|
Depression (economics)
An economic depression is a period of carried long-term economical downturn that is result of lowered economic activity in one major or more national economies. Economic depression maybe related to one specific country were there is some economic crisis that has worsened but most often reflexes historically the American Great Depression and similar economic status that may be recognized as existing at some country, several countries or even in many countries. It is often understood in economics that economic crisis and the following recession that maybe named economic depression are part of economic cycles where slowdown of economy follows the economic growth and vice versa. It is a result of more severe economic problems or a ''downturn'' than the economic recession, recession itself, which is a slowdown in economic activity over the course of the normal business cycle of growing economy. Economic depressions maybe also characterized by their length or duration, and maybe showing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English-speaking World
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the '' Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest language by number of speakers, and the third largest language by number of native speakers. England and the Scottish Lowlands, countries of the United Kingdom, are the birthplace of the English language, and the modern form of the language has been being spread around the world since the 17th century, first by the worldwide influence of England and later the United Kingdom, and then by that of the United States. Through all types of printed and electronic media of these countries, English has become the leading language of international discourse and the lingua franca in many regions and professional contexts such as science, navigation and law. The United Kingdom remains the largest English-speaking country in Europe. The United States a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Failure
A bank failure occurs when a bank is unable to meet its obligations to its depositors or other creditors because it has become insolvent or too illiquid to meet its liabilities. A bank usually fails economically when the market value of its assets declines to a value that is less than the market value of its liabilities. The insolvent bank either borrows from other solvent banks or sells its assets at a lower price than its market value to generate liquid money to pay its depositors on demand. The inability of the solvent banks to lend liquid money to the insolvent bank creates a bank panic among the depositors as more depositors try to take out cash deposits from the bank. As such, the bank is unable to fulfill the demands of all of its depositors on time. A bank may be taken over by the regulating government agency if its shareholders' equity are below the regulatory minimum. The failure of a bank is generally considered to be of more importance than the failure of other types of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
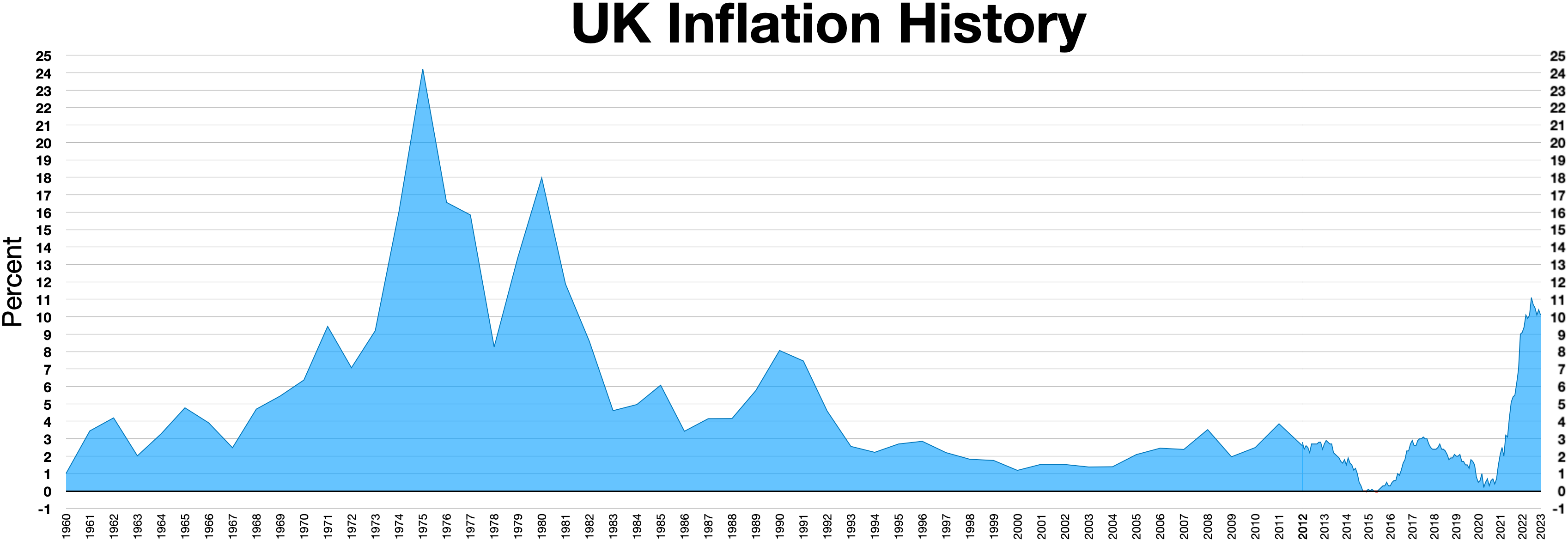
Stagflation
In economics, stagflation or recession-inflation is a situation in which the inflation rate is high or increasing, the economic growth rate slows, and unemployment remains steadily high. It presents a dilemma for economic policy, since actions intended to lower inflation may exacerbate unemployment. The term, a portmanteau of '' stagnation'' and ''inflation'', is generally attributed to Iain Macleod, a British Conservative Party politician who became Chancellor of the Exchequer in 1970. Macleod used the word in a 1965 speech to Parliament during a period of simultaneously high inflation and unemployment in the United Kingdom.Introduction, page 9. Warning the House of Commons of the gravity of the situation, he said: Macleod used the term again on 7 July 1970, and the media began also to use it, for example in ''The Economist'' on 15 August 1970, and ''Newsweek'' on 19 March 1973. John Maynard Keynes did not use the term, but some of his work refers to the conditions that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was an American politician who served as the 31st president of the United States from 1929 to 1933 and a member of the Republican Party, holding office during the onset of the Great Depression in the United States. A self-made man who became rich as a mining engineer, Hoover led the Commission for Relief in Belgium, served as the director of the U.S. Food Administration, and served as the U.S. Secretary of Commerce. Hoover was born to a Quaker family in West Branch, Iowa, but he grew up in Oregon. He was one of the first graduates of the new Stanford University in 1895. He took a position with a London-based mining company working in Australia and China. He rapidly became a wealthy mining engineer. In 1914 at the outbreak of World War I, he organized and headed the Commission for Relief in Belgium, an international relief organization that provided food to occupied Belgium. When the U.S. entered the war in 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
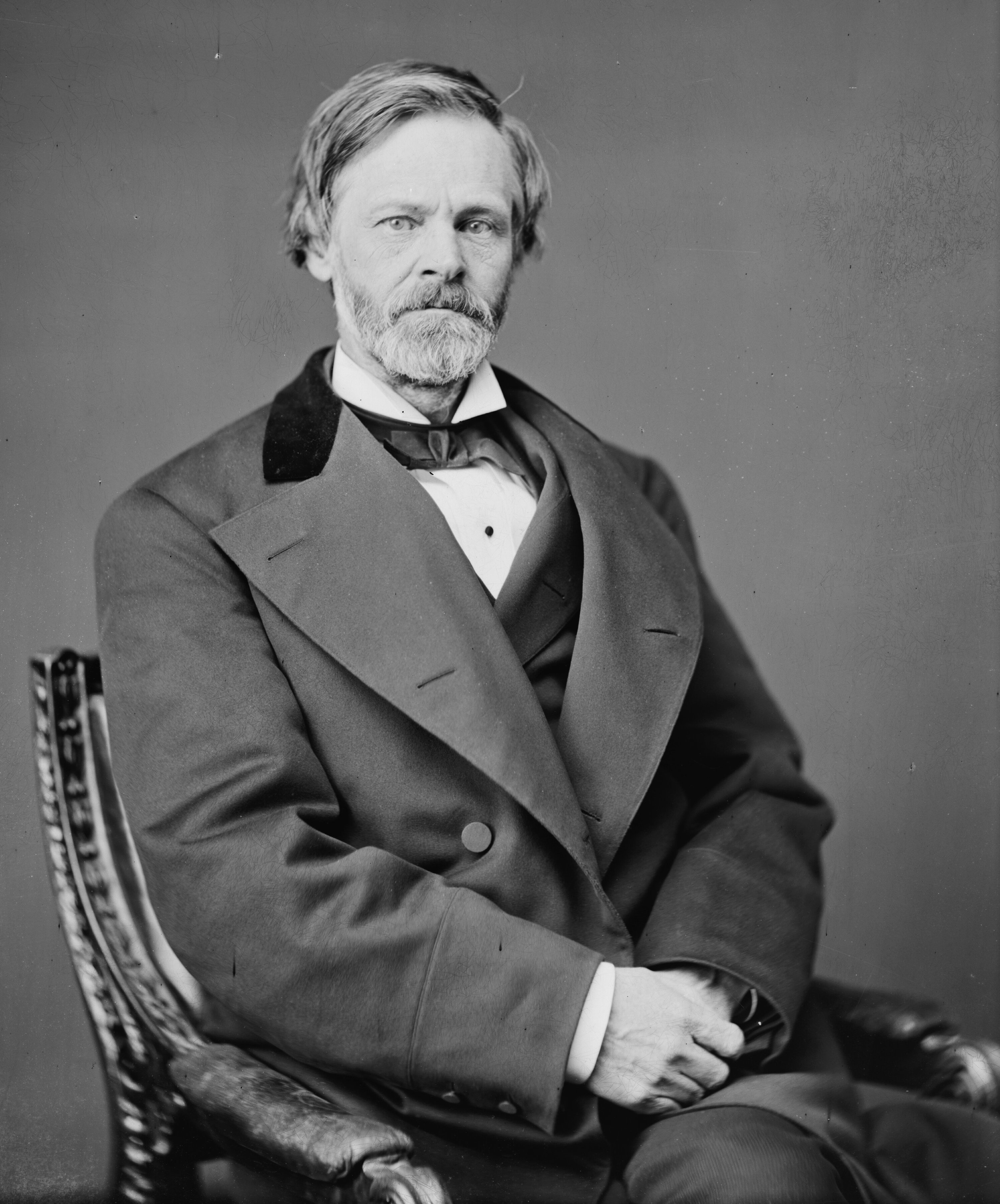
Lionel Robbins
Lionel Charles Robbins, Baron Robbins, (22 November 1898 – 15 May 1984) was a British economist, and prominent member of the economics department at the London School of Economics (LSE). He is known for his leadership at LSE, his proposed definition of economics, and for his instrumental efforts in shifting Anglo-Saxon economies, Anglo-Saxon economics from its Alfred Marshall, Marshallian direction. He is famous for the quote, "Humans want what they can't have." Early life Robbins was born in Sipson, west of London, the son of Rowland Richard Robbins (1872–1960), known as Dick, and his wife Rosa Marion Harris; his father was a farmer, a member of Middlesex County Council involved also in the National Farmers' Union of England and Wales, National Farmers' Union, and the family was Strict Baptist. His sister Caroline Robbins, Caroline became a noted Professor of History at Bryn Mawr College. Robbins was educated at home, at Hounslow College (a Preparatory school (United Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
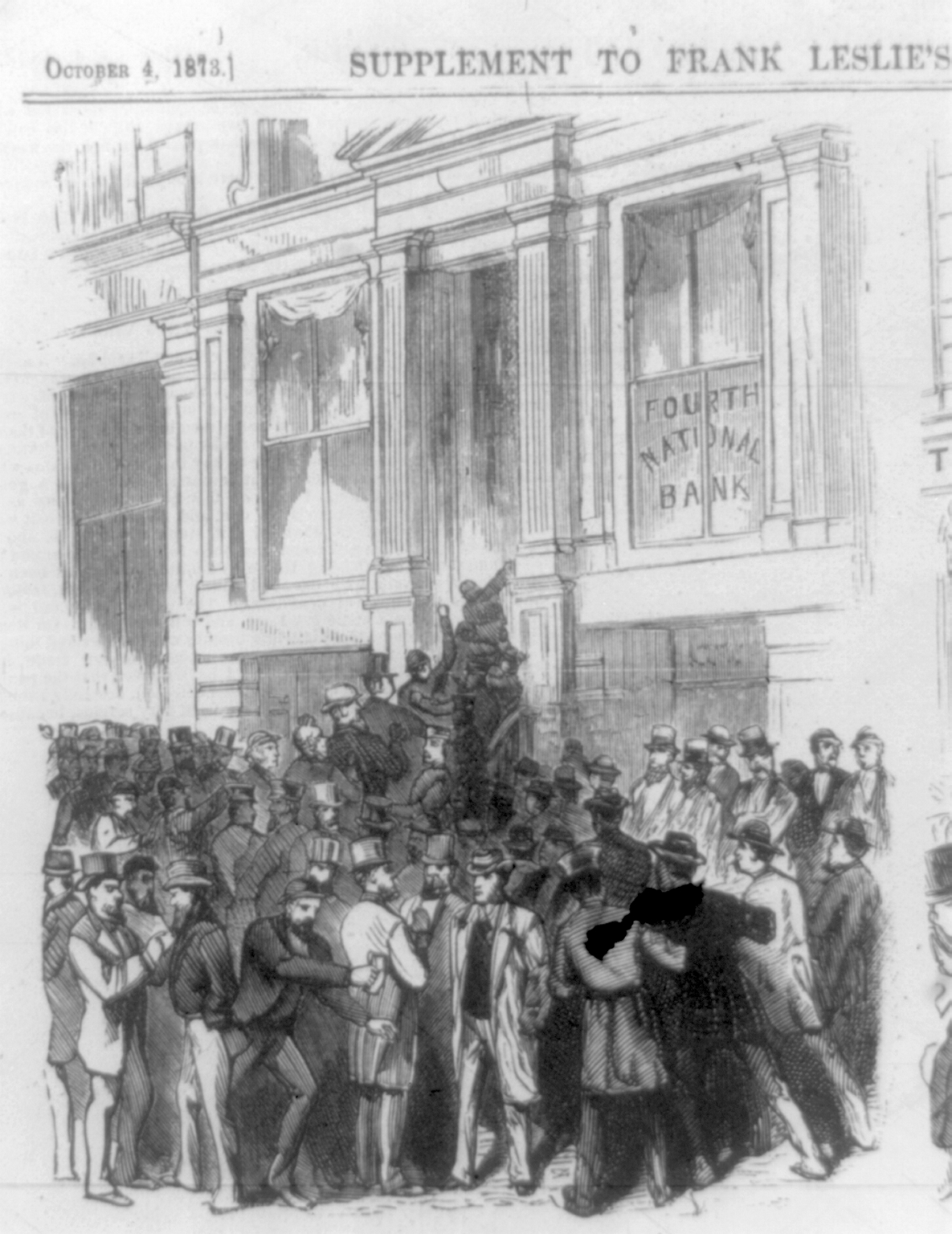
Long Depression
The Long Depression was a worldwide price and economic recession, beginning in 1873 and running either through March 1879, or 1896, depending on the metrics used. It was most severe in Europe and the United States, which had been experiencing strong economic growth fueled by the Second Industrial Revolution in the decade following the American Civil War. The episode was labeled the "Great Depression" at the time, and it held that designation until the Great Depression of the 1930s. Though a period of general deflation and a general contraction, it did not have the severe economic retrogression of the Great Depression. It was most notable in Western Europe and North America, at least in part because reliable data from the period is most readily available in those parts of the world. The United Kingdom is often considered to have been the hardest hit; during this period it lost some of its large industrial lead over the economies of continental Europe. While it was occurring, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
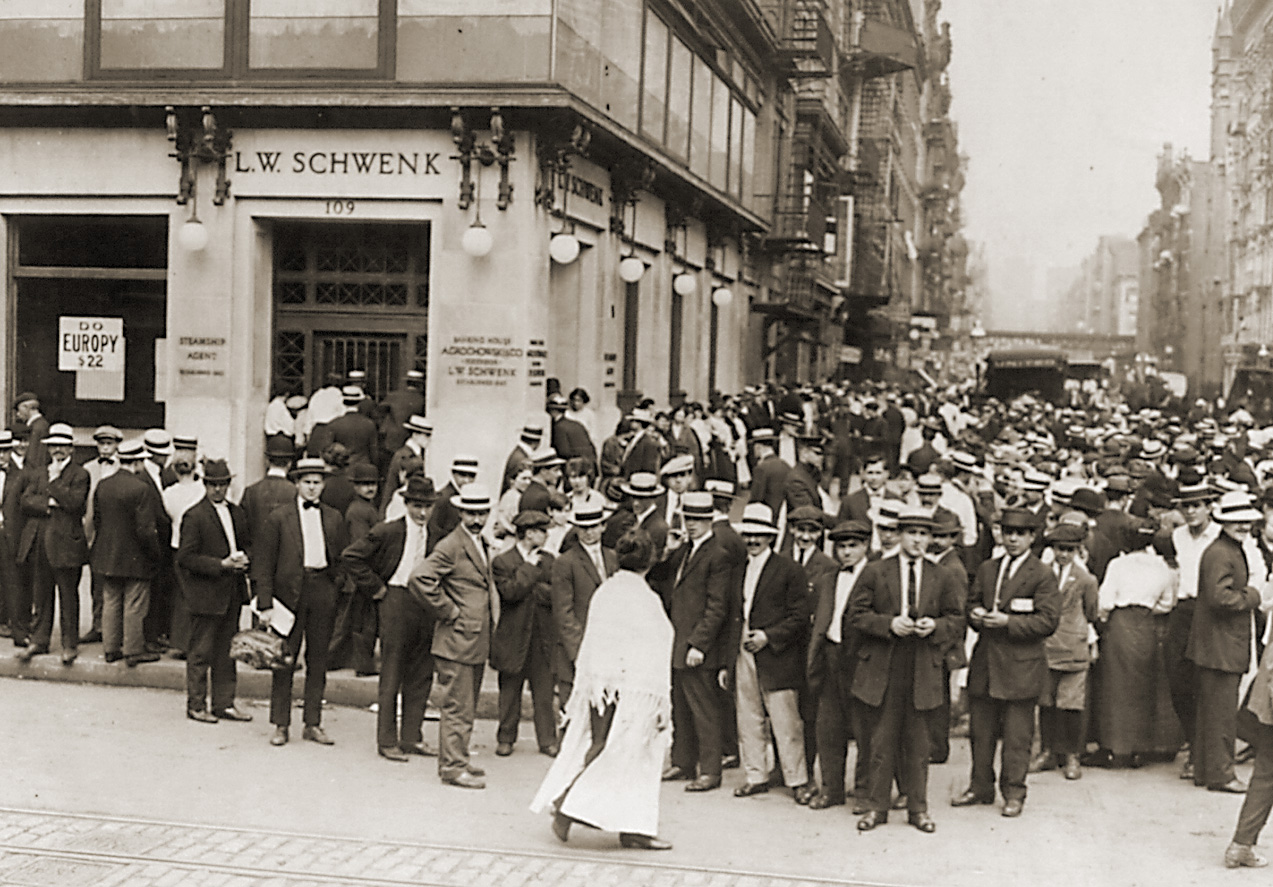
Panic Of 1910–1911
The Panic of 1910–1911 was a minor economic depression that followed the enforcement of the Sherman Antitrust Act, which regulates the competition among enterprises, trying to avoid monopolies and, generally speaking, a failure of the market itself. The short-term panic lasted approximately 1 year and led to a drop of the major U.S. stock market index by ~26%. It mostly affected the stock market and business traders who were smarting from the activities of trust busters, especially with the breakup of the Standard Oil Company and the American Tobacco company. See also * Van Schaick and Company {{Inline citations, date=June 2021 Van Schaick and Company was an investment company that operated on the East Coast of the United States between 1857 and September 1911, when it fell victim to the Panic of 1910–1911. The company declared bankrupt ..., one of several investment firms that failed during this period. * Great Depression References 1910 in the United States 1911 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panic Of 1907
The Panic of 1907, also known as the 1907 Bankers' Panic or Knickerbocker Crisis, was a financial crisis that took place in the United States over a three-week period starting in mid-October, when the New York Stock Exchange fell almost 50% from its peak the previous year. The panic occurred during a time of economic recession, and there were numerous runs on banks and on trust companies. The 1907 panic eventually spread throughout the nation when many state and local banks and businesses entered bankruptcy. The primary causes of the run included a retraction of market liquidity by a number of New York City banks and a loss of confidence among depositors, exacerbated by unregulated side bets at bucket shops. The panic was triggered by the failed attempt in October 1907 to corner the market on stock of the United Copper Company. When that bid failed, banks that had lent money to the cornering scheme suffered runs that later spread to affiliated banks and trusts, leading a week ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calvin Coolidge
Calvin Coolidge (born John Calvin Coolidge Jr.; ; July 4, 1872January 5, 1933) was the 30th president of the United States from 1923 to 1929. Born in Vermont, Coolidge was a History of the Republican Party (United States), Republican lawyer from New England who climbed up the ladder of Massachusetts state politics, becoming the state's Governor of Massachusetts, 48th governor. His response to the Boston Police Strike of 1919 thrust him into the national spotlight as a man of decisive action. Coolidge was elected the country's 29th vice president of the United States, vice president the next year, succeeding the presidency upon the sudden death of President Warren G. Harding in 1923. Elected in his own right in 1924 United States presidential election, 1924, Coolidge gained a reputation as a small-government Conservatism in the United States, conservative distinguished by a taciturn personality and dry sense of humor, receiving the nickname "Silent Cal". Though his widespread p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depression Of 1920–21
Depression may refer to: Mental health * Depression (mood), a state of low mood and aversion to activity * Mood disorders characterized by depression are commonly referred to as simply ''depression'', including: ** Dysthymia, also known as persistent depressive disorder ** Major depressive disorder, also known as clinical depression Economics * Economic depression, a sustained, long-term downturn in economic activity in one or more economies ** Great Depression, a severe economic depression during the 1930s, commonly referred to as simply ''the Depression'' ** Long Depression, an economic depression during 1873–96, known at the time as the ''Great Depression'' Biology * Depression (kinesiology), an anatomical term of motion, refers to downward movement, the opposite of elevation * Depression (physiology), a reduction in a biological variable or the function of an organ * Central nervous system depression, physiological depression of the central nervous system that can result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Monroe was the last president of the Virginia dynasty and the Republican Generation; his presidency coincided with the Era of Good Feelings, concluding the First Party System era of American politics. He is perhaps best known for issuing the Monroe Doctrine, a policy of opposing European colonialism in the Americas while effectively asserting U.S. dominance, empire, and hegemony in the hemisphere. He also served as governor of Virginia, a member of the United States Senate, U.S. ambassador to France and Britain, the seventh Secretary of State, and the eighth Secretary of War. Born into a slave-owning planter family in Westmoreland County, Virginia, Monroe served in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. After studying law u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panic Of 1819
The Panic of 1819 was the first widespread and durable financial crisis in the United States that slowed westward expansion in the Cotton Belt and was followed by a general collapse of the American economy that persisted through 1821. The Panic heralded the transition of the nation from its colonial commercial status with Europe toward an independent economy. Though the downturn was driven by global market adjustments in the aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars, its severity was compounded by excessive speculation in public lands, fueled by the unrestrained issue of paper money from banks and business concerns. The Second Bank of the United States (SBUS), itself deeply enmeshed in these inflationary practices, sought to compensate for its laxness in regulating the state bank credit market by initiating a sharp curtailment in loans by its western branches, beginning in 1818. Failing to provide gold specie from their reserves when presented with their own banknotes for redemption by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |