|
Design For X
Design for Excellence or Design For Excellence (DfX or DFX), are terms and expansions used interchangeably in the existing literature, where the ''X'' in ''design for X'' is a variable which can have one of many possible values. In many fields (e.g., very-large-scale integration (VLSI) and nanoelectronics) ''X'' may represent several traits or features including: manufacturability, power, variability, cost, yield, or reliability. Saraju Mohanty, Chapter 3 Nanoelectronics Issues in Design for excellence,Nanoelectronic Mixed-Signal System Design, and 0071825711, 1st Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2015. This gives rise to the terms design for manufacturability (DfM, DFM), design for inspection (DFI), design for variability (DfV), design for cost (DfC). Similarly, other disciplines may associate other traits, attributes, or objectives for ''X''. Under the label ''design for X'', a wide set of specific design guidelines are summarized. Each design guideline addresses a given issue that is cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saraju Mohanty
Saraju Mohanty is an American professor of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, and the director of the Smart Electronic Systems Laboratory, at the University of North Texas in Denton, Texas. Mohanty received a Glorious India Award – Rich and Famous NRIs of America in 2017 for his contributions to the discipline. Mohanty is a researcher in the areas of "consumer electronics for smart cities", "application-Specific things for efficient edge computing", and "methodologies for digital and mixed-signal hardware". He has made significant research contributions to security and IP protection of consumer electronic systems, hardware-assisted security and protection, high-level synthesis of digital signal processing (DSP) hardware, and mixed-signal integrated circuit computer-aided design and electronic design automation. Mohanty has been the editor-in-chief (EiC) of the ''IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine'' since 2016.IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, http://cesoc.ie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Engineering
Safety engineering is an engineering discipline which assures that engineered systems provide acceptable levels of safety. It is strongly related to industrial engineering/systems engineering, and the subset system safety engineering. Safety engineering assures that a life-critical system behaves as needed, even when components fail. Analysis techniques Analysis techniques can be split into two categories: qualitative and quantitative methods. Both approaches share the goal of finding causal dependencies between a hazard on system level and failures of individual components. Qualitative approaches focus on the question "What must go wrong, such that a system hazard may occur?", while quantitative methods aim at providing estimations about probabilities, rates and/or severity of consequences. The complexity of the technical systems such as Improvements of Design and Materials, Planned Inspections, Fool-proof design, and Backup Redundancy decreases risk and increases the cost. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design For Assembly
Design for assembly (DFA) is a process by which products are designed with ease of assembly in mind. If a product contains fewer parts it will take less time to assemble, thereby reducing assembly costs. In addition, if the parts are provided with features which make it easier to grasp, move, orient and insert them, this will also reduce assembly time and assembly costs. The reduction of the number of parts in an assembly has the added benefit of generally reducing the total cost of parts in the assembly. This is usually where the major cost benefits of the application of design for assembly occur. Approaches Design for assembly can take different forms. In the 1960s and 1970s various rules and recommendations were proposed in order to help designers consider assembly problems during the design process. Many of these rules and recommendations were presented together with practical examples showing how assembly difficulty could be improved. However, it was not until the 1970s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Platform
Product may refer to: Business * Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem. * Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution Mathematics * Product (mathematics) Algebra * Direct product Set theory * Cartesian product of sets Group theory * Direct product of groups * Semidirect product * Product of group subsets * Wreath product * Free product * Zappa–Szép product (or knit product), a generalization of the direct and semidirect products Ring theory * Product of rings * Ideal operations, for product of ideals Linear algebra * Scalar multiplication * Matrix multiplication * Inner product, on an inner product space * Exterior product or wedge product * Multiplication of vectors: ** Dot product ** Cross product ** Seven-dimensional cross product ** Triple product, in vector calculus * Tensor product Topology * Product topology Algebraic topology * Cap product * Cup produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Architecture
Product may refer to: Business * Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem. * Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution Mathematics * Product (mathematics) Algebra * Direct product Set theory * Cartesian product of sets Group theory * Direct product of groups * Semidirect product * Product of group subsets * Wreath product * Free product * Zappa–Szép product (or knit product), a generalization of the direct and semidirect products Ring theory * Product of rings * Ideal operations, for product of ideals Linear algebra * Scalar multiplication * Matrix multiplication * Inner product, on an inner product space * Exterior product or wedge product * Multiplication of vectors: ** Dot product ** Cross product ** Seven-dimensional cross product ** Triple product, in vector calculus * Tensor product Topology * Product topology Algebraic topology * Cap product * Cup pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Modularity
Product may refer to: Business * Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem. * Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution Mathematics * Product (mathematics) Algebra * Direct product Set theory * Cartesian product of sets Group theory * Direct product of groups * Semidirect product * Product of group subsets * Wreath product * Free product * Zappa–Szép product (or knit product), a generalization of the direct and semidirect products Ring theory * Product of rings * Ideal operations, for product of ideals Linear algebra * Scalar multiplication * Matrix multiplication * Inner product, on an inner product space * Exterior product or wedge product * Multiplication of vectors: ** Dot product ** Cross product ** Seven-dimensional cross product ** Triple product, in vector calculus * Tensor product Topology * Product topology Algebraic topology * Cap product * Cup produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interchangeable Parts
Interchangeable parts are parts (components) that are identical for practical purposes. They are made to specifications that ensure that they are so nearly identical that they will fit into any assembly of the same type. One such part can freely replace another, without any custom fitting, such as filing. This interchangeability allows easy assembly of new devices, and easier repair of existing devices, while minimizing both the time and skill required of the person doing the assembly or repair. The concept of interchangeability was crucial to the introduction of the assembly line at the beginning of the 20th century, and has become an important element of some modern manufacturing but is missing from other important industries. Interchangeability of parts was achieved by combining a number of innovations and improvements in machining operations and the invention of several machine tools, such as the slide rest lathe, screw-cutting lathe, turret lathe, milling machine and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design To Standards
{{unreferenced, date=June 2009 "Design to Standards" means to design items with generally accepted and uniform procedures, dimensions or materials. Benefits Product standardization is a technique in engineering design that aim to reduce the number of different parts within a product. The benefits are: * lower supply chain costs * product platforms * faster product design The supply chain costs are simple to reason: * less variety of supplier, less supplier in numbers * less stock keeping units (SKU) * more economics of scale * less variety of production operations Product platforms are enabled through: * standardized parts can be re-utilized across a product family * standardized parts can be re-utilized across product generations The product design process becomes faster because: * standardized parts can be pulled from an engineering database * already standardized parts do not need to be designed again Standards Standardization can occur through two ways * industry standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value Engineering
Value engineering (VE) is a systematic analysis of the functions of various components and materials to lower the cost of goods, products and services with a tolerable loss of performance or functionality. Value, as defined, is the ratio of function to cost. Value can therefore be manipulated by either improving the function or reducing the cost. It is a primary tenet of value engineering that basic functions be preserved and not be reduced as a consequence of pursuing value improvements. The term "value management" is sometimes used as a synonym of "value engineering", and both promote the planning and delivery of projects with improved performance The reasoning behind value engineering is as follows: if marketers expect a product to become practically or stylistically obsolete within a specific length of time, they can design it to only last for that specific lifetime. The products could be built with higher-grade components, but with value engineering th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
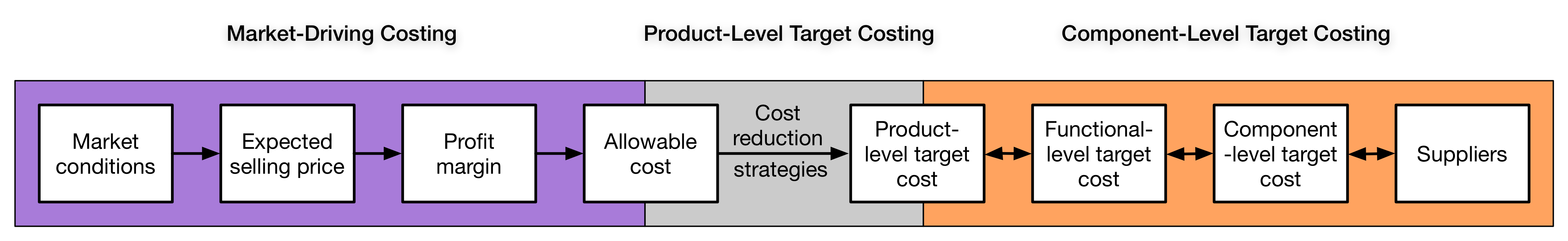
Target Costing
Target costing is an approach to determine a product's life-cycle cost which should be sufficient to develop specified functionality and quality, while ensuring its desired profit. It involves setting a target cost by subtracting a desired profit margin from a competitive market price. A target cost is the maximum amount of cost that can be incurred on a product, however, the firm can still earn the required profit margin from that product at a particular selling price. Target costing decomposes the target cost from product level to component level. Through this decomposition, target costing spreads the competitive pressure faced by the company to product's designers and suppliers. Target costing consists of cost planning in the design phase of production as well as cost control throughout the resulting product life cycle. The cardinal rule of target costing is to never exceed the target cost. However, the focus of target costing is not to minimize costs, but to achieve a desired le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design To Cost
Design-to-Cost (DTC), as part of cost management techniques, describes a systematic approach to controlling the costs of product development and manufacturing. The basic idea is that costs are designed "into the product", even from the earliest concept decisions on and are difficult to remove later. This costs are seen as an equally important parameter besides feature scope and schedule, the three taken together yielding the well-known project triangle. By taking the right design decisions as early as during the initiation and concept phase of the product life-cycle, unnecessary costs at later stages can be avoided. But DTC also tries to capture the necessary measures for cost control during the complete development cycle. In DTC, cost considerations also become part of extended requirements specifications.http://www.cs.odu.edu/~mln/ltrs-pdfs/iaa-ceso-11-90.pdf In contrast to the closely related target costing, DTC does not mean a product will exactly reach a defined cost, ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environment), often focusing on negative, undesirable consequences. Many different definitions have been proposed. The international standard definition of risk for common understanding in different applications is “effect of uncertainty on objectives”. The understanding of risk, the methods of assessment and management, the descriptions of risk and even the definitions of risk differ in different practice areas ( business, economics, environment, finance, information technology, health, insurance, safety, security etc). This article provides links to more detailed articles on these areas. The international standard for risk management, ISO 31000, provides principles and generic guidelines on managing risks faced by organizations. Def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |