|
Dermacentor Steini
''Dermacentor'' is a genus of ticks in the family Ixodidae, the hard ticks. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, with native species on all continents except Australia. Most occur in the Nearctic realm. Hosts of ''Dermacentor'' ticks include many large and small mammals, including horses, deer, cattle, lagomorphs, peccaries, porcupines, tapirs, desert bighorn sheep, and humans. The American dog tick (''D. variabilis'') is a member of the genus. ''Dermacentor'' species are vectors of many pathogens, including ''Rickettsia rickettsii'', which causes the disease Rocky Mountain spotted fever, ''Coxiella burnetii'', which causes Q fever, ''Anaplasma marginale'', which causes anaplasmosis in cattle, ''Francisella tularensis'', which causes tularemia, '' Babesia caballi'', which causes equine piroplasmosis, and the ''Flavivirus'' that causes Powassan encephalitis. ''Dermacentor'' ticks inject a neurotoxin that causes tick paralysis. Species As of 2019, about 41 species are pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermacentor Occidentalis
''Dermacentor'' is a genus of ticks in the family Ixodidae, the hard ticks. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, with native species on all continents except Australia. Most occur in the Nearctic realm. Hosts of ''Dermacentor'' ticks include many large and small mammals, including horses, deer, cattle, lagomorphs, peccaries, porcupines, tapirs, desert bighorn sheep, and humans. The American dog tick (''D. variabilis'') is a member of the genus. ''Dermacentor'' species are vectors of many pathogens, including ''Rickettsia rickettsii'', which causes the disease Rocky Mountain spotted fever, ''Coxiella burnetii'', which causes Q fever, ''Anaplasma marginale'', which causes anaplasmosis in cattle, ''Francisella tularensis'', which causes tularemia, '' Babesia caballi'', which causes equine piroplasmosis, and the ''Flavivirus'' that causes Powassan encephalitis. ''Dermacentor'' ticks inject a neurotoxin that causes tick paralysis. Species As of 2019, about 41 species are pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature, ''Eohippus'', into the large, single-toed animal of today. Humans began domesticating horses around 4000 BCE, and their domestication is believed to have been widespread by 3000 BCE. Horses in the subspecies ''caballus'' are domesticated, although some domesticated populations live in the wild as feral horses. These feral populations are not true wild horses, as this term is used to describe horses that have never been domesticated. There is an extensive, specialized vocabulary used to describe equine-related concepts, covering everything from anatomy to life stages, size, colors, markings, breeds, locomotion, and behavior. Horses are adapted to run, allowing them to quickly escape predators, and po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rickettsia Rickettsii
''Rickettsia rickettsii'' (abbreviated as ''R. rickettsii'') is a gram-negative, intracellular, coccobacillus bacterium that is around 0.8 to 2.0 μm long. ''R. rickettsii'' is the causative agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. ''R. rickettsii'' is one of the most pathogenic ''Rickettsia'' strains. It affects a large majority of the Western Hemisphere and small portions of the Eastern Hemisphere. History Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) first emerged in the Idaho Valley in 1896. At that time, not much information was known about the disease; it was originally called Black Measles because patients had a characteristic spotted rash appearance throughout their body. The first clinical description of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever was reported in 1899 by Edward E. Maxey. Howard Ricketts (1871–1910), an associate professor of pathology at the University of Chicago in 1902, was the first to identify and study ''R. rickettsii''. At this time, the trademark rash now began to slowl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the longest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector (epidemiology)
In epidemiology, a disease vector is any living agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen to another living organism; agents regarded as vectors are organisms, such as parasites or microbes. The first major discovery of a disease vector came from Ronald Ross in 1897, who discovered the malaria pathogen when he dissected a mosquito. Arthropods Arthropods form a major group of pathogen vectors with mosquitoes, flies, sand flies, lice, fleas, ticks, and mites transmitting a huge number of pathogens. Many such vectors are haematophagous, which feed on blood at some or all stages of their lives. When the insects feed on blood, the pathogen enters the blood stream of the host. This can happen in different ways. The ''Anopheles'' mosquito, a vector for malaria, filariasis, and various arthropod-borne-viruses (arboviruses), inserts its delicate mouthpart under the skin and feeds on its host's blood. The parasites the mosquito carries are usually located in its salivary gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Food And Agricultural Sciences
The University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (UF/IFAS) is a teaching, research and Extension scientific organization focused on agriculture and natural resources. It is a partnership of federal, state, and county governments that includes an Extension office in each of Florida's 67 counties, 12 off-campus research and education centers, five demonstration units, the University of Florida College of Agricultural and Life Sciences (including the School of Forest, Fisheries and Geomatics Sciences and the School of Natural Resources and Environment), three 4-H camps, portions of the UF College of Veterinary Medicine, the Florida Sea Grant program, the Emerging Pathogens Institute, the UF Water Institute and the UF Genetics Institute. UF/IFAS research and development covers natural resource industries that have a $101 billion annual impact. The program is ranked #1 in the nation in federally financed higher education R&D expenditures in agricultural sciences a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its Gainesville campus since September 1906. After the Florida state legislature's creation of performance standards in 2013, the Florida Board of Governors designated the University of Florida as a "preeminent university". For 2022, '' U.S. News & World Report'' ranked Florida as the fifth (tied) best public university and 28th (tied) best university in the United States. The University of Florida is the only member of the Association of American Universities in Florida and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". The university is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools (SACS). It is the third largest Florida university by student population,Nathan Crabbe, UF is no longer la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermacentor Variabilis
''Dermacentor variabilis'', also known as the American dog tick or wood tick, is a species of tick that is known to carry bacteria responsible for several diseases in humans, including Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia (''Francisella tularensis''). It is one of the best-known hard ticks. Diseases are spread when it sucks blood from the host. It may take several days for the host to experience symptoms. Though ''D. variabilis'' may be exposed to ''Borrelia burgdorferi'', the causative agent of Lyme disease, these ticks are not competent vectors for the transmission of this disease. The primary vectors for ''B. burgdorferi'' are the deer ticks ''Ixodes scapularis'' in eastern parts of the United States, ''Ixodes pacificus'' in California and Oregon, and ''Ixodes ricinus'' in Europe. ''D. variabilis'' may also carry ''Anaplasma phagocytophilum'', the causative agent of human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and ''Ehrlichia chaffeensis'', the causative agent of human monocytic eh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert Bighorn Sheep
The desert bighorn sheep (''Ovis canadensis nelsoni'') is a subspecies of bighorn sheep (''Ovis canadensis'') that is native to the deserts of the United States' intermountain west and southwestern regions, as well as northwestern Mexico. The Bureau of Land Management considered the subspecies "sensitive" to extinction. The trinomial of this species commemorates the American naturalist Edward William Nelson (1855–1934). The characteristics and behavior of the desert bighorn sheep generally follow those of other bighorn sheep, except for adaptation to the lack of water in the desert. They can go for extended periods of time without drinking water. The desert bighorn sheep is the state mammal of Nevada. It is also the mascot of the Universidad Autónoma de Baja California. Distribution The range of the desert bighorn sheep includes habitats in the Mojave Desert, Sonoran Desert, Great Basin Desert, and Chihuahuan Desert, as well as the Colorado Plateau. Anza-Borrego Desert State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
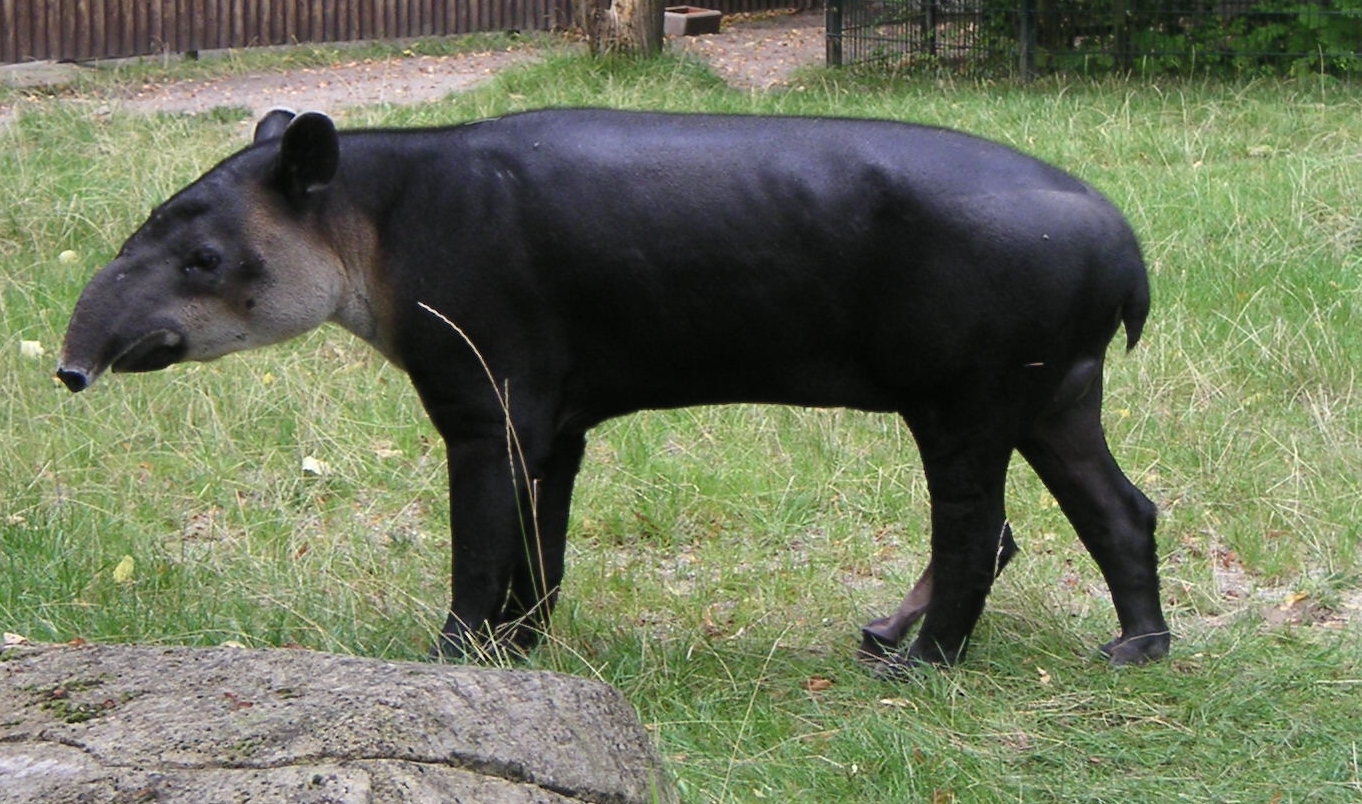
Tapir
Tapirs ( ) are large, herbivorous mammals belonging to the family Tapiridae. They are similar in shape to a pig, with a short, prehensile nose trunk. Tapirs inhabit jungle and forest regions of South and Central America, with one species inhabiting Southeast Asia. They are one of three extant branches of Perissodactyla (odd-toed ungulates), alongside equines and rhinoceros. Only a single genus, ''Tapirus'' is currently extant. Tapirs migrated into South America during the Pleistocene epoch from North America after the formation of the Isthmus of Panama as part of the Great American Interchange. Tapirs were once widespread in North America until the arrival of humans at the end of the Late Pleistocene, around 12,000 years ago. Species There are four widely recognized extant species of tapir, all in the genus ''Tapirus'' of the family Tapiridae. They are the South American tapir, the Malayan tapir, Baird's tapir, and the mountain tapir. In 2013, a group of researchers said they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porcupine
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two families of animals: the Old World porcupines of family Hystricidae, and the New World porcupines of family, Erethizontidae. Both families belong to the infraorder Hystricognathi within the profoundly diverse order Rodentia and display superficially similar coats of rigid or semi-rigid quills, which are modified hairs composed of keratin. Despite this, the two groups are distinct from one another and are not closely related to each other within the Hystricognathi. The largest species of porcupine is the third-largest living rodent in the world, after the capybara and beaver. The Old World porcupines (Hystricidae) live in Italy, Asia (western and southern), and most of Africa. They are large, terrestrial, and strictly nocturnal. The New World porcupines (Erethizontidae) are indigenous to North America and northern South America. They live in wooded area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peccary
A peccary (also javelina or skunk pig) is a medium-sized, pig-like hoofed mammal of the family Tayassuidae (New World pigs). They are found throughout Central and South America, Trinidad in the Caribbean, and in the southwestern area of North America. They usually measure between in length, and a full-grown adult usually weighs about . They represent the closest relatives of the family Suidae, which contains pigs and relatives. Together Tayassuidae and Suidae are grouped in the Suina within the Artiodactyla (even toed ungulates). Peccaries are social creatures that live in herds. They eat roots, grubs, and a variety of foods. They can identify each other by their strong odors. A group of peccaries that travel and live together is called a "squadron". A squadron of peccaries averages between six and nine members. Peccaries first appeared in North America during the Miocene, and migrated into South America during the Pliocene-Pleistocene as part of the Great American Interchange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_p174_GAINESVILLE%2C_EAST_FLORIDA_SEMINARY.jpg)