|
Dichorhavirus
''Dichorhavirus'' is a genus of negative sense, single-stranded RNA viruses of plants within the family ''Rhabdoviridae ''Rhabdoviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates (including mammals and humans), invertebrates, plants, fungi and protozoans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with member virus ...''. Dichorhaviruses have segmented genomes and their short bacilliform virions are not enveloped. Dichorhaviruses are transmitted by mites. Taxonomy The following species are recognized: * '' Citrus chlorotic spot dichorhavirus'' * '' Citrus leprosis N dichorhavirus'' * '' Clerodendrum chlorotic spot dichorhavirus'' * '' Coffee ringspot dichorhavirus'' * '' Orchid fleck dichorhavirus'' References Rhabdoviridae Virus genera {{virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabdoviridae
''Rhabdoviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates (including mammals and humans), invertebrates, plants, fungi and protozoans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with member viruses include rabies encephalitis caused by the rabies virus, and flu-like symptoms in humans caused by vesiculoviruses. The name is derived from Ancient Greek , meaning rod, referring to the shape of the viral particles. The family has 40 genera, most assigned to three subfamilies. Structure The individual virus particles (virions) of rhabdoviruses are composed of RNA, protein, carbohydrate and lipid. They have complex bacilliform or bullet-like shapes. All these viruses have structural similarities and have been classified as a single family. The virions are about 75 nm wide and 180 nm long. Rhabdoviruses are enveloped and have helical nucleocapsids and their genomes are linear, around 11–15 kb in length. Rhabdoviruses c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchid Fleck Dichorhavirus
''Orchid fleck dichorhavirus'', commonly called Orchid fleck virus (OFV), is a non-enveloped, segmented, single-stranded (ss) RNA negative-strand virus, transmitted by the false spider mite, ''Brevipalpus californicus''. OFV causes necrotic and chlorotic lesions on the leaves of many genera in the family Orchidaceae. Introduction Orchid fleck virus, despite its presence worldwide, only affects a small spectrum of human life. Orchids are not used for food but rather serve mainly as ornamental decoration. Therefore, only about 2 to 3 scientific reports are written about OFV each year. The whole genome of OFV has been sequenced and its six main protein products have been sequenced as well.Kondo H, Maeda T, Shirako Y, Tamada T 2006. Orchid fleck virus is a rhabdovirus with an unusual bipartite genome. J Gen Virol 87:2413–2421. Much is still not known about OFV including how exactly and why vector mites travel from orchid to orchid, and more host species of flowers are bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
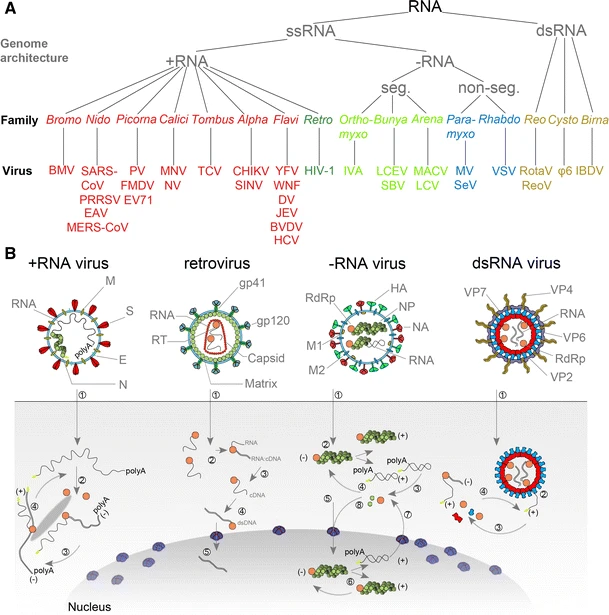
RNA Virus
An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA ( ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, MERS, Covid-19, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles. The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) classifies RNA viruses as those that belong to ''Group III'', ''Group IV'' or ''Group V'' of the Baltimore classification system. This category excludes ''Group VI'', viruses with RNA genetic material but which use DNA intermediates in their life cycle: these are called retroviruses, including HIV-1 and HIV-2 which cause AIDS. As of May 2020, all known RNA viruses encoding an RNA-directed RNA polymerase are believed to form a monophyletic group, known as the realm '' Riboviria''. The majority of such RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encased in lipid bilayers, and they infect their target cells by causing the viral envelope and cell membrane to fuse. Although there are effective vaccines against some of these viruses, there is no preventative or curative medicine for the majority of them. In most cases, the known vaccines operate by inducing antibodies that prevent the pathogen from entering cells. This happens in the case of enveloped viruses when the antibodies bind to the viral envelope proteins. The membrane fusion event that triggers viral entrance is caused by the viral fusion protein. Many enveloped viruses only have one protein visible on the surface of the particle, which is required for both mediating adhesion to the cell surface and for the subsequent membrane fusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citrus Chlorotic Spot Dichorhavirus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is native to South Asia, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Melanesia, and Australia. Various citrus species have been used and domesticated by indigenous cultures in these areas since ancient times. From there its cultivation spread into Micronesia and Polynesia by the Austronesian expansion (c. 3000–1500 BCE); and to the Middle East and the Mediterranean (c. 1200 BCE) via the incense trade route, and onwards to Europe and the Americas. History Citrus plants are native to subtropical and tropical regions of Asia, Island Southeast Asia, Near Oceania, and northeastern Australia. Domestication of citrus species involved much hybridization and introgression, leaving much uncertainty about when and where domestication first happened. A genomic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citrus Leprosis N Dichorhavirus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is native to South Asia, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Melanesia, and Australia. Various citrus species have been used and domesticated by indigenous cultures in these areas since ancient times. From there its cultivation spread into Micronesia and Polynesia by the Austronesian expansion (c. 3000–1500 BCE); and to the Middle East and the Mediterranean (c. 1200 BCE) via the incense trade route, and onwards to Europe and the Americas. History Citrus plants are native to subtropical and tropical regions of Asia, Island Southeast Asia, Near Oceania, and northeastern Australia. Domestication of citrus species involved much hybridization and introgression, leaving much uncertainty about when and where domestication first happened. A genomic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clerodendrum Chlorotic Spot Dichorhavirus
''Clerodendrum'' is a genus of flowering plants formerly placed in the family Verbenaceae, but now considered to belong to the Lamiaceae (mint) family. Its common names include glorybower, bagflower and bleeding-heart. It is currently classified in the subfamily Ajugoideae, being one of several genera transferred from Verbenaceae to Lamiaceae in the 1990s, based on phylogenetic analysis of morphological and molecular data. Estimates of the number of species in ''Clerodendrum'' vary widely, from about 150Yao-Wu Yuan, David J. Mabberley, Dorothy A. Steane, and Richard G. Olmstead. 2010. "Further disintegration and redefinition of ''Clerodendrum'' (Lamiaceae): Implications for the understanding of the evolution of an intriguing breeding strategy". ''Taxon'' 59(1):125-133. to about 450.Raymond M. Harley, Sandy Atkins, Andrey L. Budantsev, Philip D. Cantino, Barry J. Conn, Renée J. Grayer, Madeline M. Harley, Rogier P.J. de Kok, Tatyana V. Krestovskaja, Ramón Morales, Alan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffee Ringspot Dichorhavirus
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world. Seeds of the '' Coffea'' plant's fruits are separated to produce unroasted green coffee beans. The beans are roasted and then ground into fine particles that are typically steeped in hot water before being filtered out, producing a cup of coffee. It is usually served hot, although chilled or iced coffee is common. Coffee can be prepared and presented in a variety of ways (e.g., espresso, French press, caffè latte, or already-brewed canned coffee). Sugar, sugar substitutes, milk, and cream are often used to mask the bitter taste or enhance the flavor. Though coffee is now a global commodity, it has a long history tied closely to food traditions around the Red Sea. The earliest credible evidence of coffee drinking in the form of the modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
