|
Dicarboxylic Aminoaciduria
Dicarboxylic aminoaciduria is a rare form of aminoaciduria (1:35 000 births) which is an autosomal recessive disorder of urinary glutamate and aspartate due to genetic errors related to transport of these amino acids. Mutations resulting in a lack of expression of the ''SLC1A1'' gene, a member of the solute carrier family, are found to cause development of dicarboxylic aminoaciduria in humans. SLC1A1 encodes for EAAT3 which is found in the neurons, intestine, kidney, lung, and heart. EAAT3 is part of a family of high affinity glutamate transporters which transport both glutamate and aspartate across the plasma membrane. Symptoms and signs Dicarboxylic aminoaciduria involves excretion of urinary glutamate and aspartate, resulting from the incomplete reabsorption of anionic amino acids from the glomerular filtrate in the kidney. This affects a diseased individual's amino acid pool, as they will have to spend additional resources to replenish the amino acids which would have otherw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminoaciduria
Aminoaciduria occurs when the urine contains abnormally high amounts of amino acids. In the healthy kidney, the glomeruli filter all amino acids out of the blood, and the renal tubules then reabsorb over 95% of the filtered amino acids back into the blood. In overflow aminoaciduria, abnormally high concentrations of amino acids in the blood plasma overwhelm the resorptive capacity of the renal tubules, resulting in high concentrations of amino acids in the urine. This may be caused by congenital disorders of amino acid metabolism, for example, phenylketonuria, or may be secondary to liver disease. In renal aminoaciduria, the renal tubules are unable to reabsorb the filtered amino acids back into the blood, causing high concentrations of amino acids in the urine. This may be caused by a defect in the transport proteins in the renal tubule, for example, as occurs in Hartnup disease, or may be due to damage to the kidney tubule, for example, as occurs in Fanconi syndrome Fanconi s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride (edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals including h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anionic
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epitheli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptides
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterocytes
Enterocytes, or intestinal absorptive cells, are simple columnar epithelial cells which line the inner surface of the small and large intestines. A glycocalyx surface coat contains digestive enzymes. Microvilli on the apical surface increase its surface area. This facilitates transport of numerous small molecules into the enterocyte from the intestinal lumen. These include broken down proteins, fats, and sugars, as well as water, electrolytes, vitamins, and bile salts. Enterocytes also have an endocrine role, secreting hormones such as leptin. Function The major functions of enterocytes include: *Ion uptake, including sodium, calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc, and copper. This typically occurs through active transport. *Water uptake. This follows the osmotic gradient established by Na+/K+ ATPase on the basolateral surface. This can occur transcellularly or paracellularly. *Sugar uptake. Polysaccharides and disaccharidases in the glycocalyx break down large sugar molecules, which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
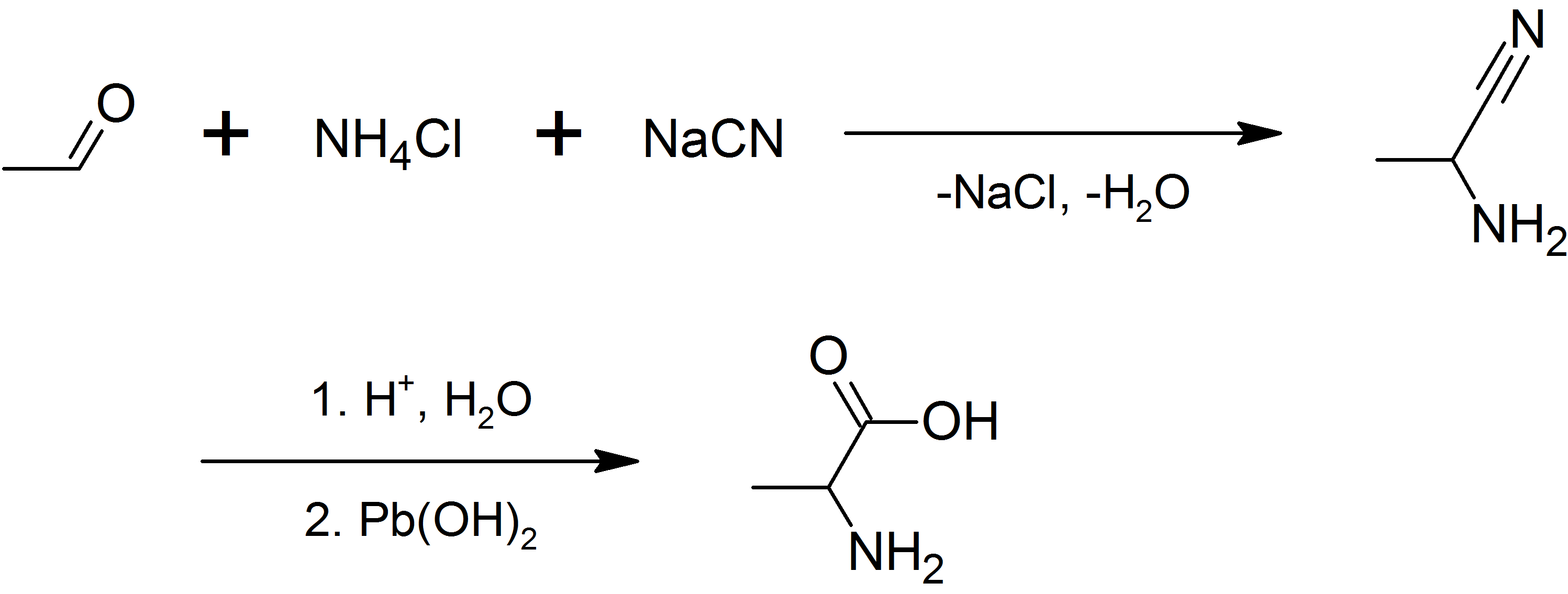
Alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side chain. Consequently, its IUPAC systematic name is 2-aminopropanoic acid, and it is classified as a nonpolar, aliphatic α-amino acid. Under biological conditions, it exists in its zwitterionic form with its amine group protonated (as −NH3+) and its carboxyl group deprotonated (as −CO2−). It is non-essential to humans as it can be synthesised metabolically and does not need to be present in the diet. It is encoded by all codons starting with GC (GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG). The L-isomer of alanine (left-handed) is the one that is incorporated into proteins. L-alanine is second only to leucine in rate of occurrence, accounting for 7.8% of the primary structure in a sample of 1,150 proteins. The right-handed form, D-alanine, occurs in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digestion, digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Nephrozoa, Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores (ostium (sponges), ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidneys
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
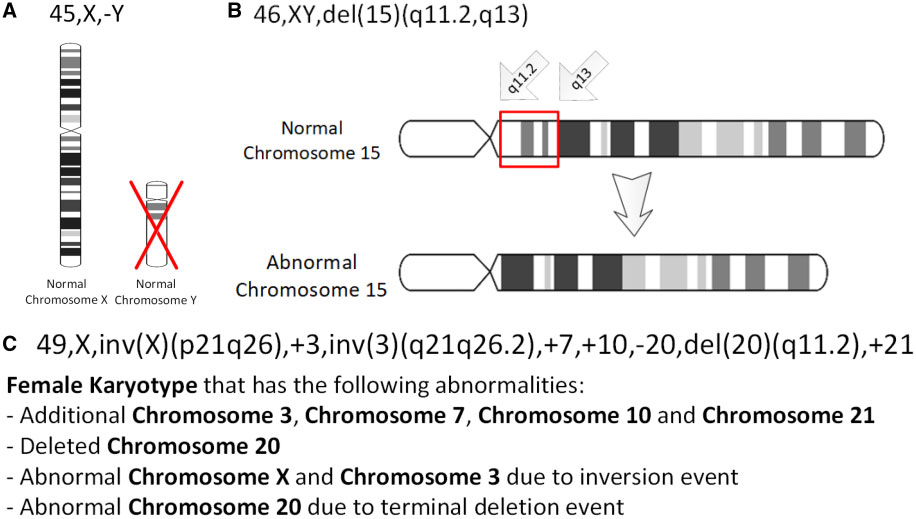
Deletion (genetics)
In genetics, a deletion (also called gene deletion, deficiency, or deletion mutation) (sign: Δ) is a mutation (a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is left out during DNA replication. Any number of nucleotides can be deleted, from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome. Some chromosomes have fragile spots where breaks occur which result in the deletion of a part of chromosome. The breaks can be induced by heat, viruses, radiations, chemicals. When a chromosome breaks, a part of it is deleted or lost, the missing piece of chromosome is referred to as deletion or a deficiency. For synapsis to occur between a chromosome with a large intercalary deficiency and a normal complete homolog, the unpaired region of the normal homolog must loop out of the linear structure into a deletion or compensation loop. The smallest single base deletion mutations occur by a single base flipping in the template DNA, followed by template DNA strand sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |