|
Derek De Solla Price
Derek John de Solla Price (22 January 1922 – 3 September 1983) was a British physicist, historian of science, and information scientist. He was known for his investigation of the Antikythera mechanism, an ancient Greek planetary computer, and for quantitative studies on scientific publications, which led to his being described as the "Herald of scientometrics". Biography Price was born in Leyton, England, to Philip Price, a tailor, and Fanny de Solla, a singer. He began work in 1938 as an assistant in a physics laboratory at the South West Essex Technical College, before studying Physics and Mathematics at the University of London, where he received a Bachelor of Science in 1942. He then worked as an assistant to Harry Lowery carrying out research on hot and molten metals, and working towards a London external Ph.D. in experimental physics which he obtained in 1946. This work led to several research papers and to a patent for an emissive-correcting optical pyrometer. He then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antikythera Mechanism
The Antikythera mechanism ( ) is an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek hand-powered orrery, described as the oldest example of an analogue computer used to predict astronomy, astronomical positions and eclipses decades in advance. It could also be used to track the four-year cycle of athletic games which was similar to an Olympiad, the cycle of the ancient Olympic Games. This artefact was among wreckage retrieved from a Antikythera wreck, shipwreck off the coast of the Greek island Antikythera in 1901. On 17 May 1902, it was identified as containing a gear by archaeologist Valerios Stais. The device, housed in the remains of a wooden-framed case of (uncertain) overall size , was found as one lump, later separated into three main fragments which are now divided into 82 separate fragments after conservation efforts. Four of these fragments contain gears, while inscriptions are found on many others. The largest gear is approximately in diameter and originally had 223 teeth. In 2008, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
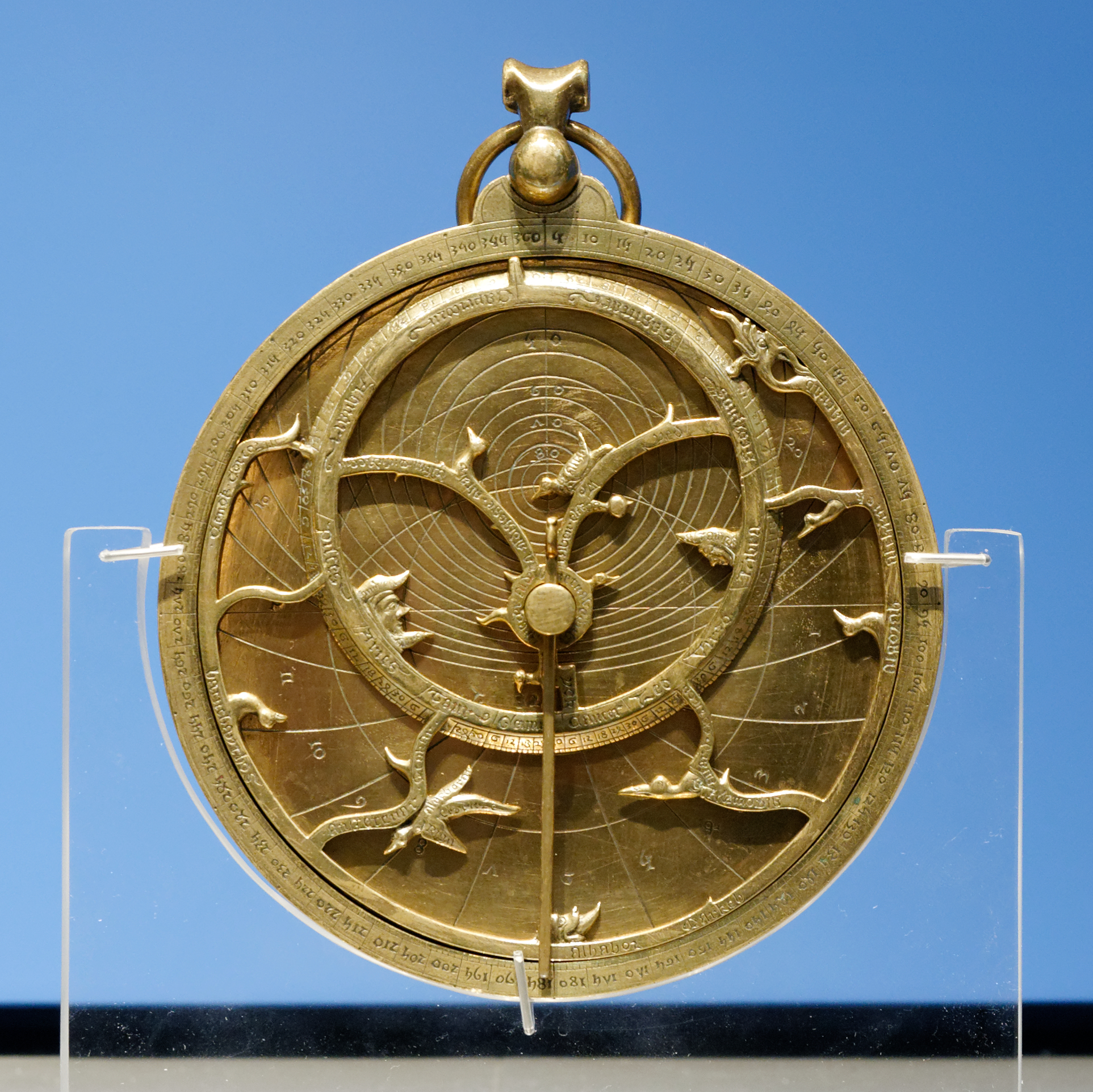
A Treatise On The Astrolabe
''A Treatise on the Astrolabe'' is a medieval instruction manual on the astrolabe by Geoffrey Chaucer. It describes both the form and the proper use of the instrument, and stands out as a prose technical work from a writer better known for poetry, written in English rather than the more typical Latin. Significance The ''Treatise'' is considered the "oldest work in English written upon an elaborate scientific instrument". It is admired for its clarity in explaining difficult concepts – although modern readers lacking an actual astrolabe may find the details of the astrolabe difficult to understand. Robinson believes that it indicates that had Chaucer written more freely composed prose it would have been superior to his translations of Boethius and Renaut de Louhans. Chaucer’s exact source is undetermined but most of his ‘conclusions’ go back, directly or indirectly, to ''Compositio et Operatio Astrolabii'', a Latin translation of Messahala's Arabic treatise of the 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer (; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for ''The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He was the first writer to be buried in what has since come to be called Poets' Corner, in Westminster Abbey. Chaucer also gained fame as a philosopher and astronomer, composing the scientific ''A Treatise on the Astrolabe'' for his 10-year-old son Lewis. He maintained a career in the civil service as a bureaucrat, courtier, diplomat, and member of parliament. Among Chaucer's many other works are ''The Book of the Duchess'', ''The House of Fame'', ''The Legend of Good Women'', and ''Troilus and Criseyde''. He is seen as crucial in legitimising the literary use of Middle English when the dominant literary languages in England were still Anglo-Norman French and Latin. Chaucer's contemporary Thomas Hoccleve hailed him as "the firste fyndere of our ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatorium
An equatorium (plural, equatoria) is an astronomical calculating instrument. It can be used for finding the positions of the Moon, Sun, and planets without arithmetic operations, using a geometrical model to represent the position of a given celestial body. History Planetary equatoria were probably made by ancient Greeks, although no findings nor descriptions have been preserved from that period. In his comment on Ptolemy's ''Handy Tables'', 4th century mathematician Theon of Alexandria introduced some diagrams to geometrically compute the position of the planets based on Ptolemy's epicyclical theory. The first description of the construction of a solar (as opposed to planetary) equatorium is contained in Proclus's fifth-century work ''Hypotyposis'', where he gives instructions on how to construct one in wood or bronze. The earliest surviving descriptions of planetary equatoria are the Latin translations of Arab works contained in the '' Libros del saber de astronomia'' ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English period. Scholarly opinion varies, but the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' specifies the period when Middle English was spoken as being from 1150 to 1500. This stage of the development of the English language roughly followed the High to the Late Middle Ages. Middle English saw significant changes to its vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and orthography. Writing conventions during the Middle English period varied widely. Examples of writing from this period that have survived show extensive regional variation. The more standardized Old English language became fragmented, localized, and was, for the most part, being improvised. By the end of the period (about 1470) and aided by the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Library
Cambridge University Library is the main research library of the University of Cambridge. It is the largest of the over 100 libraries within the university. The Library is a major scholarly resource for the members of the University of Cambridge and external researchers. It is often referred to within the university as the UL. Thirty three faculty and departmental libraries are associated with the University Library for the purpose of central governance and administration, forming "Cambridge University Libraries". Cambridge University Library is one of the six legal deposit libraries under UK law. The Library holds approximately 9 million items (including maps and sheet music) and, through legal deposit, purchase and donation it receives around 100,000 items every year. The University Library is unique among the legal deposit libraries in keeping a large proportion of its material on open access and in allowing some categories of reader to borrow from its collections. Its or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peterhouse, Cambridge
Peterhouse is the oldest constituent college of the University of Cambridge in England, founded in 1284 by Hugh de Balsham, Bishop of Ely. Today, Peterhouse has 254 undergraduates, 116 full-time graduate students and 54 fellows. It is quite often erroneously referred to as ''Peterhouse College'', although the correct name is simply ''Peterhouse''. Peterhouse alumni are notably eminent within the natural sciences, including scientists Lord Kelvin, Henry Cavendish, Charles Babbage, James Clerk Maxwell, James Dewar, Frank Whittle, and five Nobel prize winners in science: Sir John Kendrew, Sir Aaron Klug, Archer Martin, Max Perutz, and Michael Levitt. Peterhouse alumni also include the Archbishop of Canterbury John Whitgift, Lord Chancellors, Lord Chief Justices, as well as Oscar-winning film director Sam Mendes, and comedian David Mitchell. British Prime Minister Augustus FitzRoy, 3rd Duke of Grafton, and Elijah Mudenda, second prime minister of Zambia, also studied at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society
''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'' is a scientific journal published by the Royal Society. In its earliest days, it was a private venture of the Royal Society's secretary. It was established in 1665, making it the first journal in the world exclusively devoted to science, and therefore also the world's longest-running scientific journal. It became an official society publication in 1752. The use of the word ''philosophical'' in the title refers to natural philosophy, which was the equivalent of what would now be generally called ''science''. Current publication In 1887 the journal expanded and divided into two separate publications, one serving the physical sciences ('' Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences'') and the other focusing on the life sciences ('' Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences''). Both journals now publish themed issues and issues resulting from pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National University Of Singapore
The National University of Singapore (NUS) is a national public research university in Singapore. Founded in 1905 as the Straits Settlements and Federated Malay States Government Medical School, NUS is the oldest autonomous university in the country. It offers degree programmes in a wide range of disciplines at both the undergraduate and postgraduate levels, including in the sciences, medicine and dentistry, design and environment, law, arts and social sciences, engineering, business, computing, and music. NUS is one of the most highly-ranked academic institutions in the world. It has consistently featured in the top 30 of the Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) World University Rankings and the Times Higher Education (THE) World University Rankings, and in the top 100 of the Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU). As of 2022-2023, NUS is 11th worldwide according to QS and 19th worldwide according to THE. NUS's main campus is located in the southwestern part of Singapore, adja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Physics
Experimental physics is the category of disciplines and sub-disciplines in the field of physics that are concerned with the observation of physical phenomena and experiments. Methods vary from discipline to discipline, from simple experiments and observations, such as Galileo's experiments, to more complicated ones, such as the Large Hadron Collider. Overview Experimental physics encompasses all the disciplines of physics that are concerned with data acquisition, data-acquisition methods, and the detailed conceptualization (beyond simple thought experiments) and realization of laboratory experiments. It is often contrasted with theoretical physics, which is more concerned with predicting and explaining the physical behaviour of nature than the acquisition of empirical data. Although experimental and theoretical physics are concerned with different aspects of nature, they both share the same goal of understanding it and have a symbiotic relationship. The former provides data a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |