|
Diffuse Supernova Neutrino Background
The diffuse supernova neutrino background (DSNB) is a theoretical population of neutrinos (and anti-neutrinos) cumulatively originating from all of the supernovae events which have occurred throughout the Universe. Sources An individual supernova will release as many as 10^ neutrinos, which is detectable as a short burst of events on Earth provided that the supernova occurred close by enough: Within our own galaxy or one of its satellite galaxies, the only current example of which is SN1987A. In contrast the DSNB is a continuous source of neutrino events for which currently only experimental upper limits exist e.g. from the Super Kamiokande experiment at a level of 2.9 \bar \, \mathrm^ \, \mathrm^ for neutrino energies above 17.3 MeV. Predicted detections Theoretical predictions for the flux of the DSNB on Earth are difficult as they depend on many different parameters and assumptions e.g. the rate of supernovae events in the Universe as a function of time, the star formation r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles excluding massless particles. The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the strong interaction. Thus, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and undetected. Weak interactions create neutrinos in one of three leptonic flavors: electron neutrinos muon neutrinos (), or tau neutrinos (), in association with the corresponding charged lepton. Although neutrinos were long believed to be massless, it is now known that there are three discrete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Nuclear And Particle Science
Annual may refer to: * Annual publication, periodical publications appearing regularly once per year **Yearbook A yearbook, also known as an annual, is a type of a book published annually. One use is to record, highlight, and commemorate the past year of a school. The term also refers to a book of statistics or facts published annually. A yearbook often ... ** Literary annual * Annual plant * Annual report * Annual giving * Annual, Morocco, a settlement in northeastern Morocco * Annuals (band), a musical group See also * Annual Review (other) * Circannual cycle, in biology {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernova Neutrinos
Supernova neutrinos are weakly interactive elementary particles produced during a core-collapse supernova explosion. A massive star collapses at the end of its life, emitting of the order of 1058 neutrinos and antineutrinos in all lepton flavors. The luminosity of different neutrino and antineutrino species are roughly the same. They carry away about 99% of the gravitational energy of the dying star as a burst lasting tens of seconds. The typical supernova neutrino energies are 10–20 MeV. Supernovae are considered the strongest and most frequent source of cosmic neutrinos in the MeV energy range. Since neutrinos are generated in the core of a supernova, they play a crucial role in the star's collapse and explosion. Neutrino heating is believed to be a critical factor in supernova explosions. Therefore, observation of neutrinos from supernova provides detailed information about core collapse and the explosion mechanism. Further, neutrinos undergoing collective flavor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Galaxy
A satellite galaxy is a smaller companion galaxy that travels on bound orbits within the gravitational potential of a more massive and luminous host galaxy (also known as the primary galaxy). Satellite galaxies and their constituents are bound to their host galaxy, in the same way that planets within our own solar system are gravitationally bound to the Sun. While most satellite galaxies are dwarf galaxies, satellite galaxies of large galaxy clusters can be much more massive. The Milky Way is orbited by about fifty satellite galaxies, the largest of which is the Large Magellanic Cloud. Moreover, satellite galaxies are not the only astronomical objects that are gravitationally bound to larger host galaxies (see globular clusters). For this reason, astronomers have defined galaxies as gravitationally bound collections of stars that exhibit properties that cannot be explained by a combination of baryonic matter (i.e. ordinary matter) and Newton's laws of gravity. For example, meas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SN1987A
SN 1987A was a type II supernova in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It occurred approximately from Earth and was the closest observed supernova since Kepler's Supernova. 1987A's light reached Earth on February 23, 1987, and as the earliest supernova discovered that year, was labeled "1987A". Its brightness peaked in May, with an apparent magnitude of about 3. It was the first supernova that modern astronomers were able to study in great detail, and its observations have provided much insight into core-collapse supernovae. SN 1987A provided the first opportunity to confirm by direct observation the radioactive source of the energy for visible light emissions, by detecting predicted gamma-ray line radiation from two of its abundant radioactive nuclei. This proved the radioactive nature of the long-duration post-explosion glow of supernovae. For over thirty years, the expected collapsed neutron star could not be found, but in 2019, indirect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
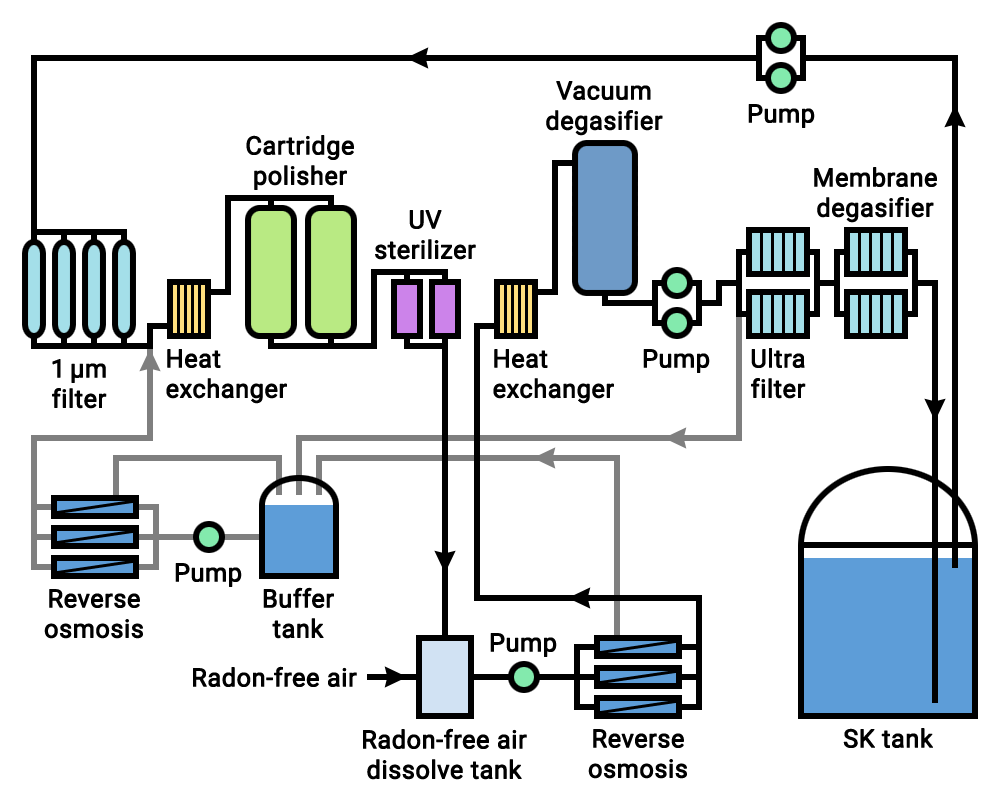
Super Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande (abbreviation of Super-Kamioka Neutrino Detection Experiment, also abbreviated to Super-K or SK; ja, スーパーカミオカンデ) is a neutrino observatory located under Mount Ikeno near the city of Hida, Gifu Prefecture, Japan. It is located underground in the Mozumi Mine in Hida's Kamioka area. The observatory was designed to detect high-energy neutrinos, to search for proton decay, study solar and atmospheric neutrinos, and keep watch for supernovae in the Milky Way Galaxy. It consists of a cylindrical stainless steel tank about in height and diameter holding 50,000 metric tons (55,000 US tons) of ultrapure water. Mounted on an inside superstructure are about 13,000 photomultiplier tubes that detect light from Cherenkov radiation. A neutrino interaction with the electrons or nuclei of water can produce an electron or positron that moves faster than the speed of light in water, which is slower than the speed of light in a vacuum. This creates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Neutrino Background
The cosmic neutrino background (CNB or CB) is the universe's background particle radiation composed of neutrinos. They are sometimes known as relic neutrinos. The CB is a relic of the Big Bang; while the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) dates from when the universe was 379,000 years old, the CB decoupled (separated) from matter when the universe was just one second old. It is estimated that today, the CB has a temperature of roughly . As neutrinos rarely interact with matter, these neutrinos still exist today. They have a very low energy, around 10 to 10 eV. Even high energy neutrinos are notoriously difficult to detect, and the CB has energies around 1010 times smaller, so the CB may not be directly observed in detail for many years, if at all. However, Big Bang cosmology makes many predictions about the CB, and there is very strong indirect evidence that the CB exists. Derivation of the CB temperature Given the temperature of the cosmic microwave ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernovae
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. Supernovae are more energetic than novae. In Latin, ''nova'' means "new", referring astronomically to what appears to be a temporary new bright star. Adding the prefix "super-" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word ''supernova'' was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1929. The last supernova to be directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appeari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |