|
Devuan
Devuan is a fork of the Debian Linux distribution that uses sysvinit, runit or OpenRC instead of systemd. Devuan aims to avoid "lock-in" by projects like systemd and aims to maintain compatibility with other init systems to avoid detaching Linux from other Unix systems. History With the release of Debian 8 some developers and users were alienated due to the project's adoption of systemd and subsequent removal of support for other existing init systems. This decision prompted some Debian community members to start a fork of Debian without systemd. Instead of continuing the Debian practice of using Toy Story character names as release codenames, Devuan aliases its releases using planet names. The first stable release shared the Debian 8 codename '' Jessie''. However, the Devuan release was named for minor planet 10464. The first stable release of Devuan was published on May 25, 2017. Devuan 2.0.0 ''ASCII'' was released on June 9, 2018, and 2.1 ''ASCII'' was released on Novembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemd
systemd is a software suite that provides an array of system components for Linux operating systems. Its main aim is to unify service configuration and behavior across Linux distributions; Its primary component is a "system and service manager"—an init system used to bootstrap user space and manage user processes. It also provides replacements for various daemons and utilities, including device management, login management, network connection management, and event logging. The name ''systemd'' adheres to the Unix convention of naming daemons by appending the letter ''d''. It also plays on the term "System D", which refers to a person's ability to adapt quickly and improvise to solve problems. Since 2015, the majority of Linux distributions have adopted systemd, having replaced other init systems such as SysV init. It has been praised by developers and users of distributions that adopted it for providing a stable, fast out-of-the-box solution for issues that had existed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debian
Debian (), also known as Debian GNU/Linux, is a Linux distribution composed of free and open-source software, developed by the community-supported Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock on August 16, 1993. The first version of Debian (0.01) was released on September 15, 1993, and its first stable version (1.1) was released on June 17, 1996. The Debian Stable branch is the most popular edition for personal computers and servers. Debian is also the basis for many other distributions, most notably Ubuntu. Debian is one of the oldest operating systems based on the Linux kernel. The project is coordinated over the Internet by a team of volunteers guided by the Debian Project Leader and three foundational documents: the Debian Social Contract, the Debian Constitution, and the Debian Free Software Guidelines. New distributions are updated continually, and the next candidate is released after a time-based freeze. Since its founding, Debian has been developed openly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
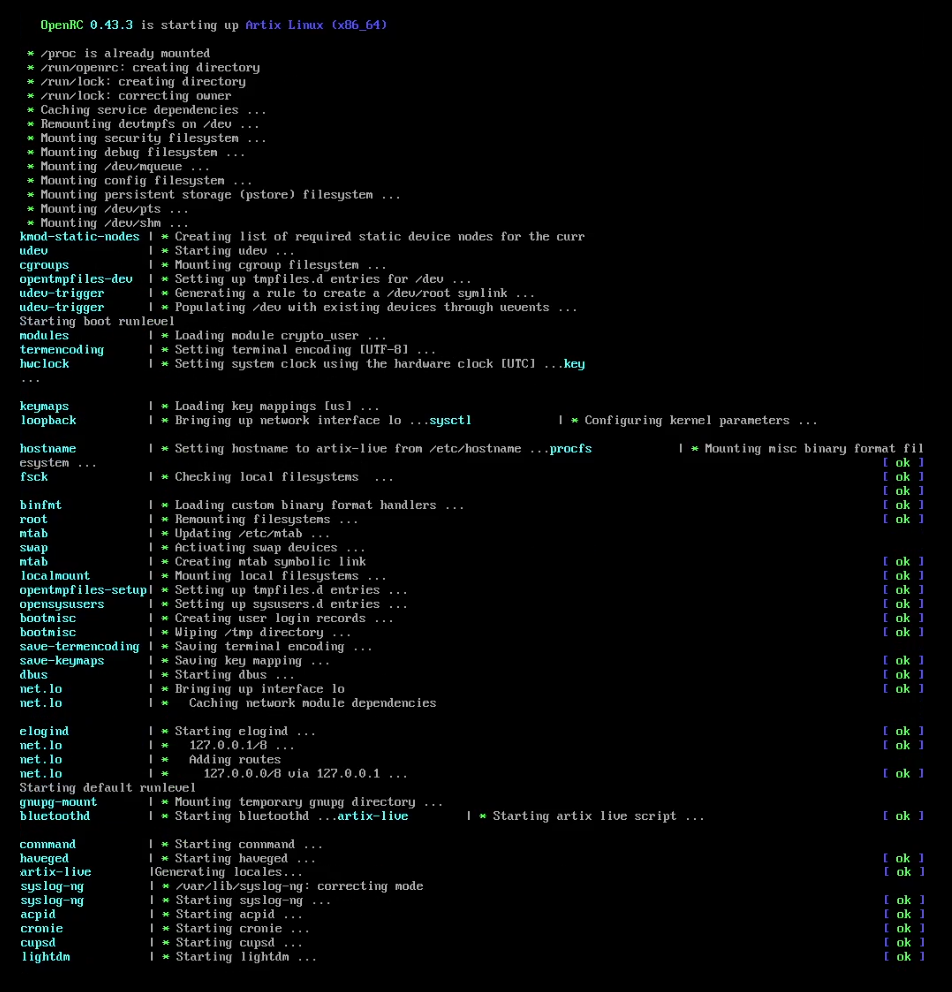
OpenRC
OpenRC is a dependency-based init system for Unix-like computer operating systems. It was created by Roy Marples, a NetBSD developer who was also active in the Gentoo project. It became more broadly adopted as an init system outside of Gentoo following the decision by some Linux distributions not to adopt systemd. Adoption OpenRC is the default init system and/or process supervisor for: * Alpine Linux * Funtoo * Gentoo Linux * Hyperbola GNU/Linux-libre * Maemo Leste * Nitrux OpenRC is an available init system and/or process supervisor for: * Artix Linux * Devuan * Parabola GNU/Linux-libre * Arch Linux Design OpenRC is made up of several modular components, the main ones being an init (optional), the core dependency management system and a daemon supervisor (optional). It is written in C and POSIX-compliant shell, making it usable on BSD and Linux systems. The core part of OpenRC handles dependency management and init script parsing. OpenRC works by scanning the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Init
In Unix-based computer operating systems, init (short for ''initialization'') is the first process started during booting of the computer system. Init is a daemon process that continues running until the system is shut down. It is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes and automatically adopts all orphaned processes. Init is started by the kernel during the booting process; a kernel panic will occur if the kernel is unable to start it. Init is typically assigned process identifier 1. In Unix systems such as System III and System V, the design of init has diverged from the functionality provided by the init in Research Unix and its BSD derivatives. Up until recently, most Linux distributions employed a traditional init that was somewhat compatible with System V, while some distributions such as Slackware use BSD-style startup scripts, and others such as Gentoo have their own customized versions. Since then, several additional init implementations ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runit
runit is an init and service management scheme for Unix-like operating systems that initializes, supervises, and ends processes throughout the operating system. Runit is a reimplementation of the daemontools process supervision toolkit that runs on many Linux-based operating systems, as well as BSD, and Solaris operating systems. Runit features parallelization of the start up of system services, which can speed up the boot time of the operating system. When running as an init daemon, Runit is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes. It is the first process started during booting, and continues running until the system is shut down. It is often used with other init systems as a separate service manager. In the service manager role, it can be used by unprivileged users to orchestrate personal services, as well as by root to manage services not otherwise managed by the init system currently in use. Design Runit focuses on being a small, modular, and portable codeb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Init
In Unix-based computer operating systems, init (short for ''initialization'') is the first process started during booting of the computer system. Init is a daemon process that continues running until the system is shut down. It is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes and automatically adopts all orphaned processes. Init is started by the kernel during the booting process; a kernel panic will occur if the kernel is unable to start it. Init is typically assigned process identifier 1. In Unix systems such as System III and System V, the design of init has diverged from the functionality provided by the init in Research Unix and its BSD derivatives. Up until recently, most Linux distributions employed a traditional init that was somewhat compatible with System V, while some distributions such as Slackware use BSD-style startup scripts, and others such as Gentoo have their own customized versions. Since then, several additional init implementations ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MATE (software)
MATE () is a desktop environment composed of free and open-source software that runs on Linux, BSD, and illumos operating systems. Name MATE is named after the South American plant yerba mate and tea made from the herb, mate. The name is stylized in all capital letters to follow the nomenclature of other Free Software desktop environments like KDE and LXDE. The recursive backronym "MATE Advanced Traditional Environment" was subsequently adopted by most of the MATE community, again in the spirit of Free Software like GNU ("GNU's Not Unix!"). The use of a new name, instead of GNOME, avoids naming conflicts with GNOME 3 components. History An Argentine user of Arch Linux, named Perberos started the MATE project to fork and continue GNOME 2 in response to the negative reception of GNOME 3, which had replaced its traditional taskbar (GNOME Panel) with GNOME Shell. MATE aims to maintain and continue the latest GNOME 2 code base, frameworks, and core applications. MATE was i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LXQt
LXQt is a free and open source lightweight desktop environment. It was formed from the merger of the LXDE and Razor-qt projects. Like its GTK predecessor LXDE, LXQt does not ship or develop its own window manager, instead LXQt lets the user decide which (supported) window manager they want to use. Linux distributions commonly default LXQt to Openbox or xfwm4 or kwin. History Dissatisfied with GTK 3, LXDE maintainer Hong Jen Yee experimented with Qt in early 2013 and released the first version of a Qt-based PCMan File Manager on 26 March 2013. He clarified, though, that this means no departure from GTK in LXDE, saying "The GTK and Qt versions will coexist". He later ported LXDE's Xrandr front-end to Qt. On 3 July 2013 Hong Jen Yee announced a Qt port of the full LXDE suite, and on 21 July 2013, Razor-qt and LXDE announced that they had decided to merge the two projects. This merge meant that the GTK and the Qt versions coexisted in the short term, but eventually development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnamon (Desktop Environment)
Cinnamon is a free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and Unix-like operating systems, deriving from GNOME 3 but following traditional desktop metaphor conventions. The development of Cinnamon began by the Linux Mint team as a reaction to the April 2011 release of GNOME 3 in which the conventional desktop metaphor of GNOME 2 was abandoned in favor of GNOME Shell. Following several attempts to extend GNOME 3 such that it would suit the Linux Mint design goals, the Mint developers forked several GNOME 3 components to build an independent desktop environment. Separation from GNOME was completed in Cinnamon 2.0, which was released in October 2013. Applets and desklets are no longer compatible with GNOME 3. As the distinguishing factor of Linux Mint, Cinnamon has generally received favorable coverage by the press, in particular for its ease of use and gentle learning curve. With respect to its conservative design model, Cinnamon is similar to the Xfce, MATE, GNOME 2 (and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desktop Environment
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphical shell. The desktop environment was seen mostly on personal computers until the rise of mobile computing. Desktop GUIs help the user to easily access and edit files, while they usually do not provide access to all of the features found in the underlying operating system. Instead, the traditional command-line interface (CLI) is still used when full control over the operating system is required. A desktop environment typically consists of icons, windows, toolbars, folders, wallpapers and desktop widgets (see Elements of graphical user interfaces and WIMP). A GUI might also provide drag and drop functionality and other features that make the desktop metaphor more complete. A desktop environment aims to be an intuitive way for the user to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10001–11000
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |