|
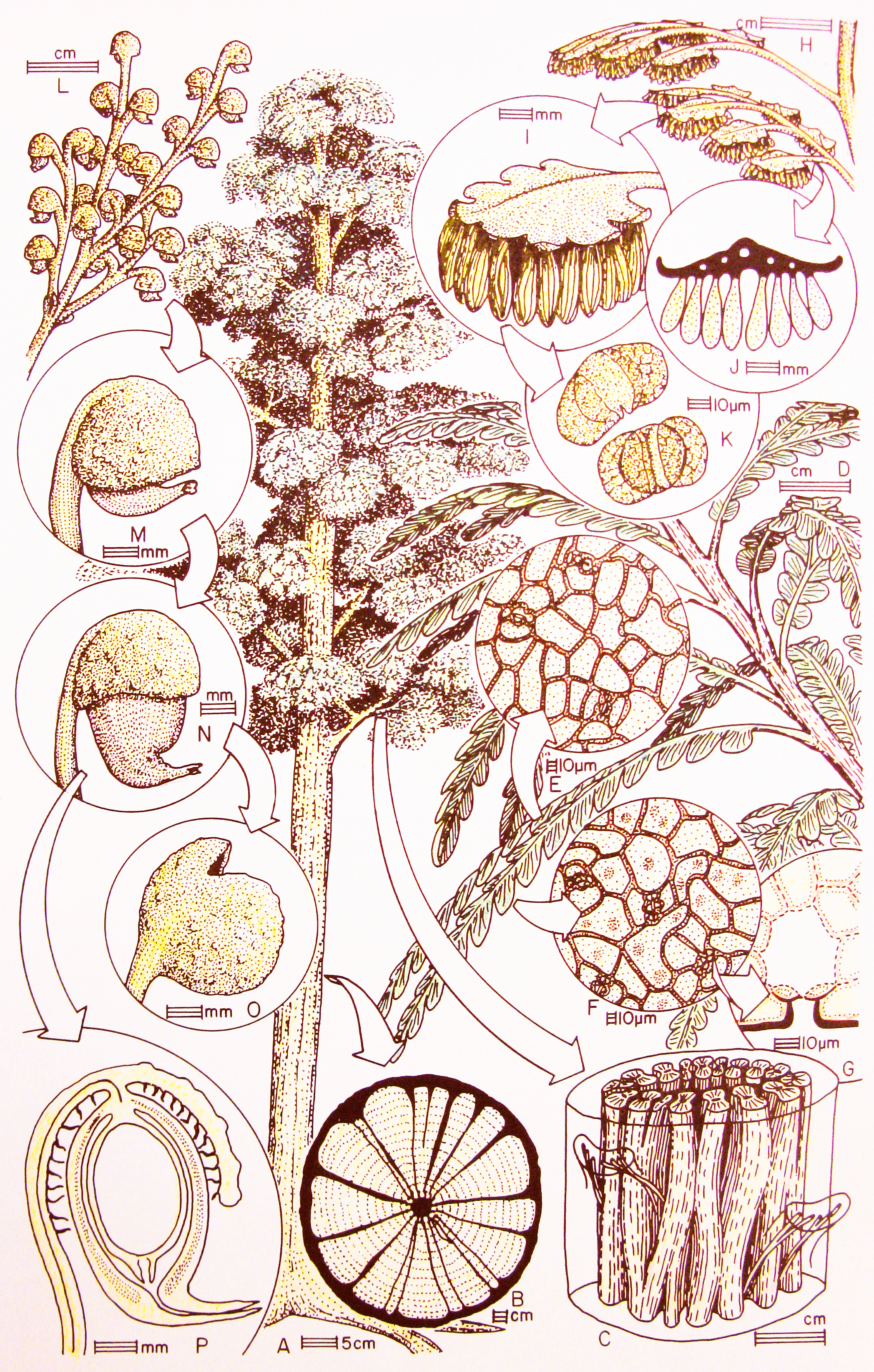
Dicroidium Odontopteroides
''Dicroidium odontopteroides'' was a common and widespread species of ''Dicroidium'' known from South Africa, Australia, New Zealand, South America and Antarctica. The species was first discovered in Triassic sediments of Tasmania and described by the palaeontologist John Morris in 1845. Description The leaves of ''Dicroidium odontopteroides'' differ from other species of ''Dicroidium ''Dicroidium'' is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed ferns that were widely distributed over Gondwana during the Triassic (). Their fossils are known from South Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Australia, New Zealand, South America, Madagascar ...'' in being unipinnate and having short rounded pinnae. Whole plant reconstructions ''Dicroidium odontopteroides'' may have been produced by the same plant as '' Umkomasia macleanii'' (ovulate structures) and '' Pteruchus africanus'' (pollen organs), based on cuticular similarities between these leaves and reproductive structures at the Umkomaas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Morris (geologist)
John Morris (19 February 1810 – 7 January 1886) was an English geologist. Life He was born in 1810 at Homerton, London, and educated at private schools. He was engaged for some years as a pharmaceutical chemist at Kensington, but soon became interested in geology and other branches of science, and ultimately retired from business. His published papers speedily attracted notice, and his ''Catalogue of British Fossils,'' published in 1845, a work involving much critical research, added greatly to his reputation. Morris was professor of geology at University College, London from 1854 to 1877. He was elected Geological Society, F.G.S. in 1845. Along with James Scott Bowerbank, Bowerbank and five others, he was a founding member of the London Clay Club. Morris was president of the Geologists' Association from 1868 to 1871 and from 1877 to 1879. He was awarded the Lyell Medal in 1876. Morris's best original work was done on Eocene and Jurassic rocks. His ''Catalogue of British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicroidium
''Dicroidium'' is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed ferns that were widely distributed over Gondwana during the Triassic (). Their fossils are known from South Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Australia, New Zealand, South America, Madagascar, the Indian subcontinent and Antarctica. They were first discovered in Triassic sediments of Tasmania by Morris in 1845. Fossils from the Umm Irna Formation in Jordan and in Pakistan indicate that these plants already existed in Late Permian. Late surviving members of the genus are known from the Early Jurassic (Sinemurian) of East Antarctica. Within paleobotany, ''Dicroidium'' is a form genus used to refers to the leaves, associated with ovuluate organs classified as '' Umkomasia'' and pollen organs classified as '' Pteruchus,'' while ''Dicroidum'' is also used collectively to refer to the whole plant. Description The leaves are similar to those of modern ferns but like all seed ferns (Pteridospermatophyta The term Pteridospermat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; and to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini. It also completely enclaves the country Lesotho. It is the southernmost country on the mainland of the Old World, and the second-most populous country located entirely south of the equator, after Tanzania. South Africa is a biodiversity hotspot, with unique biomes, plant and animal life. With over 60 million people, the country is the world's 24th-most populous nation and covers an area of . South Africa has three capital cities, with the executive, judicial and legislative branches of government based in Pretoria, Bloemfontein, and Cape Town respectively. The largest city is Johannesburg. About 80% of the population are Black South Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with Deserts of Australia, deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approximately Early human migrations#Nearby Oceania, 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British Overseas Territory), Bouvet Island ( dependency of Norway), Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umkomasia Macleanii
''Umkomasia macleanii'' is an ovulate structure of a seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta The term Pteridospermatophyta (or "seed ferns" or "Pteridospermatopsida") is a polyphyletic group of extinct seed-bearing plants (spermatophytes). The earliest fossil evidence for plants of this type is the genus ''Elkinsia'' of the late Devonia ... and the nominate genus of Family Umkomasiaceae. It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. Description The ovulate structures of ''Umkomasia macleanii'' differ from other species of '' Umkomasia'' in small size, and limited geographic distribution. Whole plant reconstructions ''Umkomasia macleanii'' may have been produced by the same plant as '' Pteruchus africanus'' (pollen organs) and '' Dicroidium odontopteroides'' (leaves), based on cuticular similarities between these leaves and reproductive structures at the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. References Triassic plants Pteridospermatop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteruchus Africanus
''Pteruchus africanus'' is a pollen organ of a seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta). It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. Description The pollen organs ''Pteruchus africanus'' differ from other species of ''Pteruchus'' in small size, and equant blade supporting the pollen sacs. Whole plant reconstructions ''Pteruchus africanus'' may have been produced by the same plant as '' Umkomasia macleanii'' (ovulate organs) and ''Dicroidium odontopteroides ''Dicroidium odontopteroides'' was a common and widespread species of ''Dicroidium'' known from South Africa, Australia, New Zealand, South America and Antarctica. The species was first discovered in Triassic sediments of Tasmania and described ...'' (leaves), based on cuticular similarities between these leaves and reproductive structures at the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. References Triassic plants Pteridospermatophyta {{triassic-plant-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic Plants
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archosaurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |