|
Diphenylcyclopropenone
Diphenylcyclopropenone (diphencyprone) is a topically administered experimental drug intended for treating alopecia areata and alopecia totalis. Topical immunotherapy using diphenylcyclopropenone may also be an effective treatment option for recalcitrant warts. It is not approved by either the Food and Drug Administration or the European Medicines Agency. Mechanism of action Diphenylcyclopropenone triggers an immune response that is thought to oppose the action of the autoreactive cells that otherwise cause hair loss. One hypothesis is that in response to DPCP treatment, the body will attempt to downregulate inflammation through a variety of pathways, resulting in a downregulation of the autoimmune response at the hair follicle. This autoinflammatory reaction would otherwise destroy body's hair follicles. Studies A study of 41 alopecia areata patients showed significant hair regrowth in 40% at 6 months, being sustained in two thirds of these after a 12-month-follow up-period. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopropenone
Cyclopropenone is an organic compound with molecular formula C3H2O consisting of a cyclopropene carbon framework with a ketone functional group. It is a colorless, volatile liquid that boils near room temperature. Neat cyclopropenone polymerizes upon standing at room temperature. The chemical properties of the compound are dominated by the strong polarization of the carbonyl group, which gives a partial positive charge with aromatic stabilization on the ring and a partial negative charge on oxygen. It is an aromatic compound. See also * Diphenylcyclopropenone * Deltic acid *Tropone Tropone or 2,4,6-cycloheptatrien-1-one is an organic compound with some importance in organic chemistry as a non-benzenoid aromatic. The compound consists of a ring of seven carbon atoms with three conjugated alkene groups and a ketone group. Th ... References {{Molecules detected in outer space Enones Simple aromatic rings Cyclopropenes Non-benzenoid aromatic carbocycles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topical Administration
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes including creams, foams, gels, lotions, and ointments. Many topical medications are epicutaneous, meaning that they are applied directly to the skin. Topical medications may also be inhalational, such as asthma medications, or applied to the surface of tissues other than the skin, such as eye drops applied to the conjunctiva, or ear drops placed in the ear, or medications applied to the surface of a tooth. The word ''topical'' derives from Greek τοπικός ''topikos'', "of a place". Justification Topical drug delivery is a route of administering drugs via the skin to provide topical therapeutic effects. As skin is one of the largest and most superficial organs in the human body, pharmacists utilise it to deliver various drugs. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalyl Chloride
Oxalyl chloride is an organic chemical compound with the formula (COCl)2. This colorless, sharp-smelling liquid, the diacyl chloride of oxalic acid, is a useful reagent in organic synthesis. Preparation Oxalyl chloride was first prepared in 1892 by the French chemist Adrien Fauconnier, who reacted diethyl oxalate with phosphorus pentachloride. It can also be prepared by treating oxalic acid with phosphorus pentachloride. Oxalyl chloride is produced commercially from ethylene carbonate. Photochlorination gives the tetrachloride, which is subsequently degraded: :C2H4O2CO + 4 Cl2 → C2Cl4O2CO + 4 HCl :C2Cl4O2CO → C2O2Cl2 + COCl2 Reactions Oxalyl chloride reacts with water giving off gaseous products only: hydrogen chloride (HCl), carbon dioxide (CO2), and carbon monoxide (CO). : In this, it is quite different from other acyl chlorides which hydrolyze with formation of hydrogen chloride and the original carboxylic acid. Applications in organic synthesis Oxidation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketones
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' is methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids (e.g., testosterone), and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considered ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzophenone
Benzophenone is the organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CO, generally abbreviated Ph2CO. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. Benzophenone is a widely used building block in organic chemistry, being the parent diarylketone. Uses Benzophenone can be used as a photo initiator in UV(Ultra-violet)-curing applications such as inks, imaging, and clear coatings in the printing industry. Benzophenone prevents ultraviolet ( UV) light from damaging scents and colors in products such as perfumes and soaps. Benzophenone can also be added to plastic packaging as a UV blocker to prevent photo-degradation of the packaging polymers or its contents. Its use allows manufacturers to package the product in clear glass or plastic (such as a PETE water bottle). Without it, opaque or dark packaging would be required. In biological applications, benzophenones have been used extensively as photophysical probes to identify and map peptide–protein interactions. Benzophenone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Reagents For Organic Synthesis
The ''Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis'' is published in print and online by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. The online version is also known as e-EROS. The encyclopedia contains a description of the use of reagents used in organic chemistry. The eight-volume print version includes 3500 alphabetically arranged articles and the online version is regularly updated to include new reagents and catalyst Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...s. References External links *Print version Encyclopedias of science Chemistry books {{encyclopedia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus Pentachloride
Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive and moisture-sensitive solid, although commercial samples can be yellowish and contaminated with hydrogen chloride. Structure The structures for the phosphorus chlorides are invariably consistent with VSEPR theory. The structure of PCl5 depends on its environment. Gaseous and molten PCl5 is a neutral molecule with trigonal bipyramidal geometry and (''D''3h) symmetry. The hypervalent nature of this species (as well as of , see below) can be explained with the inclusion of non-bonding molecular orbitals (molecular orbital theory) or resonance (valence bond theory). This trigonal bipyramidal structure persists in nonpolar solvents, such as CS2 and CCl4. In the solid state PCl5 is an ionic compound, formulated . In solutions of polar solvents, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thionyl Chloride
Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a moderately volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately per year being produced during the early 1990s, but is occasionally also used as a solvent. It is toxic, reacts with water, and is also listed under the Chemical Weapons Convention as it may be used for the production of chemical weapons. Thionyl chloride is sometimes confused with sulfuryl chloride, , but the properties of these compounds differ significantly. Sulfuryl chloride is a source of chlorine whereas thionyl chloride is a source of chloride ions. Production The major industrial synthesis involves the reaction of sulfur trioxide and sulfur dichloride: This synthesis can be adapted to the laboratory by heating oleum to slowly distill the sulfur trioxide into a cooled flask of sulfur dichloride. :SO3 + SCl2 -> SOCl2 + SO2 Other methods includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing bonding in certain molecules or polyatomic ions by the combination of several contributing structures (or ''forms'', also variously known as ''resonance structures'' or ''canonical structures'') into a resonance hybrid (or ''hybrid structure'') in valence bond theory. It has particular value for analyzing delocalized electrons where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis structure. Overview Under the framework of valence bond theory, resonance is an extension of the idea that the bonding in a chemical species can be described by a Lewis structure. For many chemical species, a single Lewis structure, consisting of atoms obeying the octet rule, possibly bearing formal charges, and connected by bonds of positive integer order, is sufficient for describing the chemical bonding and rationalizing experimentally determined molecular properties like bond lengths, angles, and dipole moment. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
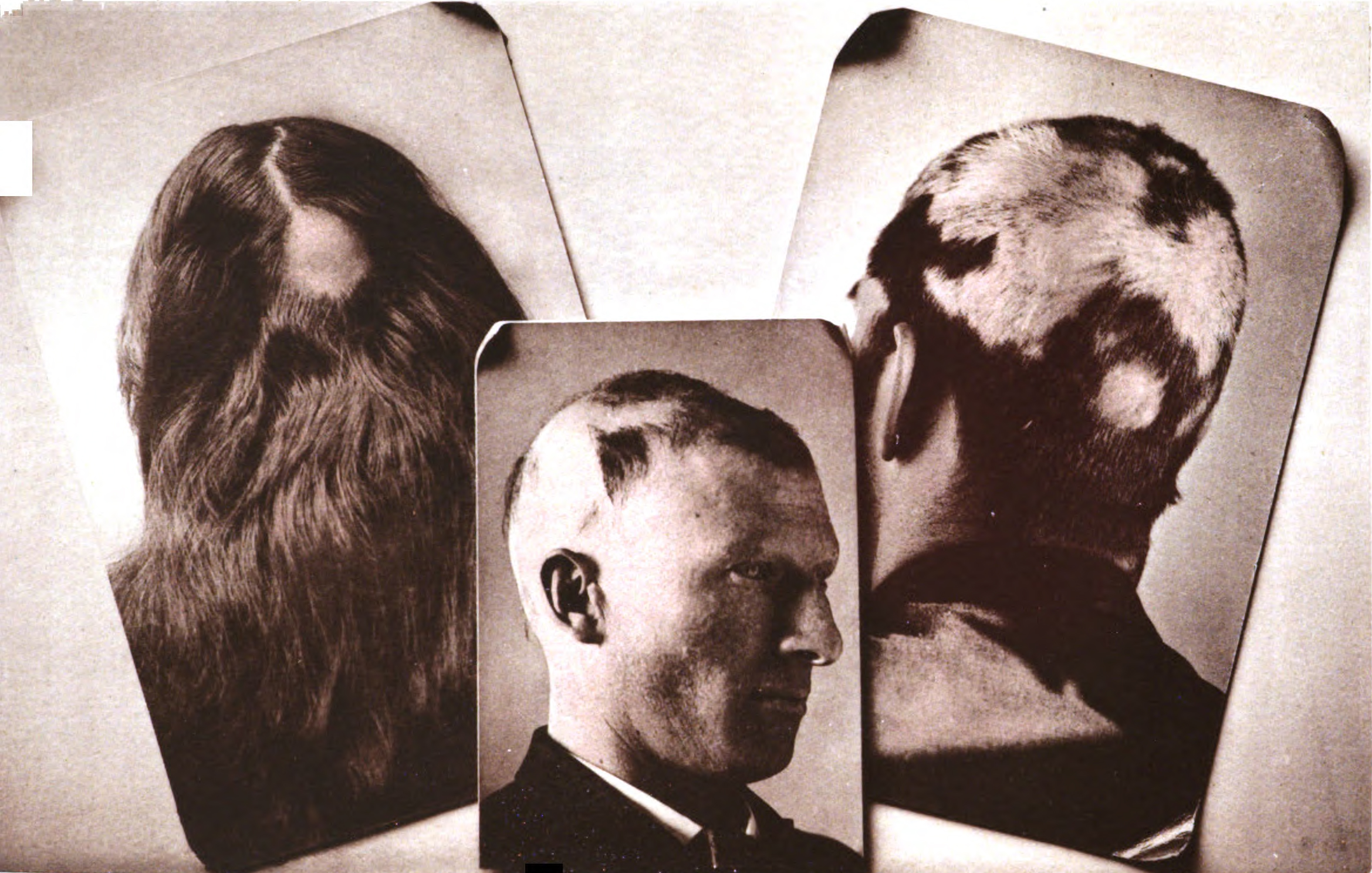
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata, also known as spot baldness, is a condition in which hair is lost from some or all areas of the body. Often, it results in a few bald spots on the scalp, each about the size of a coin. Psychological stress and illness are possible factors in bringing on alopecia areata in individuals at risk, but in most cases there is no obvious trigger. People are generally otherwise healthy. In a few cases, all the hair on the scalp is lost ('' alopecia totalis''), or all body hair is lost (''alopecia universalis''). Hair loss can be permanent, or temporary. It is distinct from pattern hair loss, which is common among males. Alopecia areata is believed to be an autoimmune disease resulting from a breach in the immune privilege of the hair follicles. Risk factors include a family history of the condition. Among identical twins, if one is affected, the other has about a 50% chance of also being affected. The underlying mechanism involves failure by the body to recognize i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromaticity
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to saturated compounds having single bonds, and other geometric or connective non-cyclic arrangements with the same set of atoms. Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. Organic compounds that are not aromatic are classified as aliphatic compounds—they might be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have enhanced stability. The term ''aromaticity'' with this meaning is historically related to the concept of having an aroma, but is a distinct property from that meaning. Since the most common aromatic compounds are derivatives of benzene (an aromatic hydrocarbon common in petroleum and its distillates), the word ''aromatic'' occasionally refers informally to benzene derivatives, and so it was first defined. Nevertheless, many non-be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)