|
Dennis Torchia
Dennis Torchia is an American biophysicist who specialized in NMR spectroscopy. He spent most of his career at the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR), part of the United States National Institutes of Health, where he served as Chief of the Structural Biology Unit before his retirement in 2006. Career Torchia received his bachelor's degree from University of California, Riverside and his Ph.D. from Yale University. He worked as a postdoctoral fellow with Elkan Blout at Harvard University, briefly worked at Bell Laboratories and the National Institute of Standards and Technology, and joined NIDCR in 1974. He collaborated extensively with fellow NIH scientists Ad Bax, Marius Clore and Angela Gronenborn in the early development of multidimensional protein NMR, pioneered the use of isotopic labeling in the preparation of NMR samples, and developed techniques for studying protein dynamics. Torchia assumed emeritus status in 2006, but has continued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biophysicist
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study Biology, biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from Molecule, molecular to organismic and Population (biology), populations. Biophysical research shares significant overlap with biochemistry, molecular biology, physical chemistry, physiology, nanotechnology, bioengineering, computational biology, biomechanics, developmental biology and systems biology. The term ''biophysics'' was originally introduced by Karl Pearson in 1892.Roland Glaser. Biophysics: An Introduction'. Springer; 23 April 2012. . The term ''biophysics'' is also regularly used in academia to indicate the study of the Physical quantity, physical quantities (e.g. electric current, temperature, Stress (mechanics), stress, entropy) in biological systems. Other List of life sciences, biological sciences also perform research on the biophysical properties of living ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad Bax
Adriaan "Ad" Bax (born 1956) is a Dutch-American molecular biophysicist. He was born in the Netherlands and is the Chief of the Section on Biophysical NMR Spectroscopy at the National Institutes of Health. He is known for his work on the methodology of biomolecular NMR spectroscopy. Biography Bax was born in the Netherlands. He studied at Delft University of Technology where he got his engineer's degree (Ir. degree) in 1978, and Ph.D. degree in applied physics in 1981, after spending considerable time working with Ray Freeman at Oxford University. He worked as a postdoc with Gary Maciel at Colorado State University, before joining the NIH's Laboratory of Chemical Physics in 1983. In 1994 he became correspondent of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences. He is currently the Chief of the Section on Biophysical NMR Spectroscopy at NIH. In 2002 he was elected a member of the National Academy of Sciences in the section on Biophysics and computational biology and a Fellow o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Biophysicists
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Analytical Symposium
The Eastern Analytical Symposium (EAS) and Exposition is an American organization that sponsors a Symposium and Exposition generally held in Princeton, New Jersey, every November. The Symposium is attended by over 2000 scientists and typically contains several hundred papers by the world's leading authorities on analytical chemistry. The associated exposition contains information on technology and information from companies that provide instrumentation and services for the community of analytical scientists. In addition, the EAS provides an ongoing education program that includes technical short courses and professional development workshops for laboratory scientists, as well as general-interest sessions directed at the public, especially students and their chemistry teachers. Sponsors The Eastern Analytical Symposium and Exposition is sponsored by the following organizations: the Analytical Division of the American Chemical Society, the American Chemical Society New York and N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emeritus
''Emeritus'' (; female: ''emerita'') is an adjective used to designate a retired chair, professor, pastor, bishop, pope, director, president, prime minister, rabbi, emperor, or other person who has been "permitted to retain as an honorary title the rank of the last office held". In some cases, the term is conferred automatically upon all persons who retire at a given rank, but in others, it remains a mark of distinguished service awarded selectively on retirement. It is also used when a person of distinction in a profession retires or hands over the position, enabling their former rank to be retained in their title, e.g., "professor emeritus". The term ''emeritus'' does not necessarily signify that a person has relinquished all the duties of their former position, and they may continue to exercise some of them. In the description of deceased professors emeritus listed at U.S. universities, the title ''emeritus'' is replaced by indicating the years of their appointmentsThe Protoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Dynamics
Proteins are generally thought to adopt unique structures determined by their amino acid sequences. However, proteins are not strictly static objects, but rather populate ensembles of (sometimes similar) conformations. Transitions between these states occur on a variety of length scales (tenths of Å to nm) and time scales (ns to s), and have been linked to functionally relevant phenomena such as allosteric signaling and enzyme catalysis. The study of protein dynamics is most directly concerned with the transitions between these states, but can also involve the nature and equilibrium populations of the states themselves. These two perspectives—kinetics and thermodynamics, respectively—can be conceptually synthesized in an "energy landscape" paradigm: highly populated states and the kinetics of transitions between them can be described by the depths of energy wells and the heights of energy barriers, respectively. Local flexibility: atoms and residues Portions of protein s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopic Labeling
Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope (an atom with a detectable variation in neutron count) through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling. In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
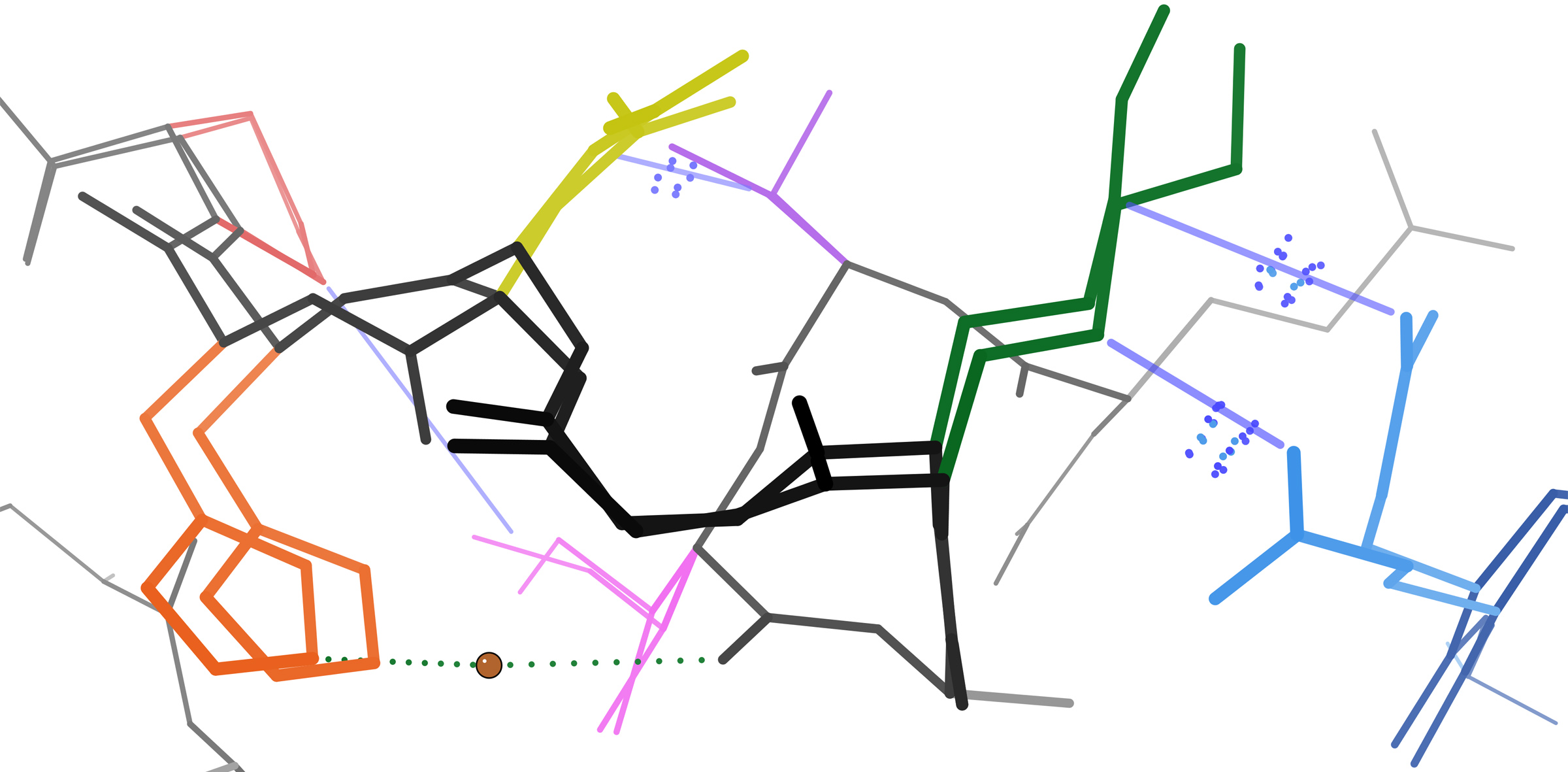
Protein NMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (usually abbreviated protein NMR) is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins, and also nucleic acids, and their complexes. The field was pioneered by Richard R. Ernst and Kurt Wüthrich at the ETH, and by Ad Bax, Marius Clore, Angela Gronenborn at the NIH, and Gerhard Wagner at Harvard University, among others. Structure determination by NMR spectroscopy usually consists of several phases, each using a separate set of highly specialized techniques. The sample is prepared, measurements are made, interpretive approaches are applied, and a structure is calculated and validated. NMR involves the quantum-mechanical properties of the central core ("nucleus") of the atom. These properties depend on the local molecular environment, and their measurement provides a map of how the atoms are linked chemically, how close they are in space, and how rapid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marius Clore
G. Marius Clore MAE, FRSC, FRS is a British-born, Anglo-American molecular biophysicist and structural biologist. He was born in London, U.K. and is a dual US/U.K. Citizen. He is a Member of the National Academy of Sciences, a Fellow of the Royal Society, a NIH Distinguished Investigator, and the Chief of the Molecular and Structural Biophysics Section in the Laboratory of Chemical Physics of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases at the U.S. National Institutes of Health. He is known for his foundational work in three-dimensional protein and nucleic acid structure determination by biomolecular NMR spectroscopy, for advancing experimental approaches to the study of large macromolecules and their complexes by NMR, and for developing NMR-based methods to study rare conformational states in protein- nucleic acid and protein-protein recognition. Clore's discovery of previously undetectable, functionally significant, rare transient states of macro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Standards And Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical science laboratory programs that include nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified in 1789, granted these powers to the new Congr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMR Spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei. The sample is placed in a magnetic field and the NMR signal is produced by excitation of the nuclei sample with radio waves into nuclear magnetic resonance, which is detected with sensitive radio receivers. The intramolecular magnetic field around an atom in a molecule changes the resonance frequency, thus giving access to details of the electronic structure of a molecule and its individual functional groups. As the fields are unique or highly characteristic to individual compounds, in modern organic chemistry practice, NMR spectroscopy is the definitive method to identify monomolecular organic compounds. The principle of NMR usually involves three sequential steps: # The alignment (polarization) of the magnetic nuclear spins in an applied, constant magnetic field B0. # The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |