|
Deucravacitinib
Deucravacitinib, sold under the brand name Sotyktu, is medication used for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. It is a tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor and it is taken by mouth. It was developed by Bristol Myers Squibb. Deucravacitinib was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2022, and in Australia in December 2022. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses Deucravacitinib is indicated for the treatment of adults with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Mechanism of action It acts as a highly selective allosteric inhibitor of non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase 2 (TYK2). Molecule design The chemical structure of deucravacitinib contains a methyl amide in which all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by deuterium Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterated Drug
A deuterated drug is a small molecule medicinal product in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms contained in the drug molecule have been replaced by its heavier stable isotope deuterium. Because of the kinetic isotope effect, deuterium-containing drugs may have significantly lower rates of metabolism, and hence a longer half-life. Mode of action Hydrogen is a chemical element with an atomic number of 1. It has just one proton and one electron. Deuterium is the heavier naturally occurring, non-radioactive, stable isotope of hydrogen. Deuterium was discovered by Harold Urey in 1931, for which he received the Nobel Prize in 1934. The deuterium isotope effect has become an important tool in the elucidation the mechanism of chemical reactions. Deuterium contains one proton, one electron, and a neutron, effectively doubling the mass of the deuterium isotope without changing its properties significantly. However, the C–D bond is a bit shorter, and it has reduced electronic polarizabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allosteric Regulation
In biochemistry, allosteric regulation (or allosteric control) is the regulation of an enzyme by binding an effector molecule at a site other than the enzyme's active site. The site to which the effector binds is termed the ''allosteric site'' or ''regulatory site''. Allosteric sites allow effectors to bind to the protein, often resulting in a conformational change and/or a change in protein dynamics. Effectors that enhance the protein's activity are referred to as ''allosteric activators'', whereas those that decrease the protein's activity are called ''allosteric inhibitors''. Allosteric regulations are a natural example of control loops, such as feedback from downstream products or feedforward from upstream substrates. Long-range allostery is especially important in cell signaling. Allosteric regulation is also particularly important in the cell's ability to adjust enzyme activity. The term ''allostery'' comes from the Ancient Greek ''allos'' (), "other", and ''stereos' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridazines
Pyridazine is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound with the molecular formula . It contains a six-membered ring with two adjacent nitrogen atoms. It is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 208 °C. It is isomeric with two other diazine () rings, pyrimidine and pyrazine. Occurrence Pyridazines are rare in nature, possibly reflecting the scarcity of naturally occurring hydrazines, common building blocks for the synthesis of these heterocycles. The pyridazine structure is a popular pharmacophore which is found within a number of herbicides such as credazine, pyridafol and pyridate. It is also found within the structure of several drugs such as cefozopran, cadralazine, minaprine, pipofezine, and hydralazine. Synthesis In the course of his classic investigation on the Fischer indole synthesis, Emil Fischer prepared the first pyridazine via the condensation of phenylhydrazine and levulinic acid. The parent heterocycle was first prepared by oxidation of benz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopropyl Compounds
A cyclopropyl group is a chemical structure derived from cyclopropane, and can participate in organic reactions that constitute cycloadditions and rearrangement organic reactions of cyclopropane. The group has an empirical formula of C3H5 and chemical bond A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules and crystals. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds, or through the sharing of ...s from each of the three carbons to both of the other two. Structure and bonding Due to the unfavoured bond angles (60°), cyclopropyl groups are highly strained. Two orbital models were proposed to describe the bonding situation. The Coulson-Moffit model uses bent bonds. The C-C bonds are formed by overlap of two sp-hybrid orbitals. To adapt to the small bond angle, there is some rehybridization resulting in sp~5-hybrids for the ring bonds and sp~2 for the C-H bonds. This model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
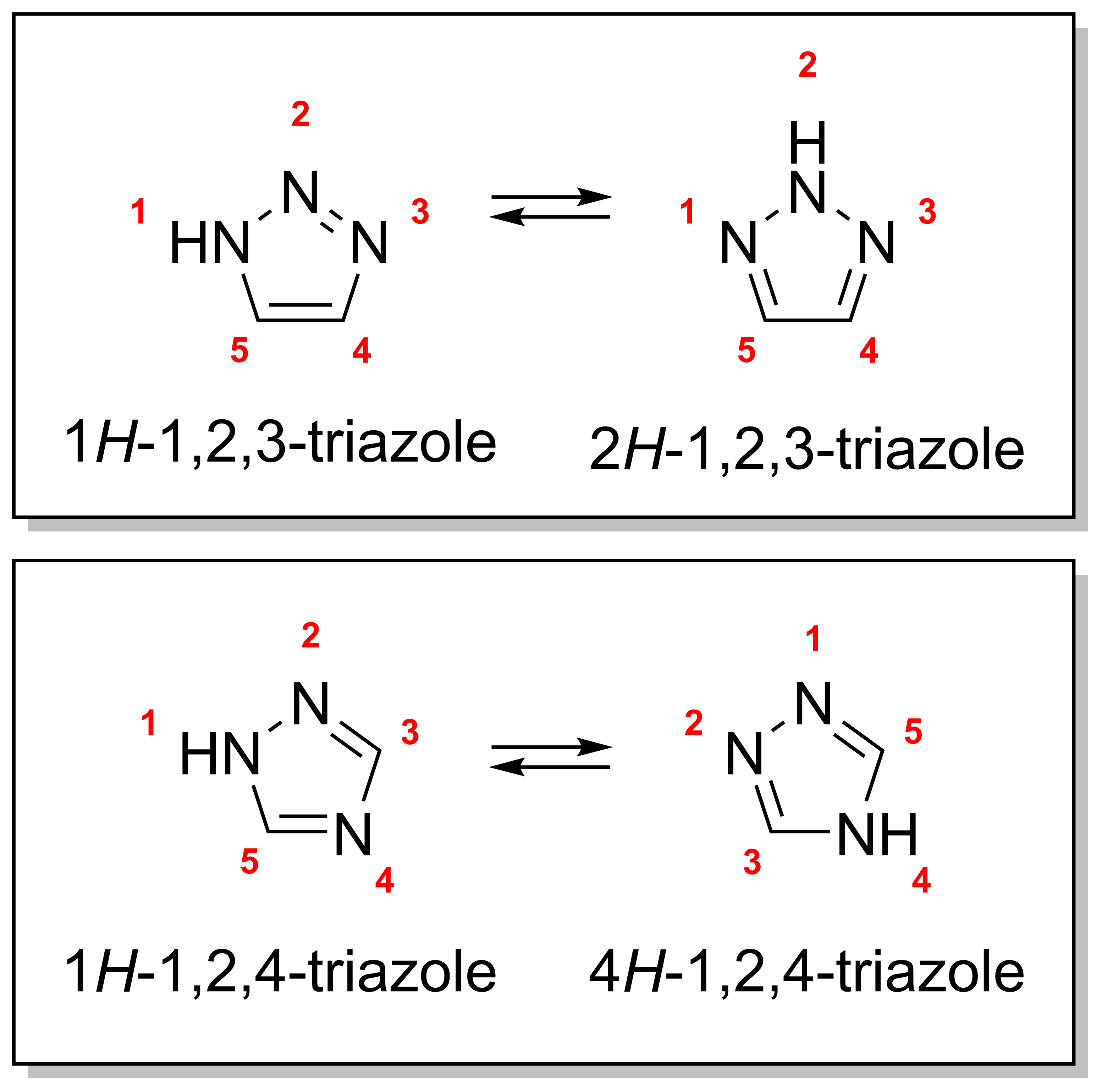
Triazoles
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring. Many triazoles are versatile, biologically active compounds commonly used as fungicides and plant retardants. However, triazoles are also useful in bioorthogonal chemistry, because the large number of nitrogen atoms causes triazoles to react similar to azides. Lastly, the many free lone pairs in triazoles make them useful as coordination compounds, although not typically as haptic ligands. Isomerism There are four triazole isomers, which are conventionally divided into two pairs of tautomers. In the 1,2,3-triazoles, the three nitrogen atoms are adjacent; in the 1,2,4-triazoles, an interstitial carbon separates out one nitrogen atom. Each category has two tautomers that differ by which nitrogen has a hydrogen bonded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterated Compounds
Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope (an atom with a detectable variation in neutron count) through a Chemical reaction, reaction, metabolic pathway, or Cell (biology), cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the product (chemistry), products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling. In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being Hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1). The atomic nucleus, nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common protium has no neutrons in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom of deuterium among all atoms of hydrogen (see heavy water). Thus deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% by number (0.0312% by mass) of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans, while protium accounts for more than 99.98%. The abundance of deuterium changes slightly from one kind of natural water to another (see Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water). (Tritium is yet another hydrogen isotope, with two neutrons, that is far more rare and is radioactive.) The name ''deuterium'' is derived from the Greek , meaning "second", to denot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indicated
In medicine, an indication is a valid reason to use a certain test, medication, procedure, or surgery. There can be multiple indications to use a procedure or medication. An indication can commonly be confused with the term diagnosis. A diagnosis is the assessment that a particular edicalcondition is present while an indication is a reason for use. The opposite of an indication is a contraindication, a reason to withhold a certain medical treatment because the risks of treatment clearly outweigh the benefits. In the United States, indications for prescription drugs are approved by the FDA. Indications are included in the Indications and Usage section of the Prescribing Information. The primary role of this section of labeling is to enable health care practitioners to readily identify appropriate therapies for patients by clearly communicating the drug’s approved indication(s). The Indications and Usage section states the disease or condition, or manifestation or symptoms thereof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)