|
Dependent-marking
A dependent-marking language has grammatical markers of agreement and case government between the words of phrases that tend to appear more on dependents than on heads. The distinction between head-marking and dependent-marking was first explored by Johanna Nichols in 1986, and has since become a central criterion in language typology in which languages are classified according to whether they are more head-marking or dependent-marking. Many languages employ both head and dependent-marking, but some employ double-marking, and yet others employ zero-marking. However, it is not clear that the head of a clause has anything to do with the head of a noun phrase, or even what the head of a clause is. In English English has few inflectional markers of agreement and so can be construed as zero-marking much of the time. Dependent-marking, however, occurs when a singular or plural noun demands the singular or plural form of the demonstrative determiner ''this/these'' or ''that/those'' and wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-marking Language
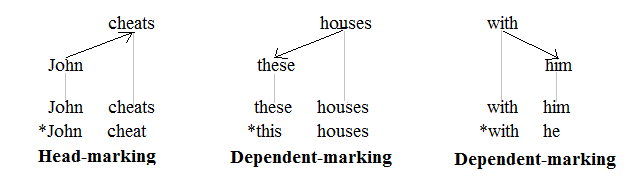
A language is head-marking if the grammatical marks showing agreement between different words of a phrase tend to be placed on the heads (or nuclei) of phrases, rather than on the modifiers or dependents. Many languages employ both head-marking and dependent-marking, and some languages double up and are thus double-marking. The concept of head/dependent-marking was proposed by Johanna Nichols in 1986 and has come to be widely used as a basic category in linguistic typology. In English The concepts of head-marking and dependent-marking are commonly applied to languages that have richer inflectional morphology than English. There are, however, a few types of agreement in English that can be used to illustrate these notions. The following graphic representations of a clause, a noun phrase, and a prepositional phrase involve agreement. The three tree structures shown are those of a dependency grammar (as opposed to those of a phrase structure grammar): :: Heads and dependents a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-marking Language
A language is head-marking if the grammatical marks showing agreement between different words of a phrase tend to be placed on the heads (or nuclei) of phrases, rather than on the modifiers or dependents. Many languages employ both head-marking and dependent-marking, and some languages double up and are thus double-marking. The concept of head/dependent-marking was proposed by Johanna Nichols in 1986 and has come to be widely used as a basic category in linguistic typology. In English The concepts of head-marking and dependent-marking are commonly applied to languages that have richer inflectional morphology than English. There are, however, a few types of agreement in English that can be used to illustrate these notions. The following graphic representations of a clause, a noun phrase, and a prepositional phrase involve agreement. The three tree structures shown are those of a dependency grammar (as opposed to those of a phrase structure grammar): :: Heads and dependents a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-marking Language
A double-marking language is one in which the grammatical marks showing relations between different constituents of a phrase tend to be placed on both the heads (or nuclei) of the phrase in question, and on the modifiers or dependents. Pervasive double-marking is rather rare, but instances of double-marking occur in many languages. For example, in Turkish, in a genitive construction involving two definite nouns, both the possessor and the possessed are marked, the former with a suffix marking the possessor (and corresponding to a possessive adjective in English) and the latter in the genitive case. For example, 'brother' is ''kardeş,'' and 'dog' is ''köpek,'' but 'brother's dog' is ''kardeşin köpeği.'' (The consonant change is part of a regular consonant lenition.) Another example is a language in which endings that mark gender or case are used to indicate the role of both nouns and their associated modifiers (such as adjectives) in a sentence (such as Russian and Spanish) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb phrase constituent, and they are thus well suited for the analysis of languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb phrase constituent, and they are thus well suited for the analysis of languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero-marking Language
A zero-marking language is one with no grammatical marks on the dependents or the modifiers or the heads or nuclei that show the relationship between different constituents of a phrase. Pervasive zero marking is very rare, but instances of zero marking in various forms occur in quite a number of languages. Vietnamese and Indonesian are two national languages listed in the World Atlas of Language Structures as having zero-marking. In many East and Southeast Asian languages, such as Thai and Chinese, the head verb and its dependents are not marked for any arguments or for the nouns' roles in the sentence. On the other hand, possession is marked in such languages by the use of clitic particles between possessor and possessed. Some languages, such as many dialects of Arabic, use a similar process, called juxtaposition, to indicate possessive relationships. In Arabic, two nouns next to each other could indicate a possessed-possessor construction: ' "Maryam's books" (literally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8th and 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependent (grammar)
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb phrase constituent, and they are thus well suited for the analysis of languages wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johanna Nichols
Johanna Nichols (born 1945, Iowa City, Iowa) is an American linguist and professor emerita in the Department of Slavic Languages and Literatures at the University of California, Berkeley. She earned her Ph.D. in Linguistics at the University of California, Berkeley, in 1973 with a dissertation titled, "The Balto-Slavic predicate instrumental: a problem in diachronic syntax." Her research interests include the Slavic languages, the linguistic prehistory of northern Eurasia, language typology, ancient linguistic prehistory, and languages of the Caucasus, chiefly Chechen and Ingush. She has made fundamental contributions to these fields. A festschrift in her honor, ''Language Typology and Historical Contingency: In honor of Johanna Nichols'', was published in 2013. Nichols's best known work, ''Linguistic Diversity in Space and Time'', won the Linguistic Society of America's Leonard Bloomfield Book Award for 1994. Books * ''Predicate Nominals: A Partial Surface Syntax of Russian.' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head (linguistics)
In linguistics, the head or nucleus of a phrase is the word that determines the syntactic category of that phrase. For example, the head of the noun phrase ''boiling hot water'' is the noun ''water''. Analogously, the head of a compound is the stem that determines the semantic category of that compound. For example, the head of the compound noun ''handbag'' is ''bag'', since a handbag is a bag, not a hand. The other elements of the phrase or compound modify the head, and are therefore the head's ''dependents''. Headed phrases and compounds are called ''endocentric'', whereas ''exocentric'' ("headless") phrases and compounds (if they exist) lack a clear head. Heads are crucial to establishing the direction of branching. Head-initial phrases are right-branching, head-final phrases are left-branching, and head-medial phrases combine left- and right-branching. Basic examples Examine the following expressions: :::big red dog :::birdsong The word ''dog'' is the head of ''big red dog' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Case Government
In linguistics, case government is government of the grammatical case of a noun, wherein a verb or adposition is said to 'govern' the grammatical case of its noun phrase complement, e.g. in German the preposition 'for' governs the accusative case: 'for me-accusative'. Case government may modify the meaning of the verb substantially, even to meanings that are unrelated. Case government is an important notion in languages with many case distinctions, such as Russian and Finnish. It plays less of a role in English, because English does not rely on grammatical cases, except for distinguishing subject pronouns (''I, he, she, we, they'') from other pronouns (''me, him, her, us, them''). In English, true case government is absent, but if the aforementioned subject pronouns are understood as regular pronouns in the accusative case, it occurs in sentences such as ''He found me'' (not for example *''He found I''). Adpositions In Standard German, there are prepositions which govern eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependent Marking 1
A dependant is a person who relies on another as a primary source of income. A common-law spouse who is financially supported by their partner may also be included in this definition. In some jurisdictions, supporting a dependant may enable the provider to claim a tax deduction. In the United Kingdom, a full-time student in higher education who financially supports another adult may qualify for an Adult Dependant's Grant. Taxation In the US, a taxpayer may claim exemptions for their dependants. See also * Military dependent A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ... References {{reflist Interpersonal relationships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
