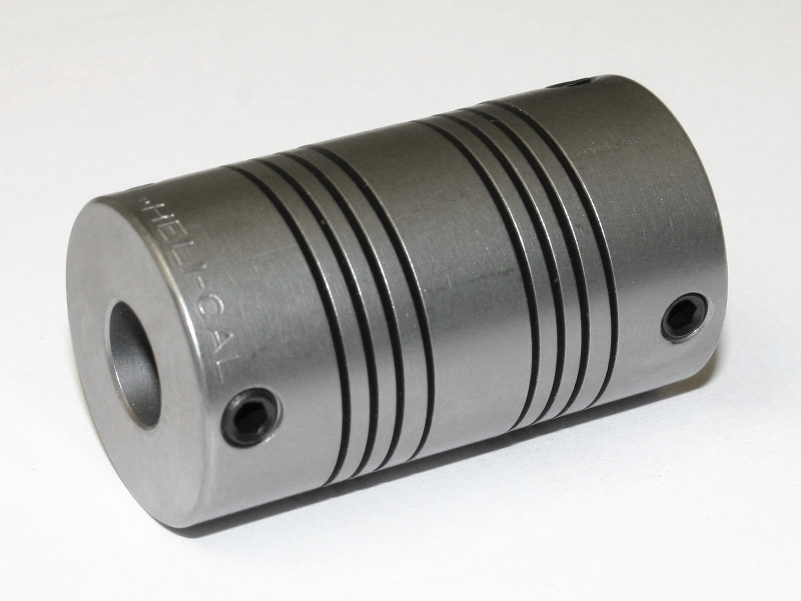
Disc Coupling
A disc coupling, by definition, transmits torque from a driving to a driven bolt or shaft tangentially on a common bolt circle. Torque is transmitted between the bolts through a series of thin, stainless steel discs assembled in a pack. Misalignment is accomplished by deforming of the material between the bolts. A disc coupling is a high performance motion control (servo) coupling designed to be the torque transmitting element (by connecting two shafts together) while accommodating for shaft misalignment. It is designed to be flexible, while remaining torsionally strong under high torque loads. Typically, disc couplings can handle speeds up to 10,000 r/min. Types There are two different styles of disc coupling: * Single disc style couplings are composed of two hubs (the ends of the coupling, which are typically made from aluminum, but stainless steel is used as well) and a single, flat, stainless steel disc spring. * Double disc style couplings are also composed of two hubs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of the body. The concept originated with the studies by Archimedes of the usage of levers, which is reflected in his famous quote: "''Give me a lever and a place to stand and I will move the Earth''". Just as a linear force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist to an object around a specific axis. Torque is defined as the product of the magnitude of the perpendicular component of the force and the distance of the line of action of a force from the point around which it is being determined. The law of conservation of energy can also be used to understand torque. The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
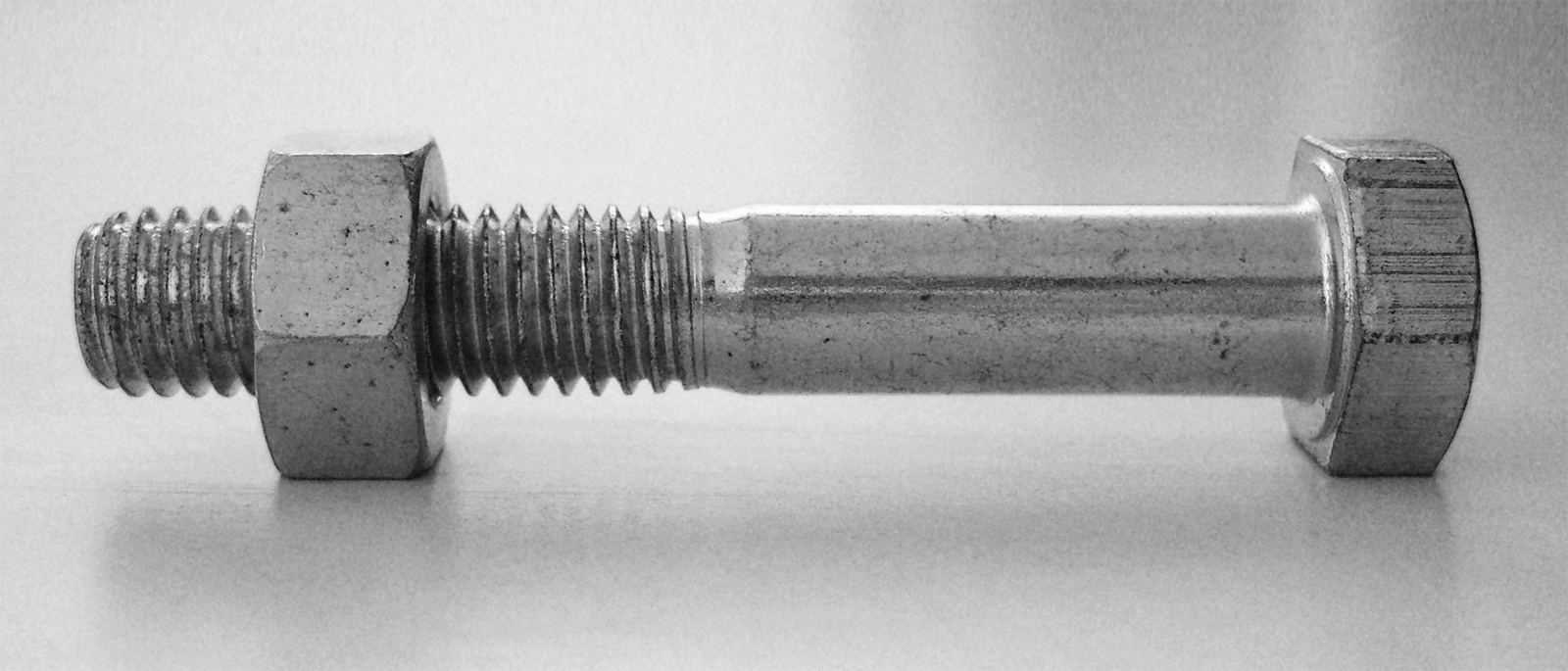
Bolt (fastener)
A bolt is a form of threaded fastener with an external male thread requiring a matching pre-formed female thread such as a nut. Bolts are very closely related to screws. Bolts vs. screws The distinction between a bolt and a screw is poorly-defined. The academic distinction, per ''Machinery's Handbook'', is in their intended design: bolts are designed to pass through an unthreaded hole in a component and be fastened with the aid of a nut, although such a fastener can be used without a nut to tighten into a threaded component such as a nut-plate or tapped housing. Screws in contrast are used in components which contain their own thread, or to cut its own internal thread into them. This definition allows ambiguity in the description of a fastener depending on the application it is actually used for, and the terms screw and bolt are widely used by different people or in different countries to apply to the same or varying fastener. Bolts are often used to make a bolted joint. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaft (mechanical Engineering)
A shaft is a rotating machine element, usually circular in cross section, which is used to transmit power from one part to another, or from a machine which produces power to a machine which absorbs power. Types They are mainly classified into two types. * Transmission shafts are used to transmit power between the source and the machine absorbing power; e.g. counter shafts and line shafts. * Machine shafts are the integral part of the machine itself; e.g. crankshaft. *Axle shaft. *Spindle shaft. Materials The material used for ordinary shafts is mild steel. When high strength is required, an alloy steel such as nickel, nickel-chromium or chromium-vanadium steel is used. Shafts are generally formed by hot rolling and finished to size by cold drawing or turning and grinding. Standard sizes Source:Mahadevan K and Reddy K.Balaveera, (2015), 'Design data hand book', CBS publishers and Distributors (P) ltd., New-Delhi, Machine shafts * Up to 25 mm steps of 0.5 mm Transmission sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolt Circle
A bolt circle diameter or pitch circle diameter (PCD), sometimes simply called bolt circle or pitch circle, is a common term for when a number of screw holes for bolts are evenly distributed with their centers along an imaginary circle with a given diameter. An example of use is mounting of car rims, where the bolt circle is one of several factors that determine whether a set of rims will fit a car. For example, a bolt circle of 5×130 or 5-130 indicates that a rim is to be attached to the car via 5 screws evenly spaced along a circle with a diameter of 130 millimeters. Other common uses for bolt circles are for indicating mounting for sim racing and real-world car steering wheels, or in the industry for mounting of servomotors or for specifying the bolt pattern of a flange. Attachment of chain rings for bicycle cranksets are also specified by a bolt circle. Examples Racing wheels On steering wheels for cars utilizing bolt circles, this usually measures 6×70 mm. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corrosion resistance, resistance to corrosion results from the chromium, which forms a Passivation (chemistry), passive film that can protect the material and self-healing material, self-heal in the presence of oxygen. The alloy's properties, such as luster and resistance to corrosion, are useful in many applications. Stainless steel can be rolled into Sheet metal, sheets, plates, bars, wire, and tubing. These can be used in cookware, cutlery, surgical instruments, major appliances, vehicles, construction material in large buildings, industrial equipment (e.g., in paper mills, chemical plants, water treatment), and storage tanks and tankers for chemicals and food products. The biological cleanability of stainless steel is superior to both alumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Servomechanism
In control engineering a servomechanism, usually shortened to servo, is an automatic device that uses error-sensing negative feedback to correct the action of a mechanism. On displacement-controlled applications, it usually includes a built-in encoder or other position feedback mechanism to ensure the output is achieving the desired effect. The term correctly applies only to systems where the feedback or error-correction signals help control mechanical position, speed, attitude or any other measurable variables. For example, an automotive power window control is not a servomechanism, as there is no automatic feedback that controls position—the operator does this by observation. By contrast a car's cruise control uses closed-loop feedback, which classifies it as a servomechanism. Applications Position control A common type of servo provides ''position control''. Commonly, servos are electric, hydraulic, or pneumatic. They operate on the principle of negative feedback, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coupling
A coupling is a device used to connect two shafts together at their ends for the purpose of transmitting power. The primary purpose of couplings is to join two pieces of rotating equipment while permitting some degree of misalignment or end movement or both. In a more general context, a coupling can also be a mechanical device that serves to connect the ends of adjacent parts or objects. Couplings do not normally allow disconnection of shafts during operation, however there are torque limiter, torque-limiting couplings which can slip or disconnect when some torque limit is exceeded. Selection, installation and maintenance of couplings can lead to reduced maintenance time and maintenance cost. Uses Shaft couplings are used in machinery for several purposes. A primary function is to transfer power from one end to another end (ex: motor transfer power to pump through coupling). Other common uses: * To alter the vibration characteristics of rotating units * To connect the driving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driveshaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them. As torque carriers, drive shafts are subject to torsion and shear stress, equivalent to the difference between the input torque and the load. They must therefore be strong enough to bear the stress, while avoiding too much additional weight as that would in turn increase their inertia. To allow for variations in the alignment and distance between the driving and driven components, drive shafts frequently incorporate one or more universal joints, jaw couplings, or rag joints, and sometimes a splined joint or prismatic joint. History The term ''driveshaft'' first appeared during the mid-19th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaft Alignment
Shaft alignment is the process of aligning two or more shafts with each other to within a tolerated margin. The resulting fault if alignment is not achieved within the demanded specifications is shaft misalignment, which may be offset or angular. Faults can lead to premature wear and damage to systems. Background When a driver like an electric motor or a turbine is coupled to a pump, generator, or any other piece of equipment, the shafts of the two pieces must be aligned. Any misalignment increases the stress on the shafts and will almost certainly result in excessive wear and premature breakdown of the equipment. This can be very costly. When the equipment is down, production requiring the equipment may be delayed. Bearings or mechanical seals may be damaged and need to be replaced. Shaft alignment is the process of aligning two or more shafts with each other to within a tolerated margin. The process is used for machinery before the machinery is put in service. Technology B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torsion (mechanics)
In the field of solid mechanics, torsion is the twisting of an object due to an applied torque. Torsion is expressed in either the pascal (Pa), an SI unit for newtons per square metre, or in pounds per square inch (psi) while torque is expressed in newton metres (N·m) or foot-pound force (ft·lbf). In sections perpendicular to the torque axis, the resultant shear stress in this section is perpendicular to the radius. In non-circular cross-sections, twisting is accompanied by a distortion called warping, in which transverse sections do not remain plane. For shafts of uniform cross-section unrestrained against warping, the torsion is: : T = \frac \tau= \frac G \varphi where: * ''T'' is the applied torque or moment of torsion in Nm. * \tau (tau) is the maximum shear stress at the outer surface * ''J''T is the torsion constant for the section. For circular rods, and tubes with constant wall thickness, it is equal to the polar moment of inertia of the section, but for other shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionless unit equal to 1, which it refers to as a revolution, but does not define the revolution as a unit. It defines a unit of rotational frequency equal to s−1. The superseded standard ISO 80000-3:2006 did however state with reference to the unit name 'one', symbol '1', that "The special name revolution, symbol r, for this unit is widely used in specifications on rotating machines." The International System of Units (SI) does not recognize rpm as a unit, and defines the unit of frequency, Hz, as equal to s−1. :\begin 1~&\text &&=& 60~&\text \\ \frac~&\text &&=& 1~&\text \end A corresponding but distinct quantity for describing rotation is angular velocity, for which the SI unit is the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compliant Mechanism
In mechanical engineering, a compliant mechanism is a flexible mechanism that achieves force and motion transmission through elastic body deformation. It gains some or all of its motion from the relative flexibility of its members rather than from rigid-body joints alone. These may be monolithic (single-piece) or jointless structures. Some common devices that use compliant mechanisms are backpack latches and paper clips. One of the oldest examples of using compliant structures is the bow and arrow. Design methods Compliant mechanisms are usually designed using two techniques: Kinematics approach Kinematic analysis can be used to design a compliant mechanism by creating a pseudo- rigid-body model of the mechanism. In this model, flexible segments are modeled as rigid links connected to revolute joints with torsional springs. Other structures can be modeled as a combination of rigid links, springs, and dampers. Structural optimization approach In this method, computationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |