|
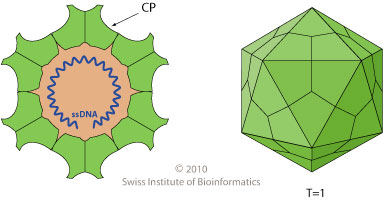
Dependovirus
''Dependoparvovirus'' (formerly ''Dependovirus'' or Adeno-associated virus group) is a genus in the subfamily ''Parvovirinae'' of the virus family ''Parvoviridae''; they are Group II viruses according to the Baltimore classification. Some dependoparvoviruses are also known as adeno-associated viruses because they cannot replicate productively in their host cell without the cell being coinfected by a helper virus such as an adenovirus, a herpesvirus, or a vaccinia virus. Species There are eleven recognized species: * ''Adeno-associated dependoparvovirus A'' * '' Adeno-associated dependoparvovirus B'' * ''Anseriform dependoparvovirus 1'' * '' Avian dependoparvovirus 1'' * '' Carnivore dependoparvovirus 1'' * '' Chiropteran dependoparvovirus 1'' * '' Pinniped dependoparvovirus 1'' * '' Rodent dependoparvovirus 1'' * '' Rodent dependoparvovirus 2'' * '' Squamate dependoparvovirus 1'' * '' Squamate dependoparvovirus 2'' Virology Dependoparvoviruses have an icosahedral shape, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parvovirinae
''Parvovirinae'' is a subfamily of viruses in the family ''Parvoviridae''. There are ten genera and 84 species assigned to this subfamily. Taxonomy The following 10 genera are recognized: *'' Amdoparvovirus'' *'' Artiparvovirus'' *'' Aveparvovirus'' *'' Bocaparvovirus'' *'' Copiparvovirus'' *''Dependoparvovirus'' *'' Erythroparvovirus'' *'' Loriparvovirus'' *''Protoparvovirus'' *''Tetraparvovirus Tetraparvovirus are a genus of viruses in the family ''Parvoviridae''. There are six recognized species: '' Chiropteran tetraparvovirus 1'', '' Primate tetraparvovirus 1'', '' Ungulate tetraparvovirus 1'', '' Ungulate tetraparvovirus 2'', '' Ungu ...'' References External links ICTV ''Parvovirinae'' {{Taxonbar, from=Q2055184 Parvoviruses Virus subfamilies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could cause serious problems to the health of the host organism if not cleared from the body. There are two distinct aspects of the immune response, the innate and the adaptive, which work together to protect against pathogens. The innate branch—the body's first reaction to an invader—is known to be a non-specific and quick response to any sort of pathogen. Components of the innate immune response include physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, immune cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and monocytes, and soluble factors including cytokines and complement. On the other hand, the adaptive branch is the body's immune response which is catered against specific antigens and thus, it takes longer to activate the components involv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from their initial isolation from human adenoids in 1953. They have a broad range of vertebrate hosts; in humans, more than 50 distinct adenoviral serotypes have been found to cause a wide range of illnesses, from mild respiratory infections in young children (known as the common cold) to life-threatening multi-organ disease in people with a weakened immune system. Virology Classification This family contains the following genera: * '' Atadenovirus'' * '' Aviadenovirus'' * '' Ichtadenovirus'' * '' Mastadenovirus'' (including all human adenoviruses) * '' Siadenovirus'' * '' Testadenovirus'' Diversity In humans, currently there are 88 human adenoviruses (HAdVs) in seven species (Human adenovirus A to G): * A: 12, 18, 31 * B: 3, 7, 11, 14, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading Strand
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is thus composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together to form. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. As a result of semi-conservative repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primer (molecular Biology)
Primer may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Primer'' (film), a 2004 feature film written and directed by Shane Carruth * ''Primer'' (video), a documentary about the funk band Living Colour Literature * Primer (textbook), a textbook used in primary education to teach the alphabet and other basic subjects * Primer (prayer book), a common name for English prayer books used from the 13th to 16th centuries * ''The New England Primer'' (1688), a Puritan book from Colonial America with morality-themed rhymes Music * ''Primer'' (album), a 1995 music album by the musical group Rockapella * Primer 55, an American alternative metal band * "The Primer", a song from the 2005 album ''Alaska'' by Between the Buried and Me Firearms * Primer (firearms), a firearm powder charge-ignition mechanism ** Centerfire ammunition, Boxer or Berdan primers used in modern centerfire cartridges ** Detonator, a small explosive device also known as an explosive primer or blasting cap ** Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy groups. Both the negatively charged anion , called hydroxide, and the neutral radical , known as the hydroxyl radical, consist of an unbonded hydroxy group. According to IUPAC definitions, the term ''hydroxyl'' refers to the hydroxyl radical () only, while the functional group is called a ''hydroxy group''. Properties Water, alcohols, carboxylic acids, and many other hydroxy-containing compounds can be readily deprotonated due to a large difference between the electronegativity of oxygen (3.5) and that of hydrogen (2.1). Hydroxy-containing compounds engage in intermolecular hydrogen bonding increasing the electrostatic attraction between molecules and thus to higher boiling and melting points than found for compounds that lack this f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional conformational isomerism, form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein protein folding, folds into its three dimensional protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the Amine, amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone chain, backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone Dihedral angle#Dihedral angles of proteins, dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icosahedral
In geometry, an icosahedron ( or ) is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes and . The plural can be either "icosahedra" () or "icosahedrons". There are infinitely many non- similar shapes of icosahedra, some of them being more symmetrical than others. The best known is the (convex, non- stellated) regular icosahedron—one of the Platonic solids—whose faces are 20 equilateral triangles. Regular icosahedra There are two objects, one convex and one nonconvex, that can both be called regular icosahedra. Each has 30 edges and 20 equilateral triangle faces with five meeting at each of its twelve vertices. Both have icosahedral symmetry. The term "regular icosahedron" generally refers to the convex variety, while the nonconvex form is called a ''great icosahedron''. Convex regular icosahedron The convex regular icosahedron is usually referred to simply as the ''regular icosahedron'', one of the five regular Platonic solids, and is represented by its Schläfli symbol , co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamate Dependoparvovirus 2
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles, comprising lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards), which are collectively known as squamates or scaled reptiles. With over 10,900 species, it is also the second-largest order of extant (living) vertebrates, after the perciform fish. Members of the order are distinguished by their skins, which bear horny scales or shields, and must periodically engage in molting. They also possess movable quadrate bones, making possible movement of the upper jaw relative to the neurocranium. This is particularly visible in snakes, which are able to open their mouths very wide to accommodate comparatively large prey. Squamata is the most variably sized order of reptiles, ranging from the dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') to the Reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus'') and the now-extinct mosasaurs, which reached lengths over . Among other reptiles, squamates are most closely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamate Dependoparvovirus 1
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles, comprising lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards), which are collectively known as squamates or scaled reptiles. With over 10,900 species, it is also the second-largest order of extant (living) vertebrates, after the perciform fish. Members of the order are distinguished by their skins, which bear horny scales or shields, and must periodically engage in molting. They also possess movable quadrate bones, making possible movement of the upper jaw relative to the neurocranium. This is particularly visible in snakes, which are able to open their mouths very wide to accommodate comparatively large prey. Squamata is the most variably sized order of reptiles, ranging from the dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') to the Reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus'') and the now-extinct mosasaurs, which reached lengths over . Among other reptiles, squamates are most closely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |