|
Dermapteridae
Dermapteridae is an extinct family of earwigs known from the Late Triassic to Mid Cretaceous, it is part of the extinct suborder Archidermaptera, alongside Protodiplatyidae and '' Turanovia.'' It was first named as a subfamily by Vishniakova in 1980, and elevated to family status by Engel in 2003 without discussion. Systematics * †'' Brevicula'' Whalley, 1985 Charmouth Mudstone Formation, United Kingdom, Early Jurassic (Sinemurian) *†'' Dacryoderma'' Engel, 2021 Charmouth Mudstone Formation, United Kingdom, Sinemurian * †'' Dermapteron'' Martynov, 1925 Karabastau Formation, Kazakhstan, Middle-Late Jurassic (Callovian/ Oxfordian) * †'' Dimapteron'' Kelly et al. 2018 Durlston Formation, United Kingdom, Early Cretaceous (Berriasian) * †'' Jurassimedeola'' Zhang, 2002 Daohugou, China, Callovian * †'' Palaeodermapteron'' Zhao et al. 2011 Daohugou, China, Callovian * †'' Phanerogramma'' Cockerell, 1915 Blackstone Formation, Australia, Late Triassic (Norian) Westbury Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
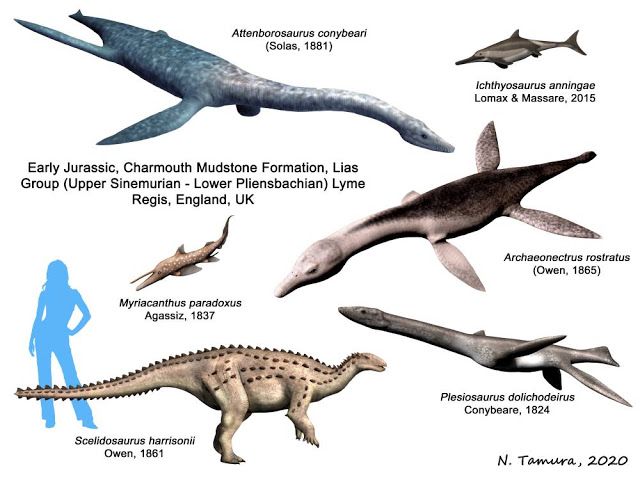
Charmouth Mudstone Formation
The Charmouth Mudstone Formation is a geological formation in England. It preserves fossils dating back to the early part of the Jurassic period (Sinemurian–Pliensbachian). It forms part of the lower Lias Group. It is most prominently exposed at its type locality in cliff section between Lyme Regis and Charmouth (alongside the underlying Blue Lias) but onshore it extends northwards to Market Weighton, Yorkshire, and in the subsurface of the East Midlands Shelf and Wessex Basin. The formation is notable for its fossils, including those of ammonites and marine reptiles and rare dinosaur remains. The formation played a prominent role in the history of early paleontology, with its Lyme Regis-Charmouth exposure being frequented by fossil collectors including Mary Anning. Stratigraphy Shales With Beef Member The Shales With Beef Member is around 28–30 metres thick in the Lyme Regis-Charmouth region and predominantly consists of thinly bedded medium to dark grey mudstone, blocky ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protodiplatyidae
Protodiplatyidae is an extinct family of earwigs. It is one of three families in the suborder Archidermaptera, alongside Dermapteridae and '' Turanovia''. Species are known from Jurassic and Early Cretaceous fossilsFabian HaasArchidermaptera Tree of Life websiteFabian HaasDermaptera: Earwigs Tree of Life website and have unsegmented cerci and tarsi with four to five segments. Genera The family includes the following genera: * '' Abrderma'' - Haifanggou Formation, China, Middle Jurassic (Callovian) * '' Aneuroderma'' - Haifanggou Formation, China, Callovian * '' Archidermapteron'' - Karabastau Formation, Kazakhstan, Late Jurassic ( Oxfordian) * '' Asiodiplatys'' - Karabastau Formation, Kazakhstan, Oxfordian * '' Barbderma'' - Yixian Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian) * '' Longicerciata'' - Laiyang Formation China, Aptian * '' Microdiplatys'' - Karabastau Formation, Kazakhstan, Oxfordian, Itat Formation, Russia, Middle Jurassic (Bathonian In the geologic time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackstone Formation, Australia
The Blackstone Formation is a geologic formation of the Ipswich Coal Measures Group in southeastern Queensland, Australia, dating to the Carnian to Norian stages of the Late Triassic. The shales, siltstones, coal and tuffs were deposited in a lacustrine environment. The Blackstone Formation contains the Denmark Hill Insect Bed. Fossil content Vertebrates Lungfish Invertebrates Ichnofossils In 1964, dinosaur footprints were discovered from the Rhondda colliery (underground coal mine) 230 metres below ground along the sandstone ceiling of the Striped Bacon coal seam. These were initially described as ''Eubrontes'', a type of predatory dinosaur (theropod) footprint. Later, these footprints were considered as evidence for the world's largest Triassic theropod, with legs towering over 2 metres tall. A 3D evaluation of the fossil indicated the footprint length was much smaller than previously reported (34 cm rather than 46 cm long) and its shape was characteristic of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beacon Limestone Formation
The Beacon Limestone Formation, historically known as the Junction Bed, is a formation of early Jurassic age (Pliensbachian–Toarcian). It lies above the Dyrham Formation and below the Bridport Sand Formation. It forms part of the Lias Group. It is found within the Wessex Basin and parts of Somerset, in England England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b .... It is well known for the Strawberry Bank Lagerstätte, which contains the 3-dimensionally preserved remains of vertebrates, including marine crocodyliformes, ichthyosaurs and fish, as well as insect compression fossils. Fossil content Among others, the following fossils have been reported from the formation: Vertebrates Invertebrates References Geologic formations of England Jurassic System of Europe Jura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barremian
The Barremian is an age in the geologic timescale (or a chronostratigraphic stage) between 129.4 ± 1.5 Ma (million years ago) and 121.4 ± 1.0 Ma). It is a subdivision of the Early Cretaceous Epoch (or Lower Cretaceous Series). It is preceded by the Hauterivian and followed by the Aptian Stage.See Gradstein ''et al.'' (2004) or the online geowhen database (link below) Stratigraphic definitions The original type locality for the Barremian Stage is in the vicinity of the village of Barrême, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence, France. Henri Coquand defined the stage and named it in 1873. The base of the Barremian is determined by the first appearance of the ammonites ''Spitidiscus hugii'' and ''Spitidiscus vandeckii''. The end of the Barremian is determined by the geomagnetic reversal at the start of the M0r chronozone, which is biologically near the first appearance of the ammonite '' Paradeshayesites oglanlensis''. Regional equivalents The Barremian falls in the Gallic epoch, a su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weald Clay Formation
Weald Clay or the Weald Clay Formation is a Lower Cretaceous sedimentary rock unit underlying areas of South East England, between the North and South Downs, in an area called the Weald Basin. It is the uppermost unit of the Wealden Group of rocks within the Weald Basin, and the upper portion of the unit is equivalent in age to the exposed portion of the Wessex Formation on the Isle of Wight. It predominantly consists of thinly bedded mudstone. The un-weathered form is blue/grey, and the yellow/orange is the weathered form, it is used in brickmaking. The formation was deposited in lagoonal, lacustrine and alluvial conditions that varied from freshwater to brackish. The clay alternates with other subordinate lithologies, notably hard red-weathering beds of ironstone, limestone (Sussex Marble) and sandstones, notably including the calcareous sandstone unit referred to as the Horsham Stone. It has a gradual, conformable contact with the underlying Tunbridge Wells Sand Formation, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toarcian
The Toarcian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, an age and stage in the Early or Lower Jurassic. It spans the time between 182.7 Ma (million years ago) and 174.1 Ma. It follows the Pliensbachian and is followed by the Aalenian. The Toarcian Age began with the Toarcian turnover, the extinction event that sets its fossil faunas apart from the previous Pliensbachian age. It is believed to have ended with a global cooling event known as the Comptum Cooling Event, although whether it represented a worldwide event is controversial. Stratigraphic definitions The Toarcian takes its name from the city of Thouars, just south of Saumur in the Loire Valley of France. The stage was introduced by French palaeontologist Alcide d'Orbigny in 1842, after examining rock strata of this age in a quarry near Thouars. In Europe this period is represented by the upper part of the Lias. The base of the Toarcian is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record where the ammonite genus '' Eoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hettangian
The Hettangian is the earliest age and lowest stage of the Jurassic The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ... Geological time scale, Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 201.3 ± 0.2 annum, Ma and 199.3 ± 0.3 Ma (million years ago). The Hettangian follows the Rhaetian (part of the Triassic Period) and is followed by the Sinemurian. In European stratigraphy the Hettangian is a part of the time span in which the Lias Group, Lias was deposited. An example is the British Blue Lias, which has an upper Rhaetian to Sinemurian age. Another example is the lower Lias from the Northern Limestone Alps where well-preserved but very rare ammonites, including Alsatites, have been found. Stratigraphic definitions The Hettangian was introduced in the literature by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Lias
The Blue Lias is a geological formation in southern, eastern and western England and parts of South Wales, part of the Lias Group. The Blue Lias consists of a sequence of limestone and shale layers, laid down in latest Triassic and early Jurassic times, between 195 and 200 million years ago. The Blue Lias is famous for its fossils, especially ammonites. Its age corresponds to the Rhaetian to lower Sinemurian stages of the geological timescale, thus fully including the Hettangian stage. It is the lowest of the three divisions of the Lower Jurassic period and, as such, is also given the name ''Lower Lias''. Stratigraphically it can be subdivided into three members: the Wilmcote Limestone, Saltford Shale and Rugby Limestone. Lithology and facies The Blue Lias comprises decimetre scale alternations of argillaceous limestone and mudstone. These alternations are caused by short-term climatic variations during the Early Jurassic attributed to orbital forcing (Milankovitch cycles). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
