|
Didsbury Village Metrolink Station
Didsbury Village is a tram stop on the South Manchester Line on the light-rail Metrolink network in Greater Manchester, England. It serves the South Manchester suburb of Didsbury. History The Manchester South District Line was opened by the Midland Railway in 1880. Originally, Didsbury was served by Didsbury railway station, which was located opposite Didsbury Library on Wilmslow Road, approximately further north along the line from the present tram stop. The railway station was closed in 1967 as part of the Beeching cuts and was demolished in 1982, and the old railway line lay derelict for several decades. In 1984, Greater Manchester Council and GMPTE announced the ''Project Light Rail'' scheme to develop a new light rail/tram system by re-opening use of disused railway lines in the region, including the route through Didsbury. The first phase of the Manchester Metrolink system opened in 1992, but it was not until 2013 that the network was expanded to reach Didsbury, as par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester Metrolink
Manchester Metrolink (branded locally simply as Metrolink) is a tram/ light rail system in Greater Manchester, England. The network has 99 stops along of standard-gauge route, making it the most extensive light rail system in the United Kingdom. Metrolink is owned by the public body Transport for Greater Manchester (TfGM) and operated and maintained under contract by a Keolis/ Amey consortium. In 2021/22, 26 million passenger journeys were made on the system. The network consists of eight lines which radiate from Manchester city centre to termini at Altrincham, Ashton-under-Lyne, Bury, East Didsbury, Eccles, Manchester Airport, Rochdale and Trafford Centre. It runs on a mixture of on-street track shared with other traffic; reserved track sections segregated from other traffic, and converted former railway lines. Metrolink is operated by a fleet of 147 high-floor Bombardier M5000 light rail vehicles. Each service runs to a 12-minute headway; stops with more than one serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beeching Cuts
The Beeching cuts (also Beeching Axe) was a plan to increase the efficiency of the nationalised British Rail, railway system in Great Britain. The plan was outlined in two reports: ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the Major Railway Trunk Routes'' (1965), written by Richard Beeching and published by the British Railways Board. The first report identified 2,363 stations and of railway line for closure, amounting to 55% of stations, 30% of route miles, and 67,700 British Rail positions, with an objective of stemming the large losses being incurred during a period of increasing competition from road transport and reducing the rail subsidies necessary to keep the network running. The second report identified a small number of major routes for significant investment. The 1963 report also recommended some less well-publicised changes, including a switch to the now-standard practice of containerisation for rail freight, and the replacement of some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tram Stops In Manchester
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are called tramways or simply trams/streetcars. Many recently built tramways use the contemporary term light rail. The vehicles are called streetcars or trolleys (not to be confused with trolleybus) in North America and trams or tramcars elsewhere. The first two terms are often used interchangeably in the United States, with ''trolley'' being the preferred term in the eastern US and ''streetcar'' in the western US. ''Streetcar'' or ''tramway'' are preferred in Canada. In parts of the United States, internally powered buses made to resemble a streetcar are often referred to as "trolleys". To avoid further confusion with trolley buses, the American Public Transportation Association (APTA) refers to them as "trolley-replica buses". In the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trackbed
The track bed or trackbed is the groundwork onto which a railway track is laid. Trackbeds of disused railways are sometimes used for recreational paths or new light rail links. According to Network Rail, the trackbed is the layers of ballast and sub-ballast above a prepared subgrade/formation (see diagram). It is designed primarily to reduce the stress on the subgrade. Other definitions include the surface of the ballast on which the track is laid,, p. 386. the area left after a track has been dismantled and the ballast removed or the track formation beneath the ballast and above the natural ground. The trackbed can significantly influence the performance of the track, especially ride quality of passenger services. See also * Embankment (transportation) * Roadbed * Subgrade In transport engineering, subgrade is the native material underneath a constructed road,http://www.highwaysmaintenance.com/drainage.htm The Idiots' Guide to Highways Maintenance ''highwaysmaintenence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are called tramways or simply trams/streetcars. Many recently built tramways use the contemporary term light rail. The vehicles are called streetcars or trolleys (not to be confused with trolleybus) in North America and trams or tramcars elsewhere. The first two terms are often used interchangeably in the United States, with ''trolley'' being the preferred term in the eastern US and ''streetcar'' in the western US. ''Streetcar'' or ''tramway'' are preferred in Canada. In parts of the United States, internally powered buses made to resemble a streetcar are often referred to as "trolleys". To avoid further confusion with trolley buses, the American Public Transportation Association (APTA) refers to them as "trolley-replica buses". In the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GMPTE
Greater Manchester Passenger Transport Executive was the public body responsible for public transport in Greater Manchester between 1974 and 2011, when it became part of Transport for Greater Manchester. SELNEC PTE Until 1969, the conurbation surrounding Manchester was divided between the two administrative counties of Lancashire and Cheshire and a number of county boroughs, such as Manchester, Salford, Stockport or Bolton. To comply with the Transport Act 1968, on 1 April 1969 the SELNEC Passenger Transport Executive was formed. ''SELNEC'' stood for ''South East Lancashire North East Cheshire'', a joint authority of the various local councils. From 1 November 1969, the PTE took over the bus fleets of 11 municipalities, and operationally, the organisation was split into three divisional areas, Northern, Central, and Southern: Northern *Bolton Corporation (249 vehicles) * Bury Corporation (96 vehicles) * Leigh Corporation (57 vehicles) *Ramsbottom Urban District Council ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Manchester Council
The Greater Manchester County Council (GMCC) was the top-tier local government administrative body for Greater Manchester from 1974 to 1986. A strategic authority, with responsibilities for roads, public transport, planning, emergency services and waste disposal, it was composed of 106 directly elected members drawn from the ten metropolitan boroughs of Greater Manchester. The Greater Manchester County Council shared power with ten lower-tier district councils, each of which directed local matters. It was also known as the Greater Manchester Council (GMC) and the Greater Manchester Metropolitan County Council (GMMCC). Established with reference to the Local Government Act 1972, elections in 1973 brought about the county council's launch as a shadow authority, several months before Greater Manchester (its zone of influence) was officially created on 1 April 1974. The Greater Manchester County Council operated from its County Hall headquarters on Portland Street in central Manch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
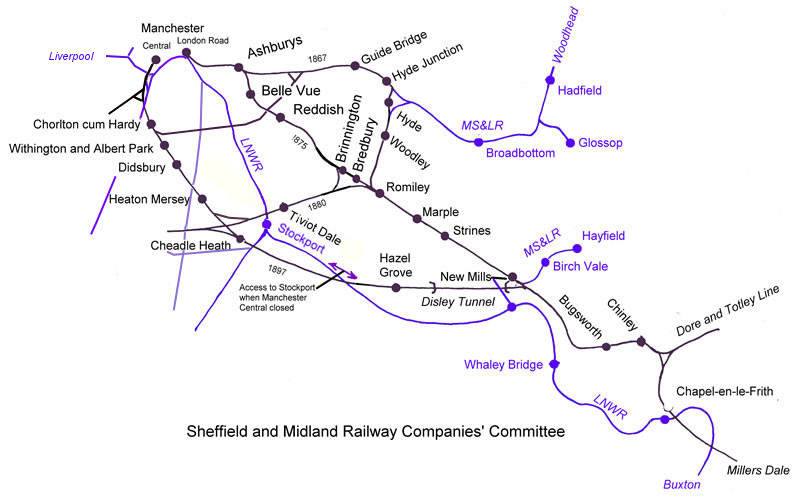
Didsbury Railway Station
Didsbury railway station is a former station in Didsbury, in the southern suburbs of Manchester, England, United Kingdom. The station was located on Wilmslow Road, just north of the junction with Barlow Moor Road and opposite Didsbury Library. Nothing now remains of the old station buildings, which have been demolished, but the surviving white Portland stone clock tower is a local landmark. Didsbury is now served by Didsbury Village tram stop which is close to the site of the former railway station. History In 1873, the Manchester South District Railway obtained permission to construct a new railway line from Manchester to Alderley. The company fell into financial difficulty and was eventually bought out by the Midland Railway in 1877, who went on to build the line. Construction began in 1878 and the line — including Didsbury Station — opened to passenger service on 1 January 1880, running from the new Manchester Central Station through south Manchester suburbs to . The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Didsbury
Didsbury is a suburban area of Manchester, England, on the north bank of the River Mersey, south of Manchester city centre. The population at the 2011 census was 26,788. Within the boundaries of the historic county of Lancashire, there are records of Didsbury existing as a small hamlet as early as the 13th century. Its early history was dominated by being part of the Manor of Withington, a feudal estate that covered a large part of what is now the south of Manchester. Didsbury was described during the 18th century as a township separate from outside influence. In 1745 Charles Edward Stuart crossed the Mersey at Didsbury in the Jacobite march south from Manchester to Derby, and again in the subsequent retreat. Didsbury was largely rural until the mid-19th century, when it underwent development and urbanisation during the Industrial Revolution. It became part of Manchester in 1904. The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds was formed in Didsbury in 1889. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midland Railway
The Midland Railway (MR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1844. The Midland was one of the largest railway companies in Britain in the early 20th century, and the largest employer in Derby, where it had its headquarters. It amalgamated with several other railways to create the London, Midland and Scottish Railway at grouping in 1922. The Midland had a large network of lines emanating from Derby, stretching to London St Pancras, Manchester, Carlisle, Birmingham, and the South West. It expanded as much through acquisitions as by building its own lines. It also operated ships from Heysham in Lancashire to Douglas and Belfast. A large amount of the Midland's infrastructure remains in use and visible, such as the Midland main line and the Settle–Carlisle line, and some of its railway hotels still bear the name '' Midland Hotel''. History Origins The Midland Railway originated from 1832 in Leicestershire / Nottinghamshire, with the purpose of serving the needs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester South District Line
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The two cities and the surrounding towns form one of the United Kingdom's most populous conurbations, the Greater Manchester Built-up Area, which has a population of 2.87 million. The history of Manchester began with the civilian settlement associated with the Roman fort (''castra'') of ''Mamucium'' or ''Mancunium'', established in about AD 79 on a sandstone bluff near the confluence of the rivers Medlock and Irwell. Historically part of Lancashire, areas of Cheshire south of the River Mersey were incorporated into Manchester in the 20th century, including Wythenshawe in 1931. Throughout the Middle Ages Manchester remained a manorial township, but began to expand "at an astonishing rate" around the turn of the 19th century. Manchester's unpla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)