|
Dependency Inversion Principle
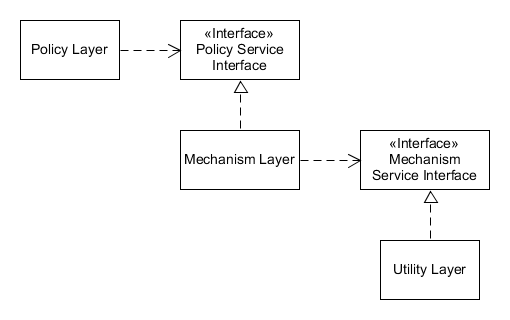
In object-oriented design, the dependency inversion principle is a specific methodology for Coupling (computer programming), loosely coupled software Modular programming, modules. When following this principle, the conventional dependency (computer science), dependency relationships established from high-level, policy-setting modules to low-level, dependency modules are reversed, thus rendering high-level modules independent of the low-level module implementation details. The principle states: By dictating that high-level and low-level objects must depend on the same abstraction, this design principle the way some people may think about object-oriented programming. The idea behind points A and B of this principle is that when designing the interaction between a high-level module and a low-level one, the interaction should be thought of as an abstract interaction between them. This has implications for the design of both the high-level and the low-level modules: the low-level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Object-oriented Design
Object-oriented analysis and design (OOAD) is a technical approach for analyzing and designing an application, system, or business by applying object-oriented programming, as well as using visual modeling throughout the software development process to guide stakeholder communication and product quality. OOAD in modern software engineering is typically conducted in an iterative and incremental way. The outputs of OOAD activities are analysis models (for OOA) and design models (for OOD) respectively. The intention is for these to be continuously refined and evolved, driven by key factors like risks and business value. History In the early days of object-oriented technology before the mid-1990s, there were many different competing methodologies for software development and object-oriented modeling, often tied to specific Computer Aided Software Engineering (CASE) tool vendors. No standard notations, consistent terms and process guides were the major concerns at the time, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dependency Inversion
In object-oriented design, the dependency inversion principle is a specific methodology for loosely coupled software modules. When following this principle, the conventional dependency relationships established from high-level, policy-setting modules to low-level, dependency modules are reversed, thus rendering high-level modules independent of the low-level module implementation details. The principle states: By dictating that high-level and low-level objects must depend on the same abstraction, this design principle the way some people may think about object-oriented programming. The idea behind points A and B of this principle is that when designing the interaction between a high-level module and a low-level one, the interaction should be thought of as an abstract interaction between them. This has implications for the design of both the high-level and the low-level modules: the low-level one should be designed with the interaction in mind and it may be necessary to cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
SOLID (object-oriented Design)
Solid is a state of matter where molecules are closely packed and can not slide past each other. Solids resist compression, expansion, or external forces that would alter its shape, with the degree to which they are resisted dependent upon the specific material under consideration. Solids also always possess the least amount of kinetic energy per atom/molecule relative to other phases or, equivalently stated, solids are formed when matter in the liquid / gas phase is cooled below a certain temperature. This temperature is called the melting point of that substance and is an intrinsic property, i.e. independent of how much of the matter there is. All matter in solids can be arranged on a microscopic scale under certain conditions. Solids are characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to applied external forces and pressure. Unlike liquids, solids do not flow to take on the shape of their container, nor do they expand to fill the entire available volume like a gas. Much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inversion Of Control
In software engineering, inversion of control (IoC) is a design principle in which custom-written portions of a computer program receive the flow of control from an external source (e.g. a framework). The term "inversion" is historical: a software architecture with this design "inverts" control as compared to procedural programming. In procedural programming, a program's custom code calls reusable libraries to take care of generic tasks, but with inversion of control, it is the external code or framework that is in control and calls the custom code. Inversion of control has been widely used by application development frameworks since the rise of GUI environments and continues to be used both in GUI environments and in web server application frameworks. Inversion of control makes the framework extensible by the methods defined by the application programmer. Event-driven programming is often implemented using IoC so that the custom code need only be concerned with the handling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inventor's Paradox
The inventor's paradox is a phenomenon that occurs in seeking a solution to a given problem. Instead of solving a specific type of problem, which would seem intuitively easier, it can be easier to solve a more general problem, which covers the specifics of the sought-after solution. The ''inventor's paradox'' has been used to describe phenomena in mathematics, programming, and logic, as well as other areas that involve critical thinking. History In the book ''How to Solve It'', Hungarian mathematician George Pólya introduces what he defines as the inventor's paradox: Or, in other words, to solve what one desires to solve, one may have to solve more than that in order to get a properly working flow of information. When solving a problem, the natural inclination typically is to remove as much excessive variability and produce limitations on the subject at hand as possible. Doing this can create unforeseen and intrinsically awkward parameters.Tate, et al., p. 110 The goal is to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Interface (computing)
In computing, an interface (American English) or interphase (British English, archaic) is a shared boundary across which two or more separate components of a computer system exchange information. The exchange can be between software, computer hardware, peripheral, peripheral devices, User interface, humans, and combinations of these. Some computer hardware devices, such as a touchscreen, can both send and receive data through the interface, while others such as a mouse or microphone may only provide an interface to send data to a given system. Hardware interfaces Hardware interfaces exist in many components, such as the various Bus (computing), buses, Computer data storage, storage devices, other I/O devices, etc. A hardware interface is described by the mechanical, electrical, and logical signals at the interface and the protocol for sequencing them (sometimes called signaling). See also: A standard interface, such as SCSI, decouples the design and introduction of computing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Design By Contract
Design by contract (DbC), also known as contract programming, programming by contract and design-by-contract programming, is an approach for designing software. It prescribes that software designers should define formal, precise and verifiable interface specifications for software components, which extend the ordinary definition of abstract data types with preconditions, postconditions and invariants. These specifications are referred to as "contracts", in accordance with a conceptual metaphor with the conditions and obligations of business contracts. The DbC approach assumes all ''client components'' that invoke an operation on a ''server component'' will meet the preconditions specified as required for that operation. Where this assumption is considered too risky (as in multi-channel or distributed computing), the inverse approach is taken, meaning that the ''server component'' tests that all relevant preconditions hold true (before, or while, processing the ''client co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adapter Pattern
In software engineering, the adapter pattern is a software design pattern (also known as wrapper, an alternative naming shared with the decorator pattern) that allows the interface of an existing class to be used as another interface. It is often used to make existing classes work with others without modifying their source code. An example is an adapter that converts the interface of a Document Object Model of an XML document into a tree structure that can be displayed. Overview The adapter design pattern is one of the twenty-three well-known Gang of Four design patterns that describe how to solve recurring design problems to design flexible and reusable object-oriented software, that is, objects that are easier to implement, change, test, and reuse. The adapter design pattern solves problems like: * How can a class be reused that does not have an interface that a client requires? * How can classes that have incompatible interfaces work together? * How can an alternative inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Robert C
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dependency Injection
In software engineering, dependency injection is a programming technique in which an object or function receives other objects or functions that it requires, as opposed to creating them internally. Dependency injection aims to separate the concerns of constructing objects and using them, leading to loosely coupled programs. The pattern ensures that an object or function that wants to use a given service should not have to know how to construct those services. Instead, the receiving " client" (object or function) is provided with its dependencies by external code (an "injector"), which it is not aware of. Dependency injection makes implicit dependencies explicit and helps solve the following problems: * How can a class be independent from the creation of the objects it depends on? * How can an application, and the objects it uses support different configurations? Dependency injection is often used to keep code in-line with the dependency inversion principle. In statically ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Service Locator Pattern
The service locator pattern is a design pattern used in software development to encapsulate the processes involved in obtaining a service with a strong abstraction layer. This pattern uses a central registry known as the "service locator", which on request returns the information necessary to perform a certain task. Proponents of the pattern say the approach simplifies component-based applications where all dependencies are cleanly listed at the beginning of the whole application design, consequently making traditional dependency injection a more complex way of connecting objects. Critics of the pattern argue that it is an anti-pattern which obscures dependencies and makes software harder to test. Advantages * The "service locator" can act as a simple run-time linker. This allows code to be added at run-time without re-compiling the application, and in some cases without having to even restart it. * Applications can optimize themselves at run-time by selectively adding and remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Plug-in (computing)
In computing, a plug-in (also spelled plugin) or add-in (also addin, add-on, or addon) is a software component that extends the functionality of an existing software system without requiring the system to be software build, re-built. A plug-in software feature, feature is one way that a system can be customizable. Applications support plug-ins for a variety of reasons including: * Enable third-party developers to extend an application * Support easily adding new features * Reduce the size of an application by not loading unused features * Separate source code from an application because of incompatible software licenses Examples Examples of plug-in use for various categories of applications: * Digital audio workstations and audio editing software use audio plug-ins to generate, process or analyze sound. Ardour (software), Ardour, Audacity (audio editor), Audacity, Cubase, FL Studio, Logic Pro, Logic Pro X and Pro Tools are examples of such systems. * Email clients use plug-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |