|
Derk Pereboom (philosopher)
Derk Pereboom (born 1957) is the Susan Linn Sage Professor in Philosophy and Ethics at Cornell University. He specializes in free will and moral responsibility, philosophy of mind, philosophy of religion, and the work of Immanuel Kant. Life and career Derk Pereboom was born in the village of Pesse, near Hoogeveen, the Netherlands, on February 6, 1957. He received his BA in philosophy at Calvin College in Grand Rapids, Michigan, in 1978, where his teachers included Alvin Plantinga and Nicholas Wolterstorff. He earned his PhD at University of California, Los Angeles in 1985, with a dissertation on Immanuel Kant's theory of mental representation under the supervision of Robert Merrihew Adams and Tyler Burge. He was an assistant professor in the Department of Philosophy at the University of Vermont from 1985 to 1991, associate professor from 1991 to 1997, and professor from 1997 to 2007. he has been professor in the Sage School of Philosophy at Cornell University. he is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pesse
Pesse is a village in the Dutch province of Drenthe. It is located in the municipality of Hoogeveen.''ANWB Topografische Atlas Nederland'', Topografische Dienst and ANWB, 2005. Overview Pesse is an ''esdorp'' which developed in the Middle Ages. It was first mentioned in 1217 as Petthe. The etymology is unclear. The village is mainly known for the Pesse canoe, believed to be the world's oldest known boat. Carbon dating indicates that the boat was constructed during the early mesolithic period between 8040 BCE and 7510 BCE. It is currently housed in the Drents Museum in Assen Assen () is a municipality and a city in the northeastern Netherlands, and is the capital (politics), capital of the province of Drenthe. It received City rights in the Netherlands, city rights in 1809. Assen is known for TT Circuit Assen, the ..., Netherlands. The canoe was found during the construction of the nearby A28. References Populated places in Drenthe Hoogeveen {{Drenthe-geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy Of Action
Action theory (or theory of action) is an area in philosophy concerned with theories about the processes causing willful human bodily movements of a more or less complex kind. This area of thought involves epistemology, ethics, metaphysics, jurisprudence, and philosophy of mind, and has attracted the strong interest of philosophers ever since Aristotle's ''Nicomachean Ethics'' (Third Book). With the advent of psychology and later neuroscience, many theories of action are now subject to empirical testing. Philosophical action theory, or the philosophy of action, should not be confused with sociological theories of social action, such as the action theory established by Talcott Parsons. Nor should it be confused with activity theory. Overview Basic action theory typically describes action as intentional behavior caused by an ''agent'' in a particular ''situation''. The agent's ''desires'' and ''beliefs'' (e.g. my wanting a glass of water and believing that the clear liqui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functionalism (philosophy Of Mind)
In philosophy of mind, functionalism is the thesis that mental states (beliefs, desires, being in pain, etc.) are constituted solely by their functional role, which means, their causal relations with other mental states, sensory inputs and behavioral outputs.Block, Ned. (1996). "What is functionalism?" a revised version of the entry on functionalism in ''The Encyclopedia of Philosophy Supplement'', Macmillan. PDF online Functionalism developed largely as an alternative to the identity theory of mind and behaviorism. Functionalism is a theoretical level between the physical implementation and behavioral output.Marr, D. (1982). ''Vision: A Computational Approach''. San Francisco: Freeman & Co. Therefore, it is different from its predecessors of Cartesian dualism (advocating independent mental and physical substances) and Skinnerian behaviorism and physicalism (declaring only physical substances) because it is only concerned with the effective functions of the brain, through its organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilary Putnam
Hilary Whitehall Putnam (; July 31, 1926 – March 13, 2016) was an American philosopher, mathematician, and computer scientist, and a major figure in analytic philosophy in the second half of the 20th century. He made significant contributions to philosophy of mind, philosophy of language, philosophy of mathematics, and philosophy of science. Outside philosophy, Putnam contributed to mathematics and computer science. Together with Martin Davis he developed the Davis–Putnam algorithm for the Boolean satisfiability problem and he helped demonstrate the unsolvability of Hilbert's tenth problem. Putnam was known for his willingness to apply equal scrutiny to his own philosophical positions as to those of others, subjecting each position to rigorous analysis until he exposed its flaws. As a result, he acquired a reputation for frequently changing his positions. In philosophy of mind, Putnam is known for his argument against the type-identity of mental and physical states based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrinsic Properties
In science and engineering, an intrinsic property is a property of a specified subject that exists itself or within the subject. An extrinsic property is not essential or inherent to the subject that is being characterized. For example, mass is an intrinsic property of any physical object, whereas weight is an extrinsic property that depends on the strength of the gravitational field in which the object is placed. Applications in science and engineering In materials science, an intrinsic property is independent of how much of a material is present and is independent of the form of the material, e.g., one large piece or a collection of small particles. Intrinsic properties are dependent mainly on the fundamental chemical composition and structure of the material. Extrinsic properties are differentiated as being dependent on the presence of avoidable chemical contaminants or structural defects. In biology, intrinsic effects originate from inside an organism or cell, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russellian Monist
Neutral monism is an umbrella term for a class of metaphysical theories in the philosophy of mind. These theories reject the dichotomy of mind and matter, believing the fundamental nature of reality to be neither mental nor physical; in other words it is "neutral". Craig, Edward. (1998). ''Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy''. Routledge. p. 816. Relations to other theories Physicalists believe reality is fundamentally material, idealists believe reality is fundamentally mental, dualists believe reality consists of both fundamentally mental and fundamentally physical elements, and neutral monists believe reality consists of elements that are neither fundamentally physical nor mental. Monism Neutral monism largely overlaps with dual-aspect theory. However, it shares little in common with other forms of monism, such as idealism and physicalism. Dualism Neutral monism is similar to dualism in that both take reality to have both mental and physical properties irreducible to one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Graziano
Michael Steven Anthony Graziano (born May 22, 1967) is an American scientist and novelist who is currently a professor of Psychology and Neuroscience at Princeton University. His scientific research focuses on the brain basis of awareness. He has proposed the "attention schema" theory, an explanation of how, and for what adaptive advantage, brains attribute the property of awareness to themselves. His previous work focused on how the |
Daniel Dennett
Daniel Clement Dennett III (born March 28, 1942) is an American philosopher, writer, and cognitive scientist whose research centers on the philosophy of mind, philosophy of science, and philosophy of biology, particularly as those fields relate to evolutionary biology and cognitive science. , he is the co-director of the Center for Cognitive Studies and the Austin B. Fletcher Professor of Philosophy at Tufts University in Massachusetts. Dennett is a member of the editorial board for ''The Rutherford Journal'' and a co-founder of The Clergy Project. A vocal atheist and secularist, Dennett is referred to as one of the "Four Horsemen of New Atheism", along with Richard Dawkins, Sam Harris, and the late Christopher Hitchens. Early life, education, and career Daniel Clement Dennett III was born on March 28, 1942, in Boston, Massachusetts, the son of Ruth Marjorie (née Leck; 1903–1971) and Daniel Clement Dennett Jr. (1910–1947). Dennett spent part of his childhood in Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Chalmers
David John Chalmers (; born 20 April 1966) is an Australian philosopher and cognitive scientist specializing in the areas of philosophy of mind and philosophy of language. He is a professor of philosophy and neural science at New York University, as well as co-director of NYU's Center for Mind, Brain and Consciousness (along with Ned Block). In 2006, he was elected a Fellow of the Australian Academy of the Humanities. In 2013, he was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts & Sciences. Chalmers is best known for formulating the hard problem of consciousness. He and David Bourget cofounded PhilPapers, a database of journal articles for philosophers. Early life and education Chalmers was born in Sydney, New South Wales, in 1966, and subsequently grew up in Adelaide, South Australia, where he attended Unley High School. As a child, he experienced synesthesia. He began coding and playing computer games at age 10 on a PDP-10 at a medical center. He also performed excep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Cameron Jackson
Frank Cameron Jackson (born 31 August 1943) is an Australian analytic philosopher and Emeritus Professor in the School of Philosophy (Research School of Social Sciences) at Australian National University (ANU) where he had spent most of the latter part of his career. His primary research interests include epistemology, metaphysics, meta-ethics and the philosophy of mind. In the latter field he is best known for the "Mary's room" knowledge argument, a thought experiment that is one of the most discussed challenges to physicalism. Biography Frank Cameron Jackson was born on 31 August 1943 in Melbourne, Australia. His parents were both philosophers. His mother Ann E. Jackson, who rose to the rank of senior tutor, taught philosophy at the University of Melbourne from 1961 to 1984. His atheistic father Allan Cameron Jackson (1911–1990) had been a student of Ludwig Wittgenstein (having gone to Cambridge in 1946 for Ph.D. studies). F. C. Jackson, in interview with Graham Oppy, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
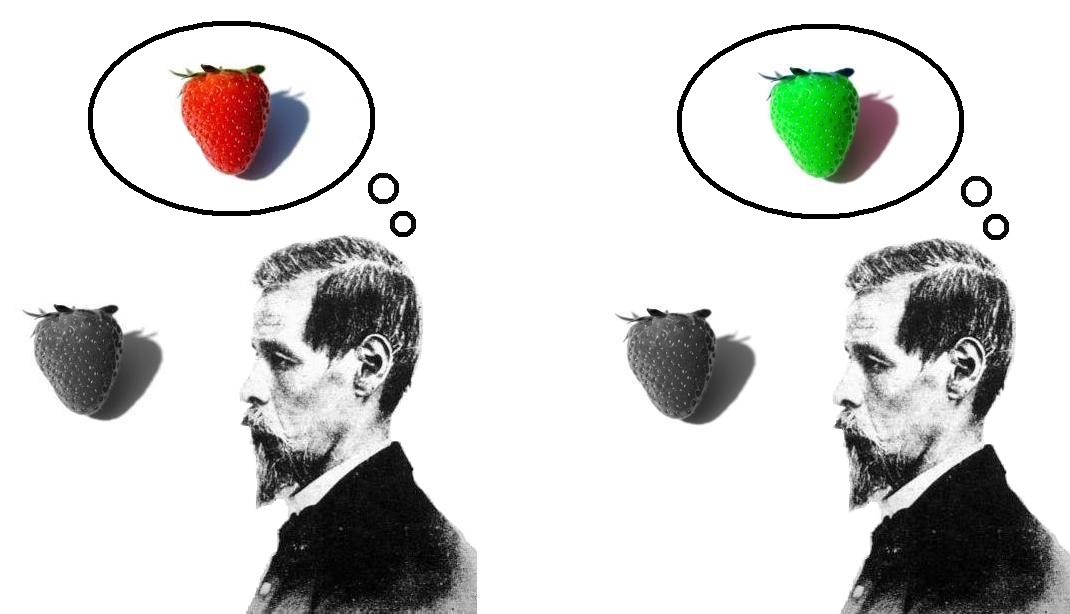
Hard Problem Of Consciousness
The hard problem of consciousness is the problem of explaining why and how humans have qualia or phenomenal experiences. This is in contrast to the "easy problems" of explaining the physical systems that give us and other animals the ability to discriminate, integrate information, and so forth. These problems are seen as relatively easy because all that is required for their solution is to specify the mechanisms that perform such functions. Philosopher David Chalmers writes that even once we have solved all such problems about the brain and experience, the hard problem will still persist. The existence of a "hard problem" is controversial. It has been accepted by philosophers of mind such as Joseph Levine, Colin McGinn, and Ned Block and cognitive neuroscientists such as Francisco Varela, Giulio Tononi, and Christof Koch. However, its existence is disputed by philosophers of mind such as Daniel Dennett, Massimo Pigliucci, Thomas Metzinger, Patricia Churchland, and Keith Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baruch Spinoza
Baruch (de) Spinoza (born Bento de Espinosa; later as an author and a correspondent ''Benedictus de Spinoza'', anglicized to ''Benedict de Spinoza''; 24 November 1632 – 21 February 1677) was a Dutch philosopher of Portuguese-Jewish origin, born in Amsterdam. One of the foremost exponents of 17th-century Rationalism and one of the early and seminal thinkers of the Enlightenment and modern biblical criticism including modern conceptions of the self and the universe, he came to be considered "one of the most important philosophers—and certainly the most radical—of the early modern period." Inspired by Stoicism, Jewish Rationalism, Machiavelli, Hobbes, Descartes, and a variety of heterodox religious thinkers of his day, Spinoza became a leading philosophical figure during the Dutch Golden Age. Spinoza's given name, which means "Blessed", varies among different languages. In Hebrew, his full name is written . In most of the documents and records contemporary with Spinoza's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |